Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
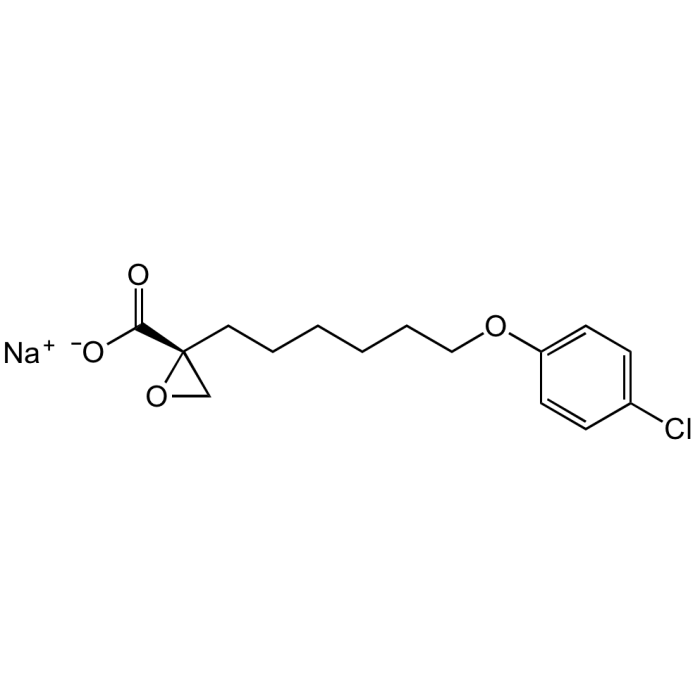
(+)-Etomoxir sodium salt
As low as
90
CHF
CHF 90.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CR1-3688-M0055 mgCHF 90.00
AG-CR1-3688-M02525 mgCHF 250.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | (R)-(+)-Etomoxir . Na; (R)-(+)-2-[6-(4-Chlorophenoxy)hexyl]-oxirane-2-carboxylic acid |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C15H18ClO4 . Na |
| MW | 297.8 . 23.0 |
| CAS | 828934-41-4 |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid. |
| Solubility | Soluble in water (5mg/ml), DMSO (5mg/ml), ethanol (1mg/ml) or DMF (5mg/ml). |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| InChi Key | RPACBEVZENYWOL-XFULWGLBSA-M |
| Smiles | O=C([C@@]1(CCCCCCOC2=CC=C(Cl)C=C2)CO1)[O-].[Na+] |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice |
Keep cool and dry. Protect from light. Protect from moisture and oxygen. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Irreversible inhibitor of carnitine palmitoyltransferase-1 (CPT-1a) a mitochondrial enzyme involved in fatty acid β-oxidation. CPR-1a on the outer face of the inner mitochondrial membrane, consequently prevents the formation of acyl carnitines, a step that is necessary for the transport of fatty acyl chains from the cytosol into the intermembrane space of the mitochondria, essential for the production of ATP from fatty acid oxidation.
- Fatty acid β-oxidation (FAO) inhibitor. By regulating fatty acid oxidation it has hypoketonaemic, hypocholesteraemic and hypolipogenic effect, and the potential to affect ketogenesis, cholesterol synthesis and gluconeogenesis.
- Useful agent for immunometabolism research.
- Anticancer, antiobesity and antidiabetes agent. Increases food intake and reduces hepatic ATP/ADP ratio. Mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation may provide NADPH for defense against oxidative stress and prevent ATP loss and cell death.
- PPARα activator/agonist.
- Shows non-specific effects on oxidative metabolism and cellular redox and induces acute production of ROS with associated evidence of severe oxidative stress in proliferating T cells at above 5μM concentration.
- Shown to have potentiating effects on chemotherapeutic agents.
Product References
- Glucose kinetics during acute and chronic treatment of rats with 2[6(4-chloro-phenoxy)hexyl]oxirane-2-carboxylate, etomoxir: Y.T. Kruszynska & H.S. Sherratt; Biochem. Pharmacol. 36, 3917 (1987)
- Etomoxir, a carnitine palmitoyltransferase I inhibitor, protects hearts from fatty acid-induced ischemic injury independent of changes in long chain acylcarnitine: G.D. Lopaschuk, et al.; Circ. Res. 63, 1036 (1988)
- Inhibition by etomoxir of carnitine palmitoyltransferase I reduces hepatic glucose production and plasma lipids in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: K. Ratheiser, et al.; Metabolism 40, 1185 (1991)
- The effect of etomoxir on the mRNA levels of enzymes involved in ketogenesis and cholesterogenesis in rat liver: G. Asins, et al.; Biochem. Pharmacol. 47, 1373 (1994)
- Improvement of myocardial function and metabolism in diabetic rats by the carnitine palmitoyl transferase inhibitor Etomoxir: F.J. Schmitz, et al.; Horm. Metab. Res. 27, 515 (1995)
- Etomoxir, sodium 2-[6-(4-chlorophenoxy)hexyl] oxirane-2-carboxylate, inhibits triacylglycerol depletion in hepatocytes and lipolysis in adipocytes: T.D. Spurway, et al.; FEBS Lett. 404, 111 (1997)
- Etomoxir-induced PPARalpha-modulated enzymes protect during acute renal failure: D. Portilla, et al.; Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 278, F667 (2000)
- Etomoxir-induced increase in UCP3 supports a role of uncoupling protein 3 as a mitochondrial fatty acid anion exporter: P. Schrauwen, et al.; FASEB J. 16, 1688 (2002)
- Etomoxir, a fatty acid oxidation inhibitor, increases food intake and reduces hepatic energy status in rats: C.C. Horn, et al.; Physiol. Behav. 81, 157 (2004)
- Potentiation of chemotherapeutic drugs by energy metabolism inhibitors 2-deoxyglucose and etomoxir: E. Hernlund, et al.; Int. J. Cancer 123, 476 (2008)
- Inhibition of fatty acid oxidation by etomoxir impairs NADPH production and increases reactive oxygen species resulting in ATP depletion and cell death in human glioblastoma cells: L.S. Pike, et al.; Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1807, 726 (2011)
- Apoptotic efficacy of etomoxir in human acute myeloid leukemia cells. Cooperation with arsenic trioxide and glycolytic inhibitors, and regulation by oxidative stress and protein kinase activities: M.C. Estan, et al.; PLoS One 9, e115250 (2014)
- A guide to immunometabolism for immunologists: L.A. O'Neill, et al.; Nat. Rev. Immunol. 16, 553 (2016) (Review)
- Identifying off-target effects of etomoxir reveals that carnitine palmitoyltransferase I is essential for cancer cell proliferation independent of β-oxidation: C.H. Yao, et al.; PLoS Biol. 16, e2003782 (2018)
- The CPT1a inhibitor, etomoxir induces severe oxidative stress at commonly used concentrations: R.S. O'Connor, et al.; Sci. Rep. 8, 6289 (2018)