Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
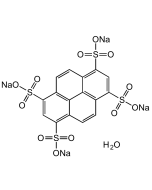
Indigo carmine
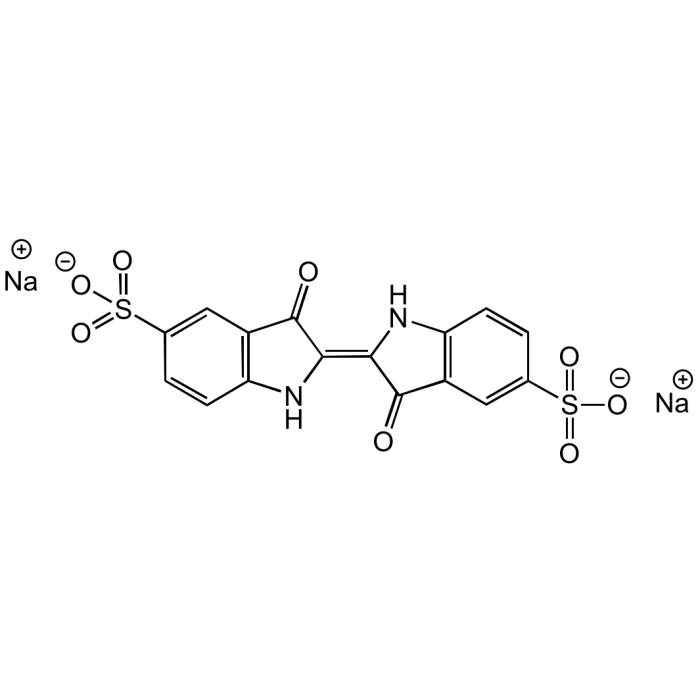
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Acid Blue 74; Indigo-5,5'-disulfonic acid disodium salt; Indigocarmine; Amacid Brilliant Blue; CI 73015 |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula | C16H8N2Na2O8S2 |
| MW | 466.35 |
| CAS | 860-22-0 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Synthetic. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥95% (UV/Vis) |
| Appearance | Dark blue powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in water. Slightly soluble in ethanol. Insoluble in benzene or chloroform. |
| Identity | Determined by NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | KHLVKKOJDHCJMG-QDBORUFSSA-L |
| Smiles | O=C(C(C=C(S(=O)([O-])=O)C=C1)=C1N/2)C2=C3C(C(C=C(S(=O)([O-])=O)C=C4)=C4N\3)=O.[Na+].[Na+] |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +20°C |
| Long Term Storage | +20°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at +20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Indigo carmine is a blue, anionic indigoid dye consisting of an indigo dimer with sodium salts of sulfonic acids at positions 5 and 5'. This compound has been used as a tissue stain, pH indicator (Blue (at pH11.5) to yellow (at pH14.0)) and tool for the determination of hypochlorite in solutions. It is also applied in detecting microorganisms, treating amyloidosis, in medical devices and drug delivery systems. It can be used as a contrast stain for plasma when red nuclear stains are used. It is widely used in food and cosmetic industry (beverages, chewing gums, candies, drinks, frozen products, sweetener, tablets, sunscreen, skin and hair products) and as an additive or as a dye for cationic cotton fabrics, filters, display devices, inks, toners, paints, photographic material and toys. Spectral Data: Absorption λmax 608nm.
(1) G.G. Reinle & E.S. Depuy; Cal. State J. Med. 18, 49 (1920) | (2) M. Mortreuil-Langlois; Stain Technol. 37, 175 (1962) | (3) K. Ikeda, et al.; Endoscopy 14, 119 (1982) | (4) F.C. Monson, et al.; J. Urol. 145, 842 (1991) | (5) M. Lee & R. Sharifi; Urology 47, 783 (1996) | (6) A. Harriram, et al.; J. Environ. Sci. Health A Tox. Hazard Subst. Environ. Eng. 3, 1055 (2003) | (7) A.G. Prado, et al.; J. Colloid Interface Sci. 277, 43 (2004) | (8) D.P. Hurlstone, et al.; Biotech. Histochem. 82, 57 (2007) (Review) | (9) R.W. Sabnis; Handbook of biological dyes and stains (2010) | (10) B.E. Lee, et al.; BMC Gastroenterol. 10, 97 (2010) | (11) Y. Ma, et al. ; J. Agric. Food Chem. 60, 10867 (2012) | (12) M. Yao, et al.; Sci. Rep. 4, 3650 (2014) | (13) A.L. Costa, et al. ; Chemistry 21, 12069 (2015)