Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
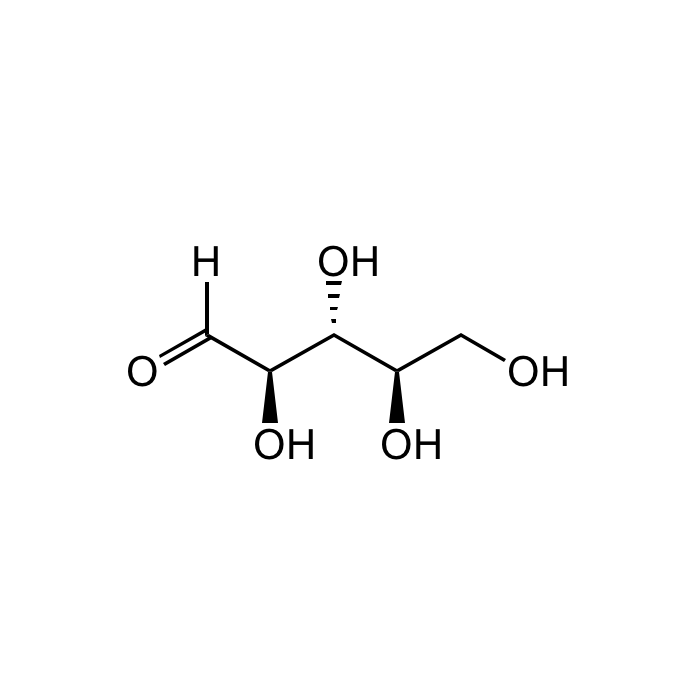
D-(-)-Ribose
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | (2R,3R,4R)-2,3,4,5-Tetrahydroxypentanal; Ribose |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula | C5H10O5 |
| MW | 150.13 |
| CAS | 50-69-1 |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | White to off-white powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in water. |
| Identity | Determined by NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | PYMYPHUHKUWMLA-LMVFSUKVSA-N |
| Smiles | O=C([H])[C@@H]([C@@H]([C@@H](CO)O)O)O |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +20°C |
| Long Term Storage | +4°C |
| Handling Advice |
Keep cool and dry. Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at +4°C. |
| Documents | |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Aldopentose monosaccharide that is phosphorylated into D-ribose 5-phosphate by ribokinase. D-ribose-5-phosphate supports the biosynthesis of the amino acids tryptophan and histidine, and is a component in the pentose phosphate pathway. D-ribose is present in all living cells and their microenvironments and is a key component of numerous biomolecules involved in many important metabolic pathways. It also participates in the glycation of proteins producing advanced glycation end products (AGEs) that lead to cell dysfunction and death. Ribosylation, has been shown to cause protein aggregation in vitro and in vivo. Has demonstrated significant enhancing abilities in replenishing deficient cellular energy levels following myocardial ischemia, improving depressed function in numerous animal investigations and showing cellular protection during oxidative stress. D-Ribose is used as a supplement in cell culture and as a building block for synthesis.
(1) L.M. Shecterle, et al.; Recent Pat. Cardiovasc. Drug Discov. 5, 138 (2010) | (2) P. Addis, et al.; J. Diet. Suppl. 9, 178 (2012) | (3) Y. Wei, et al.; Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1820, 488 (2012) | (4) N. Minakawa & A. Matsuda; Curr. Protoc. Nucleic Acid Chem. 59, 14 (2014)