Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
BioViotica
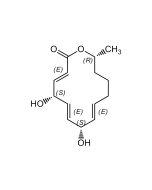
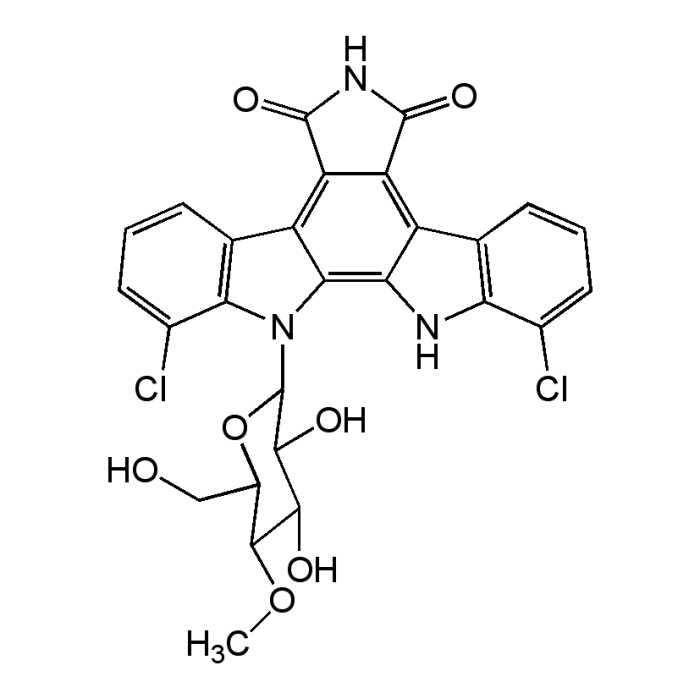
Rebeccamycin
As low as
110
CHF
CHF 110.00
In stock
Only %1 left
BVT-0139-C250250 µgCHF 110.00
BVT-0139-M0011 mgCHF 325.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | NSC 359079; BRN 4732638 |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C27H21Cl2N3O7 |
| MW | 570.4 |
| CAS | 93908-02-2 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Isolated from Streptomyces sp. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | Yellow solid. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO. |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by BioViotica. |
| InChi Key | QEHOIJJIZXRMAN-UMHCKEELSA-N |
| Smiles | COC1C(O)C(O)C(OC1CO)N1C2=C3NC4=C(C=CC=C4Cl)C3=C3C(=O)NC(=O)C3=C2C2=C1C(Cl)=CC=C2 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | BLUE ICE |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light when in solution. |
| Use/Stability |
Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at -20°C. Stock solutions are stable for at least 3 months when stored at -20°C. After reconstitution, prepare aliquots and store at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Antibiotic. Structurally similar to staurosporine.
- Selective activity against several cancer cell lines.
- DNA intercalator, resulting in catalytic inhibition of topoisomerases I.
- Shows significant antitumor properties in vitro (IC50 = 480 nM against mouse B16 melanoma cells and IC50 = 500 nM against P388 leukemia cells).
- Does not show any inhibitory activity against protein kinases.
Product References
- Production and biological activity of rebeccamycin, a novel antitumor agent: J.A. Bush, et al.; J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 40, 668 (1987)
- Induction of mammalian DNA topoisomerase I mediated DNA cleavage by antitumor indolocarbazole derivatives: Y. Yamashita, at al.; Biochemisty 31, 12069 (1992)
- DNA cleavage by topoisomerase I in the presence of indolocarbazole derivatives of rebeccamycin: C. Bailly, et al.; Biochemistry 36, 3917 (1997)
- Syntheses and biological activities (topoisomerase inhibition and antitumor and antimicrobial properties) of rebeccamycin analogues bearing modified sugar moieties and substituted on the imide nitrogen with a methyl group: F. Anizon, et al.; J. Med. Chem. 40, 3456 (1997)
- Calories from carbohydrates: energetic contribution of the carbohydrate moiety of rebeccamycin to DNA binding and the effect of its orientation on topoisomerase I inhibition: C. Bailly, et al.; Chem. Biol. 6, 277 (1999)
- Discovery of Antitumor Indolocarbazoles: Rebeccamycin, NSC 655649, and Fluoroindolocarbazoles: B.H. Long, et al.; Curr. Med. Chem. 2, 255 (2002)
- Rebeccamycin derivatives as dual DNA-damaging agents and potent checkpoint kinase 1 inhibitor: C. Marminon, et al.; Mol Pharmacol 74, 1620-1629 (2008)
- Phase II and pharmacokinetic trial of rebeccamycin analog in advanced biliary cancers: A. Dowlati, et al.; Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 65, 73-78 (2009)
- New progress of researches in carbazole compounds: F. Zhang, et al.; Chinese J. Org. Chem. 30, 783 (2010)
- Checkpoint Kinase 1 activation enhances intestinal epithelial barrier function via regulation of claudin-5 expression: A. Watari, et al.; PLoS One 11, e0145631/1 (2016)
- Rebeccamycin attenuates TNF-a-induced intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction by inhibiting myosin light chain kinase production: A. Watari, et al.; Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 41, 1924 (2017)
- The antitumor antibiotic rebeccamycin-challenges and advanced approaches in production processes: K. Pommerehne, et al.; Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 103, 3627 (2019)