Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
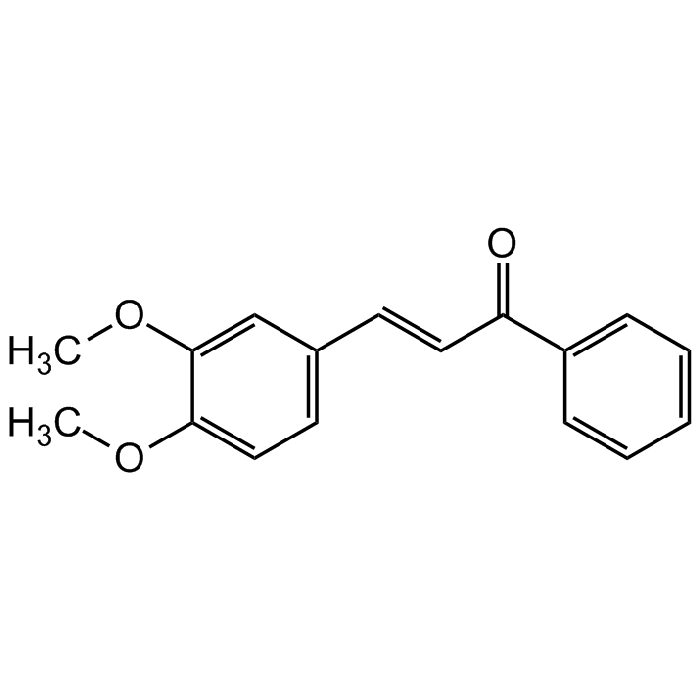
3,4-Dimethoxychalcone
As low as
35
CHF
CHF 35.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CN2-0531-M01010 mgCHF 35.00
AG-CN2-0531-M05050 mgCHF 60.00
AG-CN2-0531-M250250 mgCHF 160.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | 3,4-DMC; NSC643172; 3-(3,4-Dimethoxyphenyl)-1-phenylprop-2-en-1-one |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C17H16O3 |
| MW | 268.3 |
| CAS | 5416-71-7 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Synthetic. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | White to yellow crystalline powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO. |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR |
| InChi Key | LSHZPTCZLWATBZ-CSKARUKUSA-N |
| Smiles | COC1=CC=C(C=C1OC)/C=C/C(C2=CC=CC=C2)=O |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Keep cool and dry. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Caloric restriction mimetic (CRM). Caloric restriction mimetics (CRMs) are natural or synthetic compounds that mimic the health-promoting and longevity-extending effects of caloric restriction. CRMs provoke the deacetylation of cellular proteins coupled to an increase in autophagic flux in the absence of toxicity.
- Induces the deacetylation of cytoplasmic proteins and stimulates autophagic flux, requiring transcription factor EB (TFEB)- and E3 (TFE3)-dependent gene transcription and mRNA translation to trigger autophagy.
- Stimulates the translocation of TFEB and TFE3 into nuclei both in vitro and in vivo, in hepatocytes and cardiomyocytes. Consequently induces autophagy in vitro and in vivo, mediates autophagy-dependent cardioprotective effects and improves the efficacy of anticancer chemotherapy in vivo.
- So far this chalcone polyphenol has been used as an intermediate for synthesis of biochemical substances and was described to have weak antioxidant and antimicrobial activity.
Product References
- Antioxidant properties of phenyl styryl ketones: D.V. Rajakumar & M.N. Rao; Free Radic. Res. 22, 309 (1995)
- In vitro antifungal evaluation and structure-activity relationships of a new series of chalcone derivatives and synthetic analogues, with inhibitory properties against polymers of the fungal cell wall: S.N. Lopez, et al.; Bioorg. Med. Chem. 9, 1999 (2001)
- Quinone reductase 2 substrate specificity and inhibition pharmacology: J.A. Boutin, et al.; Chem. Biol. Interact. 151, 213 (2005)
- 3,4-Dimethoxychalcone: V. Shettigar, et al.; Acta Cryst. E62, o4646 (2006)
- 3,4-Dimethoxychalcone induces autophagy through activation of the transcription factors TFE3 and TFEB: G. Chen, et al.; EMBO Mol. Med. e10469, (2019)