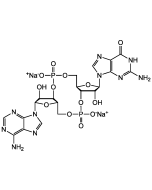Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
MSA-2
As low as
45
CHF
CHF 45.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CR1-0164-M0011 mgCHF 45.00
AG-CR1-0164-M0055 mgCHF 180.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
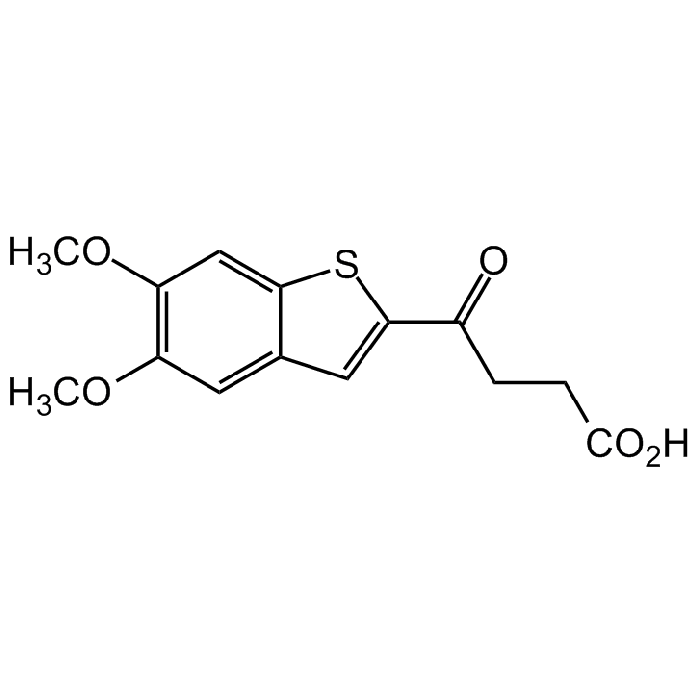
| Synonyms | 4-(5,6-Dimethoxybenzo[b]thiophen-2-yl)-4-oxobutanoic acid |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C14H14O5S |
| MW | 294.3 |
| CAS | 129425-81-6 |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO (30mg/ml) or DMF (30mg/ml). Slightly soluble in ethanol (1mg/ml). |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| InChi Key | APCLRHPWFCQIMG-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Smiles | O=C(CCC(O)=O)C1=CC2=CC(OC)=C(OC)C=C2S1 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Keep cool and dry. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- MSA-2 is a new orally available (cell permeable) non-nucleotide STING (STimulator of INterferon Genes) agonist, with EC50s of 8.3 and 24μM for human STING isoforms WT and HAQ. Activation of the STING protein by its natural ligand, cyclic guanosine monophosphate-adenosine monophosphate (cGAMP, a cytosolic double-stranded DNA sensor), triggers signaling responses, inducing the release of type I interferons and other proinflammatory cytokines. STING-controlled interferon production is involved in antiviral defense as well as antitumor immunity. Pharmacological activation of STING is considered a promising therapeutic strategy for cancer.
- MSA-2 highly induces secretion in vitro of IFN-β from THP-1 cells and mouse macrophages at concentration of 10-50μM. It shows in vivo antitumor activity in a MC38 mouse model of colon carcinoma in a dose-dependent manner, stimulating IFN-β secretion in tumors, inducing tumor regression with durable antitumor immunity when administered intratumorally (450μg), subcutaneously (50mg/kg) or orally (50mg/kg), and synergizes with anti-PD-1 therapy.
- MSA-2 is a small molecule monomer that undergoes reversible, noncovalent dimerization in solution to become a pharmacologically active ligand. MSA-2 monomers cannot bind STING, whereas the noncovalent MSA-2 dimers bind STING with nanomolar affinity. MSA-2, a weak acid, exhibits substantially higher cellular potency in an acidified tumor microenvironment (versus normal tissue), owing to increased cellular entry and retention combined with its inherent mode of interaction with STING.
Product References
- An orally available non-nucleotide STING agonist with antitumor activity: B.S. Pan, et al.; Science 369, 6506 (2020)






![anti-CD279 [PD-1] (human), mAb (ANC4H6) (preservative free)](https://adipogen.com/media/catalog/product/placeholder/default/adipogen_logo_bw_3.png)