Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
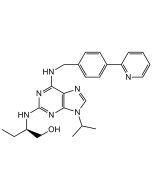
(R)-Roscovitine
As low as
40
CHF
CHF 40.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CR1-0006-M0011 mgCHF 40.00
AG-CR1-0006-M0055 mgCHF 70.00
AG-CR1-0006-M05050 mgCHF 230.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | 6-Benzylamino-2-(R)-[(1-ethyl)-2-hydroxyethylamino]-9-isopropylpurine |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C19H26N6O |
| MW | 354.5 |
| CAS | 186692-46-6 |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO or 100% ethanol; only moderately soluble in water. |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| InChi Key | BTIHMVBBUGXLCJ-OAHLLOKOSA-N |
| Smiles | CC[C@H](CO)NC1=NC2=C(N=CN2C(C)C)C(NCC2=CC=CC=C2)=N1 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Potent and selective inhibitor of CDKs [1, 2, 4, 16].
- More potent than olomoucine [3].
- Inhibits CDK1/cyclin B kinase (IC50 = 450 nM) [2], CDK2 (IC50 = 700 nM) [4] and CDK5/p35 (IC50 = 160 nM) [4,5].
- Inhibits M phase promoting factor (MPF) kinase activity [2].
- Arrests human fibroblasts in G1 phase [6].
- Antitumor compound [8].
- Activates the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway [9].
- Targets both the p53 and NF-κB pathways[10].
- Has effects on calcium channel gating [12, 17, 18].
- Prevents DNA damage-induced cyclin A1 upregulation [13].
- Apoptosis inducer [11, 15, 20].
- As CYC202 in phase I clinical trials [14].
- Reviews [3, 7, 19].
Product References
- Activation of cyclin-dependent kinases by Myc mediates induction of cyclin A, but not apoptosis: B. Rudolph, et al.; EMBO J. 15, 3065 (1996)
- Biochemical and cellular effects of roscovitine, a potent and selective inhibitor of the cyclin-dependent kinases cdc2, cdk2 and cdk5: L. Meijer, et al.; Eur. J. Biochem. 243, 527 (1997)
- Chemical inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinases: L. Meijer and S.H. Kim; Meth. Enzymol. 283, 113 (1997)
- Cytokinin-derived cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors: synthesis and cdc2 inhibitory activity of olomoucine and related compounds: L. Havlicek, et al.; J. Med. Chem. 40, 408 (1997)
- Direct in vivo inhibition of the nuclear cell cycle cascade in experimental mesangial proliferative glomerulonephritis with Roscovitine, a novel cyclin-dependent kinase antagonist: J.W. Pippin, et al.; J. Clin. Invest. 100, 2512 (1997)
- The cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors olomoucine and roscovitine arrest human fibroblasts in G1 phase by specific inhibition of CDK2 kinase activity: F. Alessi, et al.; Exp. Cell Res. 245, 8 (1998)
- The specificities of protein kinase inhibitors: an update: J. Bain, et al.; Biochem. J. 371, 199 (2003)
- In vitro and in vivo antitumor properties of the cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor CYC202 (R-roscovitine): S.J. McClue, et al.; Int. J. Cancer 102, 463 (2002)
- The Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor CYC202 (R-roscovitine) inhibits retinoblastoma protein phosphorylation, causes loss of Cyclin D1, and activates the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway: S.R. Whittaker, et al.; Cancer Res. 64, 262 (2004)
- R-Roscovitine simultaneously targets both the p53 and NF-kappaB pathways and causes potentiation of apoptosis: implications in cancer therapy: A. Dey, et al.; Cell Death Differ. 15, 263 (2008)
- The CDK inhibitor, R-roscovitine, promotes eosinophil apoptosis by down-regulation of Mcl-1: R. Duffin, et al.; FEBS Lett. 583, 2540 (2009)
- (R)-roscovitine prolongs the mean open time of unitary N-type calcium channel currents: N.R. DeStefino, et al.; Neuroscience 167, 838 (2010)
- R-Roscovitine (Seliciclib) prevents DNA damage-induced cyclin A1 upregulation and hinders non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) DNA repair: M. Federico, et al.; Mol. Cancer 9,208 (2010)
- Phase I evaluation of seliciclib (R-roscovitine), a novel oral cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, in patients with advanced malignancies: C. Le Tourneau, et al.; Eur. J. Cancer 46, 3243 (2010)
- Roscovitine, olomoucine, purvalanol: inducers of apoptosis in maturing cerebellar granule neurons: E.A. Monaco, 3rd, et al.; Biochem. Pharmacol. 67, 1947 (2004)
- Roscovitine targets, protein kinases and pyridoxal kinase: S. Bach, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 280, 31208 (2005)
- The effects of presynaptic calcium channel modulation by roscovitine on transmitter release at the adult frog neuromuscular junction: S. Cho & S.D. Meriney; Eur. J. Neurosci. 23, 3200 (2006)
- Roscovitine differentially affects CaV2 and Kv channels by binding to the open state: Z. Buraei, et al.; Neuropharmacology 52, 883 (2007)
- Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors as anticancer drugs: V. Krystof & S. Uldrijan; Curr. Drug Targets 11, 291 (2010)
- Roscovitine induces cell death and morphological changes indicative of apoptosis in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells: O.P. Mgbonyebi, et al.; Cancer Res. 59, 1903 (1999)
- Polo-like kinase 4 transcription is activated via CRE and NRF1 elements, repressed by DREAM through CDE/CHR sites and deregulated by HPV E7 protein: M. Fischer, et al.; Nucleic Acids Res. 42, 163 (2014) (AdipoGen spec.)
- Roscovitine is a proteostasis regulator that corrects the trafficking defect of F508del-CFTR by a CDK-independent mechanism: C. Norez, et al.; Br. J. Pharmacol. 171, 4831 (2014)