Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
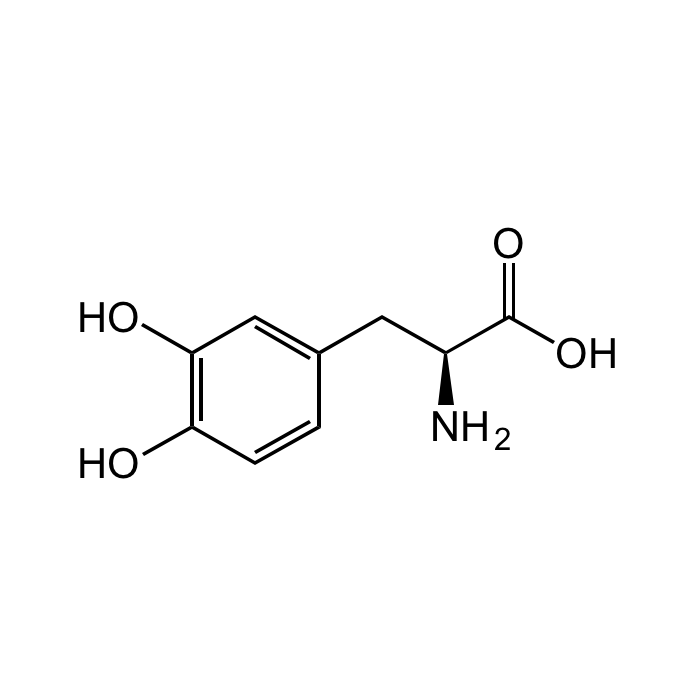
3,4-Dihydroxy-L-phenylalanine
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | 3-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-L-alanine; L-DOPA; 3-Hydroxy-L-tyrosine; Levodopa |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C9H11NO4 |
| MW | 197.19 |
| CAS | 59-92-7 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Synthetic |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% |
| Appearance | White to off-white powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in water (5-10mM), acidic and basic solutions. |
| Identity | Determined by NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | WTDRDQBEARUVNC-LURJTMIESA-N |
| Smiles | OC1=C(O)C=CC(C[C@H](N)C(O)=O)=C1 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +20°C |
| Long Term Storage | +20°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at +20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Metabolic precursor of the neurotransmitters dopamine, norepinephrine (noradrenaline), and epinephrine (adrenaline), which are collectively known as catecholamines. This amino acid is produced from L-tyrosine by tyrosine hydroxylase and metabolized by catechol-O-methyl transferase (COMT). L-DOPA is capable of crossing the blood brain barrier where it is converted to dopamine. Formulations containing L-DOPA have been used to increase dopamine concentrations in the brain as a treatment for Parkinson’s disease and stroke recovery. Mediates neurotrophic factor release by the brain and CNS. Used for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease and dopamine-responsive dystonia. In addition it is used, as a cell adhesion molecule in serum-free cultures of anchorage-dependent mammalian cells, to prevent surfaces from fouling by bonding antifouling polymers to a susceptible substrate or to stain melanocytes.
(1) O. Hornykiewicz; Life Sci. 15, 1249 (1974) (Review) | (2) Y. Misu, et al.; Adv. Pharmacol. 32, 427 (1995) (Review) | (3) J.G. Nutt; Adv. Neurol. 69,493 (1996) (Review) | (4) R.M. Kostrzewa, et al.; Amino Acids 23, 57 (2002) (Review) | (5) N.B. Mercuri & G. Bernardi; Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 26, 341 (2005) (Review) | (6) M.A. Mena, et al.; Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 9, 880 (2009) (Review) | (7) H.I. Berends, et al.; Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 45, 621 (2009) (Review) | (8) H. Iderberg, et al.; Neuroscience 211, 13 (2012) (Review) | (9) Y. Huang, et al.; Electrochim. Acta 113, 564 (2013) | (10) P. Huot, et al.; Pharmacol. Rev. 65, 171 (2013) (Review) | (11) J. Tang, et al.; Cytotechnology 66, 891 (2014) | (12) G. Fichman, et al.; ACS Nano. 8, 7220 (2014) | (13) M.M. Conti, et al.; Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. (Epub ahead of print) (2018) (Review)