Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
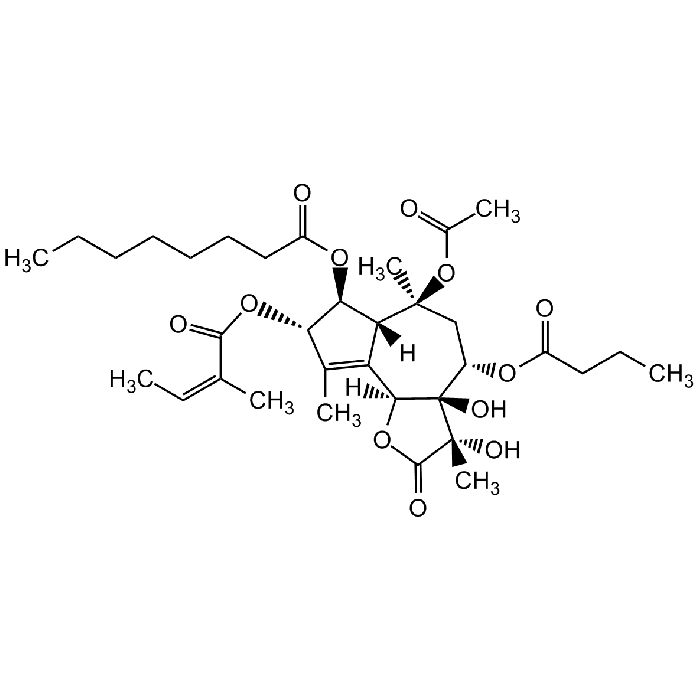
Thapsigargin (high purity)
As low as
60
CHF
CHF 60.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CN2-0003-M0011 mgCHF 60.00
AG-CN2-0003-M0055 mgCHF 240.00
AG-CN2-0003-M01010 mgCHF 380.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C34H50O12 |
| MW | 650.8 |
| Merck Index | 14: 9272 |
| CAS | 67526-95-8 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Isolated from Thapsia garganica. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | Colorless to white amorphous powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO or 100% ethanol. |
| Other Product Data |
Preparation of 1 mM stock solution: Dissolve 0.65 mg thapsigargin in 1 ml solvent. |
| InChi Key | IXFPJGBNCFXKPI-FSIHEZPISA-N |
| Smiles | O=C1O[C@@]2([H])C3=C(C)[C@H](OC(/C(C)=C\C)=O)[C@@H](OC(CCCCCCC)=O)[C@]3([H])[C@@](C)(OC(C)=O)C[C@H](OC(CCC)=O)[C@]2(O)[C@@]1(O)C |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice |
Keep cool and dry. Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Intracellular Ca2+ signaling probe [1].
- Specific and sensitive inhibitor of SERCA [2].
- Non-TPA/PMA tumor promoter [3].
- Histamine release inducer [4].
- Apoptosis inducer [5, 6, 7, 8].
- Mitochondrial dysfunction inducer [6, 8].
- NOS modulator [9].
- Angiogenesis inhibitor [10].
- Stimulator of arachidonic acid metabolism in macrophages [11].
- Autophagy inducer [12, 13].
- TRAIL sensitizer [14].
- Inducer of ER-stress in the brain.
Product References
- A tool coming of age: thapsigargin as an inhibitor of sarco-endoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+)-ATPases: M. Treiman, et al.; Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 19,131 (1998)
- Inhibition of the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ transport ATPase by thapsigargin at subnanomolar concentrations: Y. Sagara, & G. Inesi; J. Biol. Chem. 266, 13503 (1991)
- Thapsigargin, a histamine secretagogue, is a non-12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA) type tumor promoter in two-stage mouse skin carcinogenesis: H. Hakii, et al., J. Cancer. Res. Clin. Oncol. 111, 177 (1986)
- On the mechanism of histamine release induced by thapsigargin from Thapsia garganica L: S.A. Patkar, et al.; Agents Actions 9, 53 (1979)
- Thapsigargin, a Ca(2+)-ATPase inhibitor, depletes the intracellular Ca2+ pool and induces apoptosis in human hepatoma cells: A. Tsukamoto & Y. Kaneko; Cell Biol. Int. 17, 969 (1993)
- Thapsigargin induces mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis in the mastocytoma P815 cell line and in mouse thymocytes: J.P. Beaver & P. Waring; Cell Death Differ. 3, 415 (1996)
- Thapsigargin induces a calmodulin/calcineurin-dependent apoptotic cascade responsible for the death of prostatic cancer cells: B. Tombal, et al.; Prostate 43, 303 (2000)
- Thapsigargin induces biphasic fragmentation of mitochondria through calcium-mediated mitochondrial fission and apoptosis: J.R. Hom, et al.; J. Cell Physiol. 212, 498 (2007)
- Thapsigargin, a Ca(2+)-ATPase inhibitor, relaxes rat aorta via nitric oxide formation: H. Moritoki, et al.; Life Sci. 54, PL153 (1994)
- Thapsigargin inhibits angiogenesis in the rat isolated aorta: studies on the role of intracellular calcium pools: N. Shukla, et al.; Cardiovasc. Res. 49, 681 (2001)
- Stimulation of arachidonic acid metabolism in rat peritoneal macrophages by thapsigargin, a non-(12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate) (TPA)-type tumor promoter: K. Ohuchi, et al.; Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 113, 319 (1987)
- Regulation of autophagy by the inositol trisphosphate receptor: A. Criollo, et al.; Cell Death Differ. 14, 1029 (2007)
- AMPK-independent induction of autophagy by cytosolic Ca2+ increase: A. Grotemeier, et al.; Cell. Signal. 22, 914 (2010)
- Novel HTS strategy identifies TRAIL-sensitizing compounds acting specifically through the Caspase-8 apoptotic axis: D. Finlay, et al.;PLoS One 5, e13375 (2010)
- Glucose starvation induces cell death in K-ras-transformed cells by interfering with the hexosamine biosynthesis pathway and activating the unfolded protein response: R. Palorini, et al.; Cell Death Dis. 4, e732 (2013)
- Development of an Enhanced Phenotypic Screen of Cytotoxic T-Lymphocyte Lytic Granule Exocytosis Suitable for Use with Synthetic Compound and Natural Product Collections: Z. Zhao, et al.; J. Biomol. Screen 21, 556 (2016)
- Inactivation of prosurvival Bcl-2 proteins activates Bax/Bak through the outer mitochondrial membrane: K.L. O'Neill, et al.; Genes Dev. 30, 973 (2016)
- Disulfide bond disrupting agents activate the unfolded protein response in EGFR- and HER2-positive breast tumor cells: R.B. Ferreira, et al.; Oncotarget 8, 28971 (2017)
- Unbiased proteomic screening identifies a novel role for the E3 ubiquitin ligase Nedd4-2 in translational suppression during ER stress: D.E. Eagleman, et al.; J. Neurochem. ahead of print (2020)






![Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate [PMA]](https://adipogen.com/media/catalog/product/cache/60eb5af712bc93baae8d55513bd31b01/a/g/ag-cn2-0010_pma.png)