Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
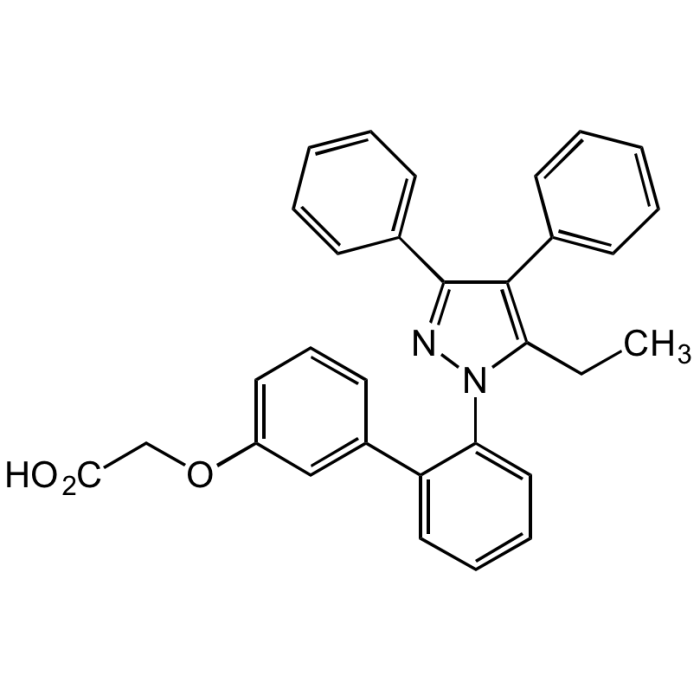
BMS-309403
As low as
45
CHF
CHF 45.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CR1-3640-M0011 mgCHF 45.00
AG-CR1-3640-M0055 mgCHF 80.00
AG-CR1-3640-M02525 mgCHF 260.00
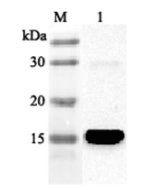
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | BMS309403; BMS 309403; FABP4 Inhibitor; 2-[[2'-(5-Ethyl-3,4-diphenyl-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)[1,1'-biphenyl]-3-yl]oxy]acetic acid |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C31H26N2O3 |
| MW | 474.6 |
| CAS | 300657-03-8 |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO (25mg/ml), ethanol (30mg/ml), dimethylformamide (30mg/ml) or methanol. Almost insoluble in water. |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| InChi Key | SJRVJRYZAQYCEE-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Smiles | CCC1=C(C2=CC=CC=C2)C(C3=CC=CC=C3)=NN1C4=CC=CC=C4C5=CC(OCC(O)=O)=CC=C5 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice |
Keep cool and dry. Protect from moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Cell permeable, potent and selective fatty acid binding protein 4 (FABP4; A-FABP; ALBP; adipocyteP2 protein) inhibitor that competitively targets the fatty acid-binding pocket (Ki= <2nM). Inhibits FABP3 (muscle) and FABP5 (epidermal) with lower affinity (Ki=250nM and 350nM, respectively). FABP4 is an intracellular lipid-binding protein responsible for the transportation of fatty acids. It is expressed primarily in adipose tissue and is associated with inflammation, obesity, diabetes and cardiovascular diseases.
- Glucose uptake stimulator. Reduces blood glucose levels and increases insulin sensitivity in a mouse model of obesity. Protects against the development of insulin resistance associated with genetic or diet-induced obesity in mice.
- Anti-atherosclerotic. Decreases fatty acid uptake in adipocytes in vitro and reduces atherosclerotic lesion area in a mouse model of atherosclerosis.
Product References
- Potent and selective biphenyl azole inhibitors of adipocyte fatty acid binding protein (aFABP): R. Sulsky, et al.; Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 17, 3511 (2007)
- Treatment of diabetes and atherosclerosis by inhibiting fatty-acid-binding protein aP2: M. Furuhashi, et al.; Nature 447, 959 (2007)
- BMS309403 stimulates glucose uptake in myotubes through activation of AMP-activated protein kinase: W. Lin, et al.; PLoS One 7, e44570 (2012)
- FABP4 attenuates PPARγ and adipogenesis and is inversely correlated with PPARγ in adipose tissues: T. Garin-Shkolnik, et al.; Diabetes 63, 900 (2014)
- FABP4 inhibition suppresses PPARγ activity and VLDL-induced foam cell formation in IL-4-polarized human macrophages: M. Boss, et al.; Atherosclerosis 240, 424 (2015)
- Chlamydia pneumoniae Lung Infection in Mice Induces Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 4-Dependent White Adipose Tissue Pathology: Y. Kurihara, et al.; J. Immunol. ahead of print (2023)