Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
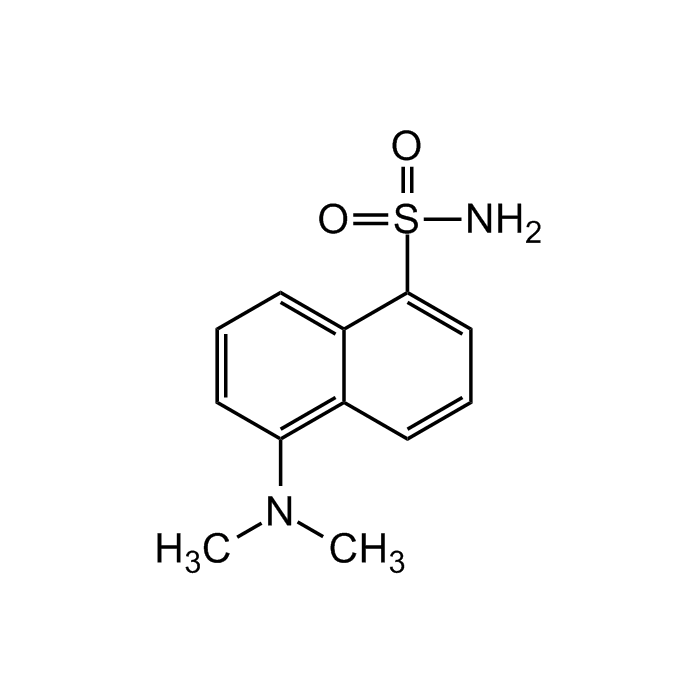
Dansylamide
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | 5-(Dimethylamino)-1-naphthalenesulfonamide; DNSA; Dansyl Amide |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C12H14N2O2S |
| MW | 250.3 |
| CAS | 1431-39-6 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Synthetic. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥97% (NMR) |
| Appearance | White to off-white powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO (20mg/ml). |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | TYNBFJJKZPTRKS-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Smiles | O=S(C1=CC=CC2=C(N(C)C)C=CC=C21)(N)=O |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +20°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Dansylamide (DNSA) is a fluorescent dye that forms in a reaction between dansyl chloride and ammonia. Dansylamide is widely used in biochemistry and chemistry to label substances with the fluorescent dansyl group. The dansyl group can be introduced into amino acids or other amines. The excitation maximum (350 nm) is essentially independent on the medium, whereas the emission maximum strongly depends on the solvent and varies from 520 to 550 nm. The fluorescent dye dansylamide selectively interacts with the binding site I of human serum albumin (HSA). Changes in probe fluorescence can be analyzed by fluorescence titrations as a result of competitive displacement by drugs and pharmaceuticals. Dansylamide can also be used as an active site probe for carbonic anhydrase and as an effective acceptor in FRET probes to quantify protein fluorescence. Dansylamide is also used as building block or intermediate in synthesis of fluorescent dyes.
(1) Y. Tapuhi, et al.; Anal. Biochem. 115, 123 (1981) | (2) A. Jain, et al.; J. Med. Chem. 37, 2100 (1994) | (3) N. Muller, et al.; J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 46, 300 (1994) | (4) M. Asano, et al.; Macromolecules 28, 5861 (1995) | (5) K. Yamasaki, et al.; Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1432, 313 (1999) | (6) A. Misra, et al.; Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 44, 291 (2000) | (7) A.L. Banerjee, et al.; Biochemistry 44, 3673 (2005) | (8) A. Thorarensen, et al.; Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 17, 4646 (2007) | (9) S. Manokaran, et al.; Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1804, 1965 (2010) | (10) Y. Zhang, et al.; J. Fluoresc. 23, 147 (2013) | (11) J.C. Er, et al.; ACS Comb. Sci. 15, 452 (2013)