Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
anti-FOXP3 (mouse), mAb (MF333F)
Replaces Item #AG-20A-0025

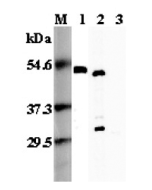
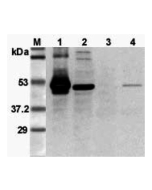
1. Recombinant mouse Foxp3 (His-tagged).
2. Transfected mouse Foxp3 full length cell lysate (HEK 293).
3. Mock Transfected HEK293 cell lysate.
4. PHA- treated mouse T cell (CD4+) lysate.
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Forkhead Box Protein P3; Scurfin |
| Product Type | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Properties | |
| Clone | MF333F |
| Isotype | Rat IgG2aκ |
| Source/Host | Purified from concentrated hybridoma tissue culture supernatant. |
| Immunogen/Antigen | Recombinant mouse FOXP3. |
| Application |
ELISA: (direct or indirect: 1:2'000-1:10'000) |
| Crossreactivity | Mouse |
| Specificity |
Recognizes mouse FOXP3. Detects a band of ~46-49kDa by Western blot. |
| Purity | ≥95% (SDS-PAGE) |
| Purity Detail | Protein G-affinity purified. |
| Concentration | 1mg/ml |
| Formulation | Liquid. 0.2μm-filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.4. Contains no preservatives. |
| Isotype Negative Control | |
| Other Product Data |
Uniprot: FOXP3 (mouse) |
| Accession Number | Q99JB6 |
| RRID | AB_2490107 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | BLUE ICE |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice |
After opening, prepare aliquots and store at -20°C. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
FOXP3 is involved in immune system responses. It functions as the master regulator in the development and function of regulatory T cells. FOX proteins belong to the forkhead/winged-helix family of transcriptional regulators and are presumed to exert control via similar DNA binding interactions during transcription. Defects in FOXP3 are the cause of immunodeficiency polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, X-linked syndrome (IPEX); also known as X-linked autoimmunity-immunodeficiency syndrome. IPEX is characterized by neonatal onset insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, infections, secretory diarrhea, trombocytopenia, anemia and eczema.
- Alternatively activated dendritic cells preferentially secrete IL-10, expand Foxp3+CD4+ T cells, and induce long-term organ allograft survival in combination with CTLA4-Ig: Y.Y. Lan, et al.; J. Immunol. 177, 5868 (2006)
- Dendritic cells expressing transgenic galectin-1 delay onset of autoimmune diabetes in mice: M.J. Perone, et al.; J. Immunol. 177, 5278 (2006)
- Immunosurveillance of Erbb2 carcinogenesis in transgenic mice is concealed by a dominant regulatory T-cell self-tolerance: E. Ambrosino, et al.; Cancer Res. 66, 7734 (2006)
- Regulated compartmentalization of programmed cell death-1 discriminates CD4+CD25+ resting regulatory T cells from activated T cells: G. Raimondi, et al.; J. Immunol. 176, 2808 (2006)
- Antimetastatic activity of a preventive cancer vaccine: P. Nanni, et al.; Cancer Res. 67, 11037 (2007)
- Rapamycin-conditioned dendritic cells are poor stimulators of allogeneic CD4+ T cells, but enrich for antigen-specific Foxp3+ T regulatory cells and promote organ transplant tolerance: H.R. Turnquist, et al.; J. Immunol. 178, 7018 (2007)
- Pretransplant infusion of mesenchymal stem cells prolongs the survival of a semiallogeneic heart transplant through the generation of regulatory T cells: F. Casiraghi, et al.; J. Immunol. 181, 3933 (2008)
- Suppression of autoimmune diabetes by soluble galectin-1: M.J. Perone, et al.; J. Immunol. 182, 2641 (2009)
- Protective role for TLR4 signaling in atherosclerosis progression as revealed by infection with a common oral pathogen: C. Hayashi, et al.; J. Immunol. 189, 3681 (2012)
- Acceleration of diabetes development in CXC chemokine receptor 3 (CXCR3)-deficient NOD mice: Y. Yamada, et al.; Diabetologia 55, 2238 (2012)
- Characteristics of CD4 + CD25 + Foxp3 + regulatory T cells in patients with multiple organ dysfunction syndrome: X. Zhang, et al.; Exp. Ther. Med. 11, 1908 (2016)