Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
JaICA
UIBC Colorimetric Assay Kit (Bathophenanthroline Method)
As low as
557
CHF
CHF 557.00
In stock
Only %1 left
JAI-CBC-800100 testsCHF 557.00

| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Unsaturated Iron Binding Capacity Assay Kit |
| Product Type | Kit |
| Properties | |
| Application Set | Quantitative ELISA |
| Specificity | Detection of unsaturated iron binding capacity (UIBC) by measuring a proportional difference between Fe2+ and Fe3+. |
| Crossreactivity | All |
| Quantity | Enough reagents for 100 tests. |
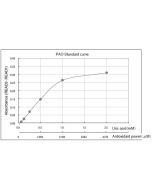
| Range | 10 - 800μg/dL |
| Sample Type |
Plasma Serum |
| Detection Type | Colorimetric |
| Kit Contains |
1 x 20 ml R-1 Buffer (Iron concentration 80μg/dL) (ready to use) 1 x 3 ml R-2 Chelate color (ready to use) |
| Other Product Data |
This MC-Reagent UIBC Assay Kit is intended for the quantitative determination of unsaturated iron binding capacity (UIBC) in samples by 96-well reader use. The kit utilizes the chromogen bathophenanthroline to bind Fe2+. Fe3+ is then reduced to Fe2+ by a reducing agent. The Fe2+ reacts with bathophenanthroline to form a colored complex which is measured by 96-well reader or spectrophotometer and is proportional to the amount of iron present. Absorbance of the Fe2+-complex is measured at 546nm and 600nm (reference wavelength). EDTA-Plasma samples cannot be used due to interference with the chromogenic system. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by JaICA. |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | BLUE ICE |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | +4°C |
| Handling Advice | Do not freeze. |
| Use/Stability | 12 months after the day of manufacturing. See expiry date on ELISA Kit box. |
| Documents | |
| Manual |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
Iron is an essential element in mammalians and is contained in various enzymes and is involved in oxidation reactions. Iron is essential during transport of oxygen as composition element of hemoglobin or myoglobin. 30% of the transferrin is associated with Fe3+ in blood. Free transferrin is not associated to iron. TIBC (Total iron binding capacity) = UIBC (Unsaturated iron binding capacity) + Serum iron. TIBC levels change in blood disorders, hepatic diseases, tumors and inflammation. UIBC levels are increased in patients with iron deficiency. Decreased levels of UIBC are seen in patients with infectious diseases, nephrotic syndrome and low proteinosis.
Product References
- Biliary excretion of excess iron in mice requires hepatocyte iron import by Slc39a14: M. Prajapati, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 297, 100835 (2021)