Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
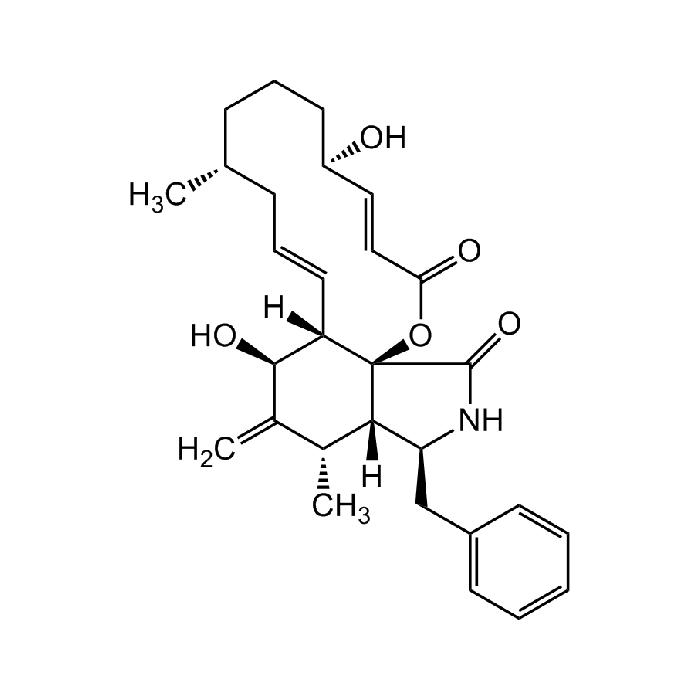
Cytochalasin B
As low as
60
CHF
CHF 60.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CN2-0504-M0011 mgCHF 60.00
AG-CN2-0504-M0055 mgCHF 180.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Phomin; NSC 107658 |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C29H37NO5 |
| MW | 479.6 |
| CAS | 14930-96-2 |
| RTECS | RO0205000 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Isolated from Drechslera dematoidea. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | White solid. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO, methanol, ethanol or DMF. |
| InChi Key | GBOGMAARMMDZGR-TYHYBEHESA-N |
| Smiles | C[C@@H]1C([C@@H](O)[C@@]2([H])[C@@]3(OC(/C=C/[C@H](O)CCC[C@@H](C)C/C=C/2)=O)[C@]1([H])[C@H](CC4=CC=CC=C4)NC3=O)=C |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice |
Keep cool and dry. Protect from light. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Cell permeable mycotoxin.
- Actin polymerization inhibitor. Binds to the barbed end of actin, reversibly inhibiting the elongation and shortening of actin filaments. Induces nuclear extrusion.
- By disrupting actin polymerization, blocks diverse cellular functions, including cell division, migration, phagocytosis, exocytosis and chemotaxis. Induces DNA fragmentation.
- Used in cytoskeletal reorganization, cell imaging and organelle trafficking studies.
- Potent antitumor activity. Causes cell cycle arrest and induces apoptosis in cancer cells. Shown to have an inhibitory effect on tumor cell growth without causing immunosuppressive effects.
- Non-competitive glucose transport inhibitor. Inhibits of GLUT1/GLUT2 mediated monosaccharide transport across the plasma membrane. Does not inhibit GLUT5.
- Used for testing the genotoxicity of substances in the cytokinesis-block micronucleus cytome (CBMN cyt) assay.
- Used in cloning through nuclear transfer. Enucleated recipient cells are treated with cytochalasin B. Cytochalasin B makes the cytoplasm of the oocytes more fluid and makes it possible to aspirate the nuclear genome of the oocyte within a small vesicle of plasma membrane into a micro-needle.
- Decreases the expression levels of DNMT1, DNMT3a, DNMT3b, HAT1 and HDAC1 at the pronuclear stage in porcine embryos.
- Phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylethanolamine biosynthesis inhibitor.
- Platelet aggregation inhibitor.
Product References
- Cytochalasin B. 3. Inhibition of human polymorphonuclear leukocyte phagocytosis: A.T. Davis, et al.; Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 137, 161 (1971)
- Cytochalasin B: Inhibition of glucose and glucosamine transport: R.D. Estensen & P.G.W. Plagemann; PNAS 69, 1430 (1972)
- Enucleation of mammalian cells with cytochalasin B: D.M. Prescott, et al.; Exp. Cell Res. 71, 480 (1972)
- Inhibition and reversal of platelet activation by cytochalasin B or colcemid: M.M. Boyle Kay & H.H. Fudenberg; Nature 244, 288 (1973)
- Cytochalasin B: inhibition of glucose-induced insulin release from isolated rat pancreatic islets: P. Schauders & H. Frerichs; Diabetologia 10, 85 (1974)
- Reversible inhibition of the motility of human spermatozoa by cytochalasin B: R.N. Peterson & M. Freund; Fertil. Steril. 28, 257 (1977)
- Effects of cytochalasin B on endocytosis and exocytosis: P. Davies & A.C. Allison; Front. Biol. 46, 143 (1978)
- Mechanism of action of cytochalasin B on actin: S: MacLean-Fletcher & T.D. Pollard; Cell. 20, 329 (1980)
- Effect of cytochalasin B on glucose uptake, utilization, oxidation and insulinotropic action in tumoral insulin-producing cells: W.J. Malaisse; Cell. Biochem. Funct. 5, 183 (1987)
- Cytochalasin B induces cellular DNA fragmentation: M.A. Kolber, et al.; FASEB J. 4, 3021 (1990)
- Inhibition of Phosphatidylcholine and Phosphatidylethanoamine Biosynthesis by Cytochalasin B in Cultured Glioma Cells: Potential Regulation of Biosynthesis by Ca2+-Dependent Mechanisms: T.P. George, et al.; Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1084, 185 (1991)
- Cytochalasin B may shorten actin filaments by a mechanism independent of barbed end capping: P.A. Theodoropoulos, et al.; Biochem. Pharmacol. 47, 1875 (1994)
- Production of mice entirely derived from embryonic stem (ES) cell with many passages by coculture of ES cells with cytochalasin B induced tetraploid embryos: O. Ueda; Exp. Anim. 44, 205 (1995)
- The inhibition of GLUT1 glucose transport and cytochalasin B binding activity by tricyclic antidepressants: H.B. Pinkofsky, et al.; Life. Sci. 66, 271 (2000)
- Cytokinesis-block micronucleus cytome assay: M. Fenech; Nat. Protocols 2, 1084 (2007)
- The chemistry and biology of cytochalasans: K. Scherlach, et al.; Nat. Prod. Rep. 27, 869 (2010) (Review)
- Cytochalasin B treatment of mouse oocytes during intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) increases embryo survival without impairment of development: L.L. Hu, et al.; Zygote 20, 361 (2012)
- Cytochalasin B induces apoptosis through the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway in HeLa human cervical carcinoma cells: J. Hwang, et al.; Oncol. Rep. 30, 1929 (2013)
- Preparation, In Vivo Administration, Dose-Limiting Toxicities, and Antineoplastic Activity of Cytochalasin B: M. Trendowski, et al.; Transl. Oncol. 8, 308 (2015)
- Mechanisms underlying effect of the mycotoxin cytochalasin B on induction of cytotoxicity, modulation of cell cycle, Ca2+ homeostasis and ROS production in human breast cells: H.T. Chang, et al.; Toxicol. 31, 1 (2016)
- Effects of cytochalasin B on DNA methylation and histone modification in parthenogenetically activated porcine embryos: X. Hou, et al.; Reproduction 152, 519 (2016)







