Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
anti-FliD (Pseudomonas aeruginosa), mAb (rec.) (SH1579-B7)

| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Flagellar Hook-associated Protein 2; HAP2; Filament Cap Protein |
| Product Type | Recombinant Antibody |
| Properties | |
| Clone | SH1579-B7 |
| Isotype | Human IgG1 |
| Source/Host | Produced without the use of animals. Purified from HEK 293 cell culture supernatant. |
| Immunogen/Antigen | Recombinant FliD (Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 strain, aa 78–273). |
| Application |
ELISA |
| Crossreactivity | Pseudomonas aeruginosa |
| Specificity |
Recognizes FliD from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. |
| Purity | ≥95% (SDS-PAGE) |
| Purity Detail | Protein A purified from animal component-free supernatant. |
| Concentration | Lot dependent. |
| Formulation | Liquid. In PBS. |
| Isotype Negative Control | |
| Other Product Data |
This is an antibody developed by antibody phage display technology using a human naive antibody gene library. These libraries consist of scFv (single chain fragment variable) composed of VH (variable domain of the human immunoglobulin heavy chain) and VL (variable domain of the human immunoglobulin light chain) connected by a polypeptide linker. The antibody fragments are displayed on the surface of filamentous bacteriophage (M13). This scFv was selected by affinity selection on antigen in a process termed panning. Multiple rounds of panning are performed to enrich for antigen-specific scFv-phage. Monoclonal antibodies are subsequently identified by screening after each round of selection. The selected monoclonal scFv is cloned into an appropriate vector containing a Fc portion of interest and then produced in mammalian cells to generate an IgG like scFv-Fc fusion protein. |
| Accession Number | Q9K3C5 |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Abcalis |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | BLUE ICE |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice |
After opening, prepare aliquots and store at -20°C. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. Please handle under sterile conditions to avoid contamination. |
| Use/Stability |
Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at -20°C. Stable for at least 1 week when stored at +4°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
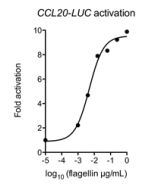
Pathogenic bacteria cause a multitude of deadly human diseases. Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a predominant organism within the hospital environment, an increasingly multidrug-resistant microbe, and the most common gram-negative pathogen causing nosocomial pneumonia in the United States. Nearly all P. aeruginosa infections are associated with compromised host defenses, which may include patients with severe burns, diabetes, cancer, organ transplants or additional immunodeficiencies. Many of these pathogenic bacteria possess flagella, molecular machines responsible for cell motility, adherence to host cells, and pathogenicity. Flagella are helix-shaped hollow attachments formed predominantly by thousands of copies of the protein flagellin (also called FliC), anchored in the bacterial membrane by a hook (or joint) that is attached to the basal body and that is composed of rotary motor proteins. A FliD (also called HAP2) oligomer forms the cap protein complex that is located at the tip of the flagellar filament. This complex controls the distal growth of the filament by regulating the assembly of FliC molecules, which are transported through the hollow filament from the cytoplasm to the tip of the flagellum. In the absence of FliD, flagella are not formed, resulting in impaired motility and infectivity.
- Bacterial flagellar capping proteins adopt diverse oligomeric states: S. Postel, et al.; eLife 5, e18857 (2016)