Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
SouthBayBio
Ubiquitin aldehyde (human) (rec.)
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Protein |
| Properties | |
| Source/Host | E. coli |
| Sequence | Human ubiquitin (aa1-76) (Accession Nr. P0CG47) with a C-terminal aldehyde. |
| Crossreactivity | Human |
| Application | Typical working concentration range is 1-5 μM. Reaction conditions will need to be optimized for each specific application. |
| MW | ~9kDa |
| Purity | ≥97% (LCMS) |
| Concentration | Lot dependent. |
| Accession Number | P0CG47 |
| Formulation | Liquid. In 50mM NaOAc pH 5.0. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for a Typical Lot-specific Product Datasheet from the Original Manufacturer |
| Declaration | Manufactured by South Bay Bio. |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | DRY ICE |
| Short Term Storage | -20°C |
| Long Term Storage | -80°C |
| Handling Advice | Aliquot to avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at -80°C. |
| Documents | |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
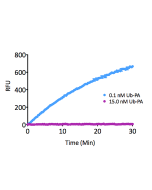
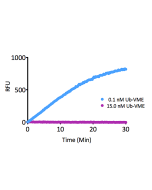
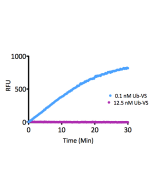
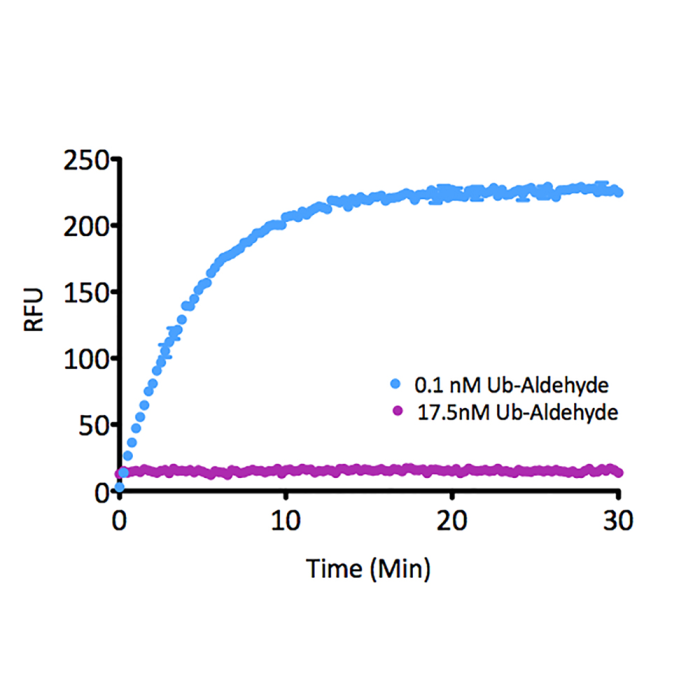
Ubiquitin is a small (8.5kDa) regulatory protein that has been found in almost all tissues of eukaryotic organisms. The addition of ubiquitin to a substrate protein is called ubiquitination or ubiquitylation. Ubiquitination can affect proteins in many ways: it can signal for their degradation via the proteasome, alter their cellular location, affect their activity and promote or prevent protein interactions. Removal of ubiquitin from a substrate protein occurs via deconjugating enzymes, of which there are nearly 100 known enzymes with various linkage specificities. This product consists of a full-length human, mature ubiquitin polypeptide (amino acids 1-76), expressed in E.coli with a C-terminal warhead (Aldehyde). Ubiquitin aldehyde is a potent, irreversible and specific inhibitor of deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs) based on a C-terminal electrophilic aldehyde group. Ubiquitin aldehyde can be used for activity profiling experiments and determining DUB inhibitor specificity. It targets four of the five major DUB families: UCH (Ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolases), USP (Ubiquitin specific proteases), OTU (Ovarian tumor proteases) and MJD (Machado-Josephin domain proteases) while JAMM metalloproteases are not inhibited.