Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
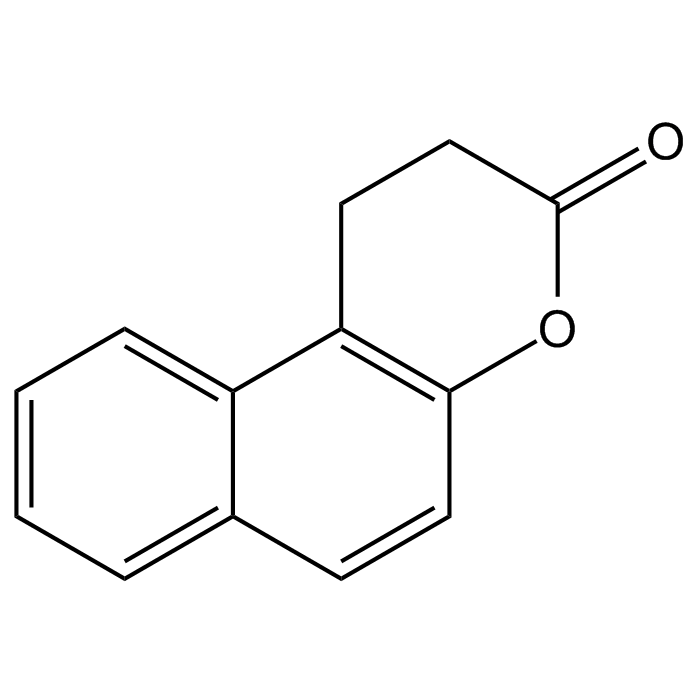
Splitomicin
As low as
35
CHF
CHF 35.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CR1-0088-M0011 mgCHF 35.00
AG-CR1-0088-M0055 mgCHF 60.00
AG-CR1-0088-M02525 mgCHF 240.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Splitomycin; 1,2-Dihydro-3H-naphtho[2,1-b]pyran-3-one; 1-Naphthalen propanoic acid |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C13H10O2 |
| MW | 198.2 |
| CAS | 5690-03-9 |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (NMR) |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid. |
| Solubility | Soluble in methanol, ethanol or DMSO. |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| Other Product Data |
Handling Note: After reconstitution use immediately due to decomposition. We recommend to use fresh solutions. If you prepare aliquots store immediately at -20°C. |
| InChi Key | ISFPDBUKMJDAJH-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Smiles | O=C1CCC2=C(O1)C=CC1=CC=CC=C21 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice |
After reconstitution, prepare aliquots and store at -20°C. Keep cool and dry. Keep under inert gas. Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Potent cell permeable and selective inhibitor of yeast NAD+-dependent histone deacetylase (HDAC) Sir2p [1-4].
- Displays higher activity in vivo than in vitro [1-4].
- Sensitizes mammalian cells to a variety of DNA-damaging agents by abrogating Sir2p activity on p53. Acts by either altering or blocking access to the acetylated histone binding pocket [5].
- Shown to have diverse effects also in mammalian cells [6-10].
Product References
- Identification of a small molecule inhibitor of Sir2p: A. Bedalov, et al.; PNAS 98, 15113 (2001)
- Identification of selective inhibitors of NAD+-dependent deacetylases using phenotypic screens in yeast: M. Hirao, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 278, 52773 (2003)
- Inhibitors of Sir2: evaluation of splitomicin analogues: J. Posakony, et al.; J. Med. Chem. 47, 2635 (2004)
- The Sir 2 family of protein deacetylases: J.M. Denu; Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 9, 431 (2005) (Review)
- Histone deacetylase inhibitor-mediated radiosensitization of human cancer cells: class differences and the potential influence of p53: I.A. Kim, et al.; Clin. Cancer Res. 12, 940 (2006)
- SIRT1 inhibition alleviates gene silencing in Fragile X mental retardation syndrome: R. Biacsi, et al.; PLoS Genet. 4, e1000017 (2008)
- Splitomicin suppresses human platelet aggregation via inhibition of cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase and intracellular Ca++ release: F.C. Liu, et al.; Thromb. Res. 124, 199 (2009)
- Reciprocal roles of SIRT1 and SKIP in the regulation of RAR activity: implication in the retinoic acid-induced neuronal differentiation of P19 cells: M.R. Kang, et al.; Nucleic Acids Res. 38, 822 (2010)
- Sirt1 inhibition promotes in vivo arterial thrombosis and tissue factor expression in stimulated cells: A. Breitenstein, et al.; Cardiovasc. Res. 89, 464 (2011)
- Sirtuin-1 targeting promotes Foxp3+ T-regulatory cell function and prolongs allograft survival: U.H. Beier, et al.; Mol. Cell Biol. 31, 1022 (2011)