Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
Suramin . sodium salt
As low as
60
CHF
CHF 60.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CR1-3575V-M05050 mgCHF 60.00
AG-CR1-3575V-M250250 mgCHF 240.00
AG-CR1-3575V-G0011 gCHF 720.00
BULK available!
Research Use Only (RUO). NOT ALLOWED FOR USE IN HUMANS.

| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Germanin; NSC 34936; SK 24728 |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
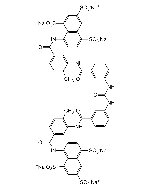
C51H34N6O23S6 . 6Na |
| MW | 1291.2 . 137.9 |
| Merck Index | 14: 9006 |
| CAS | 129-46-4 |
| RTECS | QM7000000 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Synthetic. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC). |
| Appearance | White to off-white powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in water (50mM) or DMSO (10mM). Sparingly soluble in ethanol. |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| Other Product Data |
Water Content (by Karl Fischer): ≤15% Sodium Content: 8.0 - 9.5% Methanol Content: ≤0.1%. Material from competitors contains ~5 times higher levels of methanol. |
| InChi Key | VAPNKLKDKUDFHK-UHFFFAOYSA-H |
| Smiles | [Na+].[Na+].[Na+].[Na+].[Na+].[Na+].CC1=CC=C(C=C1NC(=O)C1=CC(NC(=O)NC2=CC=CC(=C2)C(=O)NC2=C(C)C=CC(=C2)C(=O)NC2=C3C(C=C(C=C3S([O-])(=O)=O)S([O-])(=O)=O)=C(C=C2)S([O-])(=O)=O)=CC=C1)C(=O)NC1=CC=C(C2=C1C(=CC(=C2)S([O-])(=O)=O)S([O-])(=O)=O)S([O-])(=O)=O |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | +4°C |
| Handling Advice | Keep cool and dry. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at +4°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Potent ATPase inhibitor [1].
- Potent competitive inhibitor of reverse transcriptase. Shows anti-HIV activity [2, 3].
- Anticancer compound [4, 5, 15].
- Protein kinase C (PKC) inhibitor [4].
- Potent inhibitor of melanoma heparanase and tumor cell metastasis [6].
- Non-specific growth factors inhibitor (including PDGF, EGF, aFGF and bFGF) [7, 16].
- TGF-β1 inhibitor [8].
- Topoisomerase I and II inhibitor [9].
- Interleukin-1 (IL-1) inhibitor [10].
- Interleukin-4 (IL-4) inhibitor [11].
- G protein inhibitor [12].
- P2X and P2Y purinergic receptor antagonist [13].
- Antiangiogenic. Potent VEGF inhibitor [14, 15].
- Telomerase inhibitor [17].
- Shows adjuvant properties [18].
- Regulates ryanodine receptor [19].
- Direct adenylyl cyclase inhibitor [20].
- Protein synthesis inhibitor [21].
- SIRT1 (sirtuin 1) and SIRT5 (sirtuin 5) inhibitor [22, 23].
- Immunosuppressive [24].
- Antifibrotic agent [25].
- Antiparasitic. Antiprotozoal. Athelmintic [26].
- Cullin-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase inhibitor [29].
- Inhibitor of the STING pathway via the inhibition of cGAMP synthase (cGAS) enzymatic activity [32].
- Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 infection in cell culture by blocking early steps (binding/fusion) of the replication cycle. Potentially binds and inhibits nsp12 of SARS-CoV-2, binding to motifs harbouring the RNA-dependent RNA polymerases (RdRps) activity [34, 36].
- Inhibits several dsDNA-binding proteins, including cGAS (inhibiting cGAS-STING and TLR9 mediated inflammatory responses), Mcm1040 and DNA topoisomerase II, and most recently also the AIM2 inflammasome. Effective inhibitor of dsDNA-induced inflammation [38].
Product References
- Suramin: a potent ATPase inhibitor which acts on the inside surface of the sodium pump: P.A. Fortes, et al.; Biochim. Biophys. Acta 318, 262 (1973)
- Suramin: a potent inhibitor of the reverse transcriptase of RNA tumor viruses: E. De Clerq; Cancer Lett. 8, 9 (1979)
- Suramin protection of T cells in vitro against infectivity and cytopathic effect of HTLV-III: H. Mitsuya, et al.; Science 226, 172 (1984)
- Suramin, an anti-cancer drug, inhibits protein kinase C and induces differentiation in neuroblastoma cell clone NB2A: C.E. Hensey, et al.; FEBS Lett. 258, 156 (1989)
- Suramin: prototype of a new generation of antitumor compounds: R.V. La Rocca, et al.; Cancer Cells 2, 106 (1990) (Review)
- Suramin. A potent inhibitor of melanoma heparanase and invasion: M. Nakajima, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 266, 9661 (1991)
- Nature of the interaction of growth factors with suramin: C.R. Middaugh, et al.; Biochemistry 31, 9016 (1992)
- The antiproliferative effect of suramin on the cancer cell line SW-13 is mediated by the inhibition of transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGF-beta 1): R. Danesi, et al.; Pharmacol. Res. 25, 17 (1992)
- Suramin inhibits DNA damage in human prostate cancer cells treated with topoisomerase inhibitors in vitro: H. Yamazaki, et al.; Prostate 23, 25 (1993)
- Suramin blocks the binding of interleukin-1 to its receptor and neutralizes IL-1 biological activities: G. Strassmann, et al.; Int. J. Immunopharmacol. 16, 931 (1994)
- Suramin blocks binding of interleukin-4 to its receptors on human tumor cells and interleukin-4-induced mitogenic response: P. Leland, et al.; Oncol. Res. 7, 227 (1995)
- Suramin analogues as subtype-selective G protein inhibitors: M. Freissmuth, et al.; Mol. Pharmacol. 49, 602 (1996)
- PPADS and suramin as antagonists at cloned P2Y- and P2U-purinoceptors: S.J. Charlton, et al.; Br. J. Pharmacol. 118, 704 (1996)
- Suramin is a potent inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor. A contribution to the molecular basis of its antiangiogenic action: J. Waltenberger, et al.; J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 28, 1523 (1996)
- Antiangiogenic and antiproliferative activity of suramin analogues: A.R. Gagliardi, et al.; Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 41, 117 (1998)
- Suppression of myocardial inflammation using suramin, a growth factor blocker: T. Shiono, et al.; Circ. J. 66, 385 (2002)
- Suramin suppresses growth, alkaline-phosphatase and telomerase activity of human osteosarcoma cells in vitro: K. Trieb & H. Blahovec; Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 35, 1066 (2003)
- Suramin has adjuvant properties and promotes expansion of antigen-specific Th1 and Th2 cells in vivo: M. Denkinger, et al.; Int. Immunopharmacol. 4, 15 (2004)
- Functional regulation of the cardiac ryanodine receptor by suramin and calmodulin involves multiple binding sites: A.P. Hill, et al; Mol. Pharmacol. 65, 1258 (2004)
- Modulation of adenylyl cyclase activity in young and adult rat brain cortex. Identification of suramin as a direct inhibitor of adenylyl cyclase: J. Stöhr, et al.; J. Cell Mol. Med. 9, 940 (2005)
- Inhibition by suramin of protein synthesis in vitro. Ribosomes as the target of the drug: M. Brigotti, et al.; Biochimie 88, 497 (2006)
- Structure-activity studies on suramin analogues as inhibitors of NAD+-dependent histone deacetylases (sirtuins): J. Trapp, et al.; ChemMedChem 2, 1419 (2007)
- Structural basis of inhibition of the human NAD+-dependent deacetylase SIRT5 by suramin: A. Schuetz, et al.; Structure 15, 377 (2007)
- Suramin inhibits the CD40-CD154 costimulatory interaction: a possible mechanism for immunosuppressive effects: E. Margolles-Clark, et al.; Biochem. Pharmacol. 77, 1236 (2009)
- Tissue protective and anti-fibrotic actions of suramin: new uses of an old drug: N. Liu & S. Zhuang; Curr. Clin. Pharmacol. 6, 137 (2011) (Review)
- The trypanocidal drug suramin and other trypan blue mimetics are inhibitors of pyruvate kinases and bind to the adenosine site: H.P. Morgan, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 286, 31232 (2011)
- Neutralization of Apis mellifera bee venom activities by suramin: C.Z. El-Kik, et al.; Toxicon 67, 55 (2013)
- Suramin inhibits helicase activity of NS3 protein of dengue virus in a fluorescence-based high throughput assay format: C. Basavannacharya & S.G. Vasudevan; BBRC 453, 539 (2014)
- Suramin inhibits cullin-RING E3 ubiquitin ligases: K. Wu, et al.; PNAS 113, E2011 (2016)
- Suramin is a potent inhibitor of Chikungunya and Ebola virus cell entry: L. Henss, et al.; Virol. J. 13, 149 (2016)
- Suramin is a novel competitive antagonist selective to α1β2γ2 GABAA over ρ1 GABAC receptors: H. Luo, et al.; Neuropharmacol. 141, 148 (2018)
- Suramin potently inhibits cGAMP synthase, cGAS, in THP1 cells to modulate IFN-β levels: M. Wang, et al.; Future Med. Chem. 10, 1301 (2018)
- Evaluating the impact of suramin additive on CHO cells producing Fc-fusion protein: J.-H. Lim, et al.; Biotechnol. Lett. 41, 1255 (2019)
- Suramin inhibits SARS-CoV-2 infection in cell culture by interfering 2 with early steps of the replication cycle: C. Salgado, et al.; Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 64, e00900 (2020)
- 100 Years of Suramin: N. Wiedemar, et al.; Antimicr. Agents Chemother. 64, e01168-19 (2020) (Review)
- Suramin, Penciclovir and Anidulafungin bind nsp12, which governs the RNA-dependent-RNA polymerase activity of SARS-CoV-2, with higher interaction energy than Remdesivir, indicating potential in the treatment of Covid-19 infection: S.K. Dey, et al.; J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 40, 14067 (2022)
- High Throughput Screening Targeting the Dengue NS3-NS5 Interface Identifies Antivirals against Dengue, Zika and West Nile Viruses: S.N.Y. Yang, et al.; Cells 11, 730 (2022)
- Discovery of an inhibitor of DNA-driven inflammation that preferentially targets the AIM2 inflammasome: J.P. Green, et al.; iScience 26, 106758 (2023)