Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
DLK1, Soluble (human) ELISA Kit
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Protein Delta Homolog 1; pG2; Fetal Antigen 1; FA 1 |
| Product Type | Kit |
| Properties | |
| Application Set | Quantitative ELISA |
| Specificity |
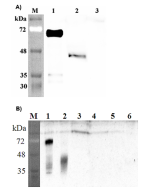
Detects human DLK1. Does not cross-react with human DLL1, human DNER or mouse DLK1. |
| Crossreactivity | Human |
| Quantity |
1 x 96 wells |
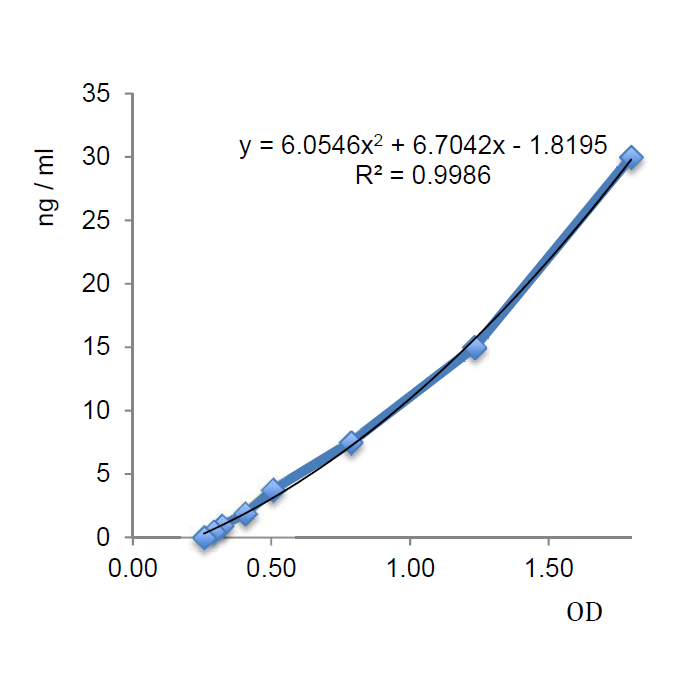
| Sensitivity | 336pg/ml |
| Range | 0.47 to 30ng/ml |
| Sample Type |
Cell Culture Supernatant Serum |
| Assay Type | Sandwich |
| Detection Type | Colorimetric |
| RRID | AB_3431933, AB_3095182, AB_2934107 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | BLUE ICE |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | +4°C |
| Handling Advice |
After standard reconstitution, prepare aliquots and store at -20°C. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. Plate and reagents should reach room temperature before use. |
| Use/Stability | 12 months after the day of manufacturing. See expiry date on ELISA Kit box. |
| Documents | |
| Manual |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
The Notch signaling pathway is essential for appropriate cell differentiation and cell fate decisions. DLK1 (Protein delta homolog 1; Preadipocyte factor 1; Pref-1) is a regulator of adipocyte differentiation found in serum and urine. DLK1 shifts nutrient metabolism towards FA oxidation. Serum or plasma levels of soluble DLK1 affect negatively or positively adipogenesis and control mesenchymal cell fate. DLK1 is frequently upregulated in myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) patients compared to non-leukemic individuals. Fetus is the source of maternal circulating DLK1 during pregnancy. It has been recently reported that measurement of DLK1 in maternal blood may be a valuable method for diagnosing human disorders associated with impaired DLK1 expression, and to predict poor intrauterine growth and complications of pregnancy.
- Identification of adipokine clusters related to parameters of fat mass, insulin sensitivity and inflammation: G. Flehmig, et al.; PLos One 9, e99785 (2014)
- Fetus-derived DLK1 is required for maternal metabolic adaptations to pregnancy and is associated with fetal growth restriction: M. Cleaton, et al.; Nat. Genet. 48, 1473 (2016)
- Paternally Inherited DLK1 Deletion Associated With Familial Central Precocious Puberty: A. Dauber, et al.; J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 102, 1557 (2017)
- Low Maternal DLK1 Levels at 26 Weeks Is Associated With Small for Gestational Age at Birth: A. Pham, et al.; Front. Endocrinol. 13, 836731 (2022)
- Novel MKRN3 Missense Mutations Associated With Central Precocious Puberty Reveal Distinct Effects on Ubiquitination: J.C. Magnotto, et al.; J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 108, 1646 (2023)
- Kisspeptin and DLK1 levels for monitoring treatment of girls with central precocious puberty: W. Onsoi, et al.; Clin. Exp. Pediatr. 67, 296 (2024)
- Comprehensive Study on Central Precocious Puberty: Molecular and Clinical Analyses in 90 Patients: H. Narusawa, et al.; J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. (ePub ahead) (2024)
- Serum DLK1 During Minipuberty and Pubertal Transition in Healthy Girls and in Girls with Precocious Puberty: L. Vilmann, et al.; J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. (ePub ahead) (2024)