Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
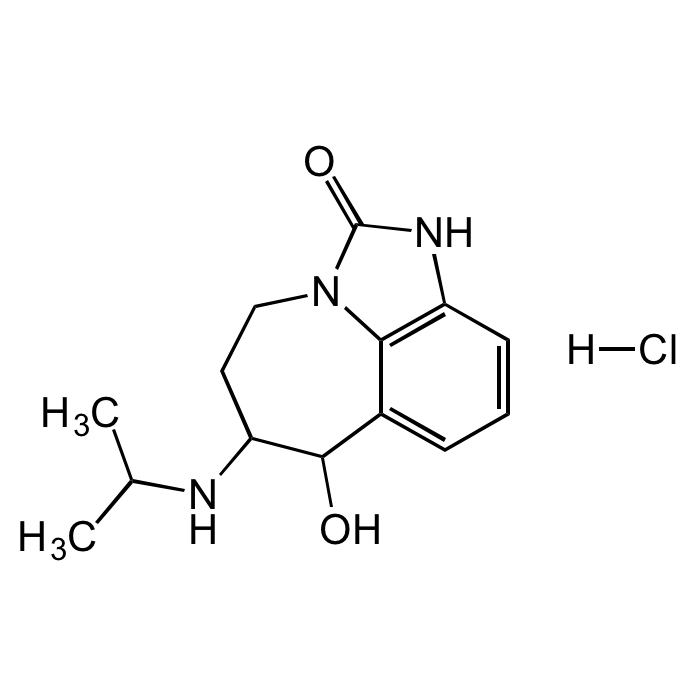
Zilpaterol hydrochloride
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | (6RS,7RS)-4,5,6,7-Tetrahydro-7-hydroxy-6-[(1-methylethyl) amino]imidazo[ 4,5,1-jk][1]benzazepin-2(1H)-one hydrochloride; Zilmax |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula | C14H19N3O2 . HCl |
| MW | 297.78 |
| CAS | 119520-06-8 |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥97% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | White to off-white powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in water. Slightly soluble in methanol. |
| Identity | Determined by NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | GIEFXLLRTJNFGT-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Smiles | O=C1NC2=C(N1CCC(NC(C)C)C3O)C3=CC=C2.[H]Cl |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice |
Keep cool and dry. Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Synthetic β2-adrenoreceptor agonist that binds with the muscle β-adrenoreceptors, leading to the activation of protein kinase A, an enzyme responsible for changes in protein synthesis and degradation, in particular in skeletal muscles. Due to its partial activity towards β1-adrenoreceptors, has also the potential to affect cardiac muscle. In consequence, application of zilpaterol leads to preferential induction of fast glycolytic fibre types over slow oxidative fibre types resulting in enhanced growth efficiency and carcass leanness. Used as a veterinary drug in cattle to enhance growth performance in several countries.
(1) B. Bocca, et al.; J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 783, 141 (2003) | (2) C.P. Birkelo; Vet. Clin. North Am. Food Anim. Pract. 19, 599 (2003) (Review) | (3) K.C. Verhoeckx, et al.; J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 28, 531 (2005) | (4) J.L. Montgomery, et al.; J. Anim. Sci. 87, 1374 (2009) | (5) J.M. Leheska, et al.; J. Anim. Sci. 87, 1384 (2009) | (6) C. Kern, et al.; J. Med. Chem. 52, 1773 (2009) | (7) T.J. Centner, et al.; J. Anim. Sci. 92, 4234 (2014) (Review) | (8) C.L. Van Bibber-Krueger, et al.; J. Anim. Sci. 93, 2419 (2015)