Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
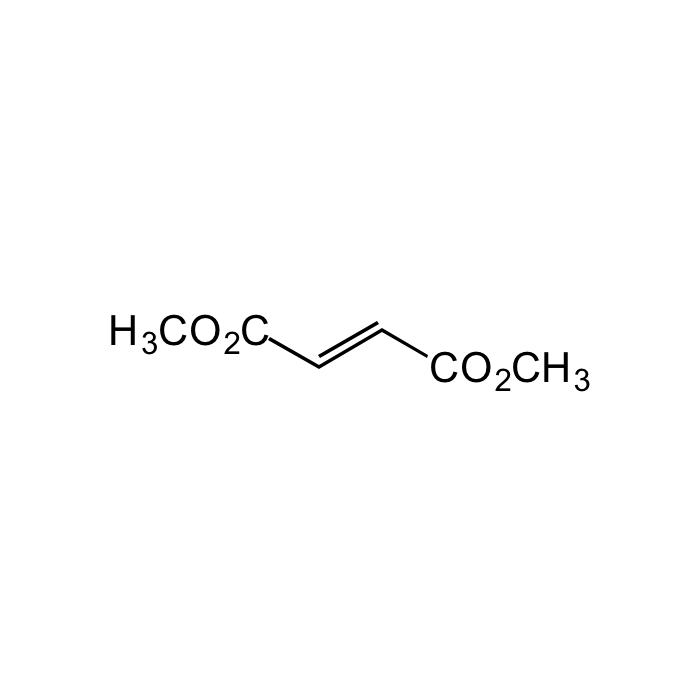
Dimethyl fumarate
As low as
20
CHF
CHF 20.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CR1-3701-G0011 gCHF 20.00
AG-CR1-3701-G0055 gCHF 28.00
AG-CR1-3701-G02525 gCHF 40.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | DMF; DMFu; Fumaric Acid Dimethyl Ester; BG00012; NSC25942; NSC167432; trans-Butenedioic acid dimethyl ester |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C6H8O4 |
| MW | 144.1 |
| CAS | 624-49-7 |
| RTECS | EM6125000 |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥95% |
| Appearance | White to off-white powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO (10mg/ml), ethanol (5mg/ml) or DMF (10mg/ml). Sparingly soluble in aqueous buffers. |
| InChi Key | LDCRTTXIJACKKU-ONEGZZNKSA-N |
| Smiles | O=C(/C=C/C(OC)=O)OC |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Keep cool and dry. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory agent used in patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (MS) and psoriasis. Causes an immune switch characterized by induction of anti-inflammatory/regulatory innate and adaptive immune cell populations such as regulatory T cells (Tregs) and inhibition or apoptosis of pro-inflammatory cells, such as T helper 1 (Th1) and Th17 subsets.
- Blocks immune cell activation through inhibition of glycolysis via post-transcriptional modification (succination) of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) in vitro and in vivo and is therefore a useful agent for immunometabolism research. GAPDH catalyzes the conversion of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate to 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate during glycolysis, an essential metabolic pathway where glucose is converted to pyruvate, to fuel the TCA cycle and oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) for the production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) as an energy source. GAPDH was previously reported to be succinated on the cysteine-152 in the active site, a modification that leads to the irreversible inactivation of its enzymatic activity.
- Immunomodulatory effects have been shown on both tissue and immune cells. Possible targets include the engagement of antioxidant responses through activation of nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 (Nrf2), inhibition of nuclear factor κ-light-chain enhancer of activated B cells (NF-kB) and engagement with a putative receptor called HCA2.
- Suppresses NLRP3 inflammasome activation through Nrf2 activation.
- Dimethyl fumarate (DMF) affects inflammatory responses by inhibiting cleavage of Gasdermin D and consequently pyroptotic cell death, by succination of a critical cysteine of Gasdermin D (GSDMD) to prevent its interaction with caspases, its oligomerization to form membrane pore and its capacity to induce cell death.
- Anticancer agent. Angiogenesis inhibitor in vitro and in vivo. Blocks NF-κB activity in multiple breast cancer cell lines and abrogates NF-κB-dependent mammosphere formation, inhibits cell proliferation and significantly impairs xenograft tumor growth.
- Exerts neuroprotective effects in vivo in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.
- Has antimicrobial and antifungal activity.
- Derivative of the TCA cycle intermediate fumarate. Rapidly interacts in a Michael addition reaction with glutathione or is metabolized to monomethyl fumarate.
Product References
- Inhibition of Escherichia coli by dimethyl fumarate: H.H. Wang, et al.; Int. J. Food Microbiol. 65, 125 (2001)
- Dimethyl fumarate, a small molecule drug for psoriasis, inhibits Nuclear Factor-kappaB and reduces myocardial infarct size in rats: S. Meili-Butz, et al.; Eur. J. Pharmacol. 586, 251 (2008)
- Dimethylfumarate inhibits angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo: a possible role for its antipsoriatic effect?: M. Garcia-Caballero, et al.; J. Invest. Dermatol. 131, 1347 (2011)
- Dimethyl fumarate: a Janus-faced substance? F. Kees; Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 14, 1559 (2013) (Review)
- Dimethyl fumarate modulation of immune and antioxidant responses: application to HIV therapy: A.J. Gill & D.L. Kolson; Crit. Rev. Immunol. 33, 307 (2013) (Review)
- Dimethyl fumarate (Tecfidera): a new oral agent for multiple sclerosis: J.V. Venci & M.A. Gandhi; Ann. Pharmacother. 47, 1697 (2013) (Review)
- Dimethyl fumarate inhibits the expression and function of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α): G. Zhao, et al.; BBRC 448, 303 (2014)
- Dimethyl fumarate induces apoptosis of hematopoietic tumor cells via inhibition of NF-κB nuclear translocation and down-regulation of Bcl-xL and XIAP: M. Tsubaki, et al.; Biomed. Pharmacother. 68, 999 (2014)
- Dimethyl fumarate induces necroptosis in colon cancer cells through GSH depletion/ROS increase/MAPKs activation pathway: X. Xie, et al.; Br. J. Pharmacol. 172, 3929 (2015)
- Dimethyl fumarate ameliorates dextran sulfate sodium-induced murine experimental colitis by activating Nrf2 and suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome activation: X. Liu, et al.; Biochem. Pharmacol. 112, 37 (2016)
- Dimethyl Fumarate Controls the NRF2/DJ-1 Axis in Cancer Cells: Therapeutic Applications: N.E. Saidu, et al.; Mol. Cancer Ther. 16, 529 (2017)
- Dimethyl Fumarate Induces Glutathione Recycling by Upregulation of Glutathione Reductase: C. Hoffmann, et al.; Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2017, 6093903 (2017)
- Targeting Thioredoxin-1 by dimethyl fumarate induces ripoptosome-mediated cell death: A. Schroeder, et al.; Sci. Rep. 7, 43168 (2017)
- Opposing effects of Nrf2 and Nrf2-activating compounds on the NLRP3 inflammasome independent of Nrf2-mediated gene expression: M. Garstkiewicz, et al.; Eur. J. Immunol. 47, 806 (2017)
- Dimethyl fumarate targets GAPDH and aerobic glycolysis to modulate immunity: M.D. Kornberg, et al.; Science 360, 449 (2018)
- Dimethyl fumarate downregulates the immune response through the HCA2/GPR109A pathway: Implications for the treatment of multiple sclerosis: F. von Glehn, et al.; Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 23, 46 (2018) (Review)
- Dimethyl fumarate: targeting glycolysis to treat MS: S. Angiari & A. O'Neill; Cell Res. 28, 613 (2018) (Comment)
- Succination inactivates gasdermin D and blocks pyroptosis: F. Humphries, et al.; Science 369, 1633 (2020)