Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
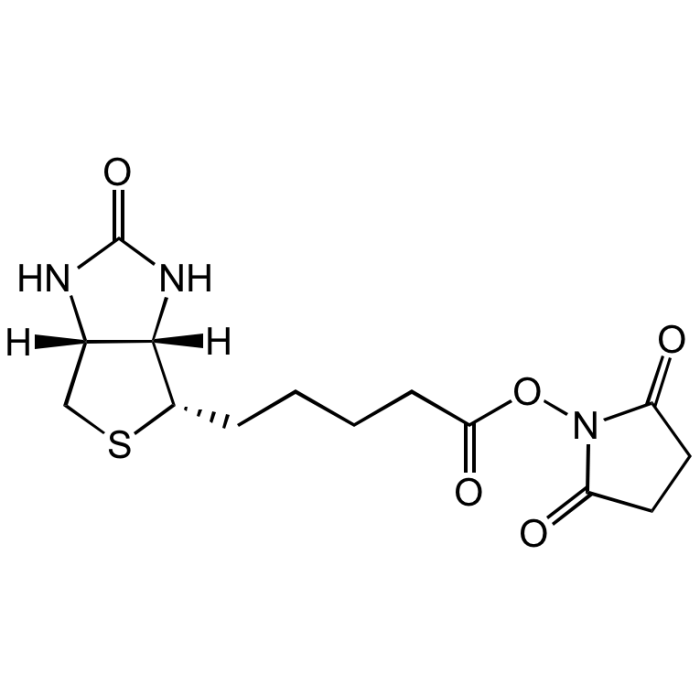
(+)-Biotin N-hydroxysuccinimide ester
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | (+)-Biotin N-succinimidyl ester; d-Biotin NHS ester; BNHS; Biotinyl-N-hydroxy-succinimide; N-Hydroxysuccinimidobiotin; N-Succinimidyl D-biotinate; NHS-Biotin; Biotin-Osu; NSC 345668 |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C14H19N3O5S |
| MW | 341.38 |
| CAS | 35013-72-0 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Synthetic. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | White to off-white powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO or DMF. |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | YMXHPSHLTSZXKH-RVBZMBCESA-N |
| Smiles | O=C(ON1C(CCC1=O)=O)CCCC[C@@H]2SC[C@@]3([H])[C@]2([H])NC(N3)=O |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Biotin succinimidyl ester is the most popular amine-reactive biotinylating agent for modifying proteins, peptides, antibodies, oligonucleotides, microbeads and other biological molecules. It forms irreversible amide bonds. Typically coupled to primary amine in the pH range 6.5-8.5. This cell-permable activated biotin derivative can be readily coupled to primary or secondary amines of analyte compounds or proteins under mild conditions. The resulting biotinylated derivatives have been widely used in streptavidin or avidin systems and labeling methods, with many applications in immunology and histochemistry. It is used to selectively label Escherichia coli cell envelope proteins in vivo. It preferentially labels outer membrane, periplasmic, and inner membrane proteins as well as a specific inner membrane marker protein (Tet-LacZ).
(1) D.M. Boorsma, et al.; J. Microsc. 143, 197 (1986) | (2) P. Kongtawelert & P. Ghosh; Clin. Chem. Acta 195, 17 (1990) | (3) G. Paganelli, et al.; Int. J. Cancer 45, 1184 (1990) | (4) C. Wagener, et al.; Meth. Enzymol. 184, 518 (1990) | (5) B. Baumeister, et al.; Int. J. Pep. Res. Therap. 11, 139 (2005) | (6) G.T. Hermanson; Bioconjugate Techn. 2nd p506-545 (2008)





