Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
RevMab
anti-EGFRvIII (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM419) (Biotin)

| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Variant III |
| Product Type | Recombinant Antibody |
| Properties | |
| Clone | RM419 |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Source/Host | Rabbit |
| Immunogen/Antigen | A peptide corresponding to epidermal growth factor receptor variant III (EGFRvIII). |
| Label/Conjugates | Biotin |
| Application |
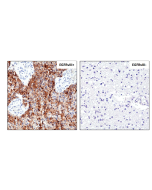
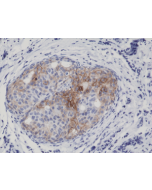
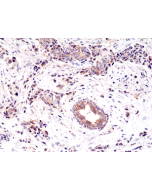
Immunohistochemistry (IHC): 1:100-1:200 dilution |
| Crossreactivity | Human |
| Specificity |
This antibody reacts to human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Variant III. No cross reactivity with wild type EGF receptor. |
| Purity | Protein A purified. |
| Purity Detail | Protein A affinity purified from an animal origin-free culture supernatant. |
| Concentration | N/A |
| Formulation | Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| Accession Number | P00533 |
| Declaration | Manufactured by RevMab Biosciences. |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | BLUE ICE |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
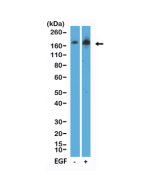
EGFR (Epidermal growth factor receptor, HER1, ErbB1) belongs to the HER/ERbB family of proteins that includes three other receptor tyrosine kinases, ERbB2, ERbB3, ERbB4. EGFR is a transmembrane receptor and binding of its cognate ligands such as EGF (Epidermal Growth Factor) and TGF alpha (Transforming Growth Factor alpha) to the extracellular domain leads to EGFR dimerization followed by autophosphorylation of the tyrosine residues in the cytoplasmic domain (these include Y992, Y1045, Y1068, Y1148 and Y1173). Phosphorylation of EGF receptor (EGFR) at Tyr845 in the kinase domain is implicated in stabilizing the activation loop, maintaining the active state enzyme, and providing a binding surface for substrate proteins. The SH2 domain of PLCγ binds at phospho-Tyr992, resulting in activation of PLCγ-mediated downstream signaling. Phosphorylation of EGFR at Tyr1045 creates a major docking site for the adaptor protein c-Cbl, leading to receptor ubiquitination and degradation following EGFR activation. The GRB2 adaptor protein binds activated EGFR at phospho-Tyr1068. A pair of phosphorylated EGFR residues (Tyr1148 and Tyr1173) provide a docking site for the Shc scaffold protein, with both sites involved in MAP kinase signaling activation. Phosphorylation of EGFR at specific serine and threonine residues attenuates EGFR kinase activity. EGFR carboxy-terminal residues Ser1046 and Ser1047 are phosphorylated by CaM kinase II; mutation of either of these serines results in upregulated EGFR tyrosine autophosphorylation. EGFR activation signals multiple downstream signaling cascades such as the Ras - ERK, PI3K - Akt, Jak - STAT and PKC pathways that help in growth and proliferation of cells. Mutations in the EGFR gene (e.g. L858R) are associated with lung cancer and multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants encode different protein isoforms of EGFR have been found. The type III EGF deletion-mutant receptor (EGFRvIII) is the most common mutation and was first identified in primary human glioblastoma tumors. Increased production or activation of EGFR has been associated with poor prognosis in a variety of tumors. Moreover, EGFR overexpression is observed in tumors of the head and neck, brain, bladder, stomach, breast, lung, endometrium, cervix, vulva, ovary, esophagus, stomach and in squamous cell carcinoma. Deficient signaling of the EGFR and other receptor tyrosine kinases in humans is associated with diseases such as Alzheimer's.