Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
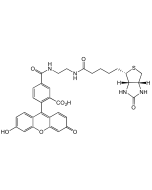
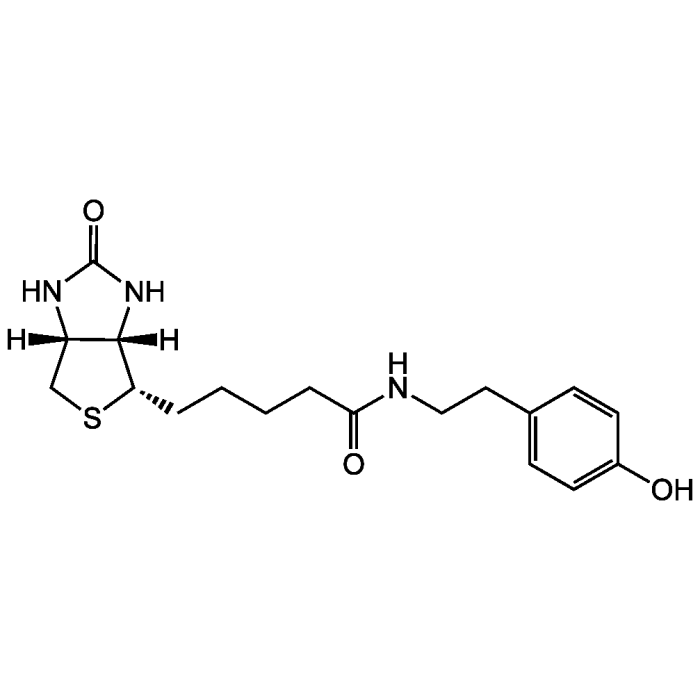
Biotinyl tyramide

| Product Details | |
|---|---|
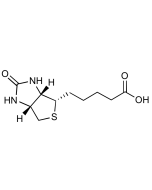
| Synonyms | Biotin-Phenol; BP; N-(4-Hydroxyphenethyl)-5-((3aS,4S,6aR)-2-oxohexahydro-1H-thieno[3,4-d]imidazol-4-yl)pentanamide |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula | C18H25N3O3S |
| MW | 363.5 |
| CAS | 41994-02-9 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Synthetic. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥97% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | White to light pink solid. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO or acetonitrile. |
| Identity | Determined by NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | VZWXNOBHWODXCW-ZOBUZTSGSA-N |
| Smiles | [H][C@]12CS[C@@H](CCCCC(=O)NCCC3=CC=C(O)C=C3)[C@@]1([H])NC(=O)N2 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice |
Keep cool and dry. Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Biotin derivative. Substrate of the horseradish peroxidase enzyme and used as a reagent to amplify immunohistochemical signals. It is based on the HRP-catalyzed deposition of tyramide conjugates (such as biotinyl-tyramide) on a solid phase. Subsequent reaction with streptavidin fluorophore results in the localization of the fluorophore at the site of tyramide deposition. This fluorescence-based tyramide signal amplification (TSA) has been widely used in immunohistochemistry, immunoelectron microscopy, fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) and fluorescence ELISA. The TSA method has been reported to increase the detection sensitivity up to 100-fold as compared with conventional avidin–biotinylated enzyme complex procedures. It can be used together with both chromogenic and fluorescence visualization methods. It can be added to any other standard IHC protocol and reduces the use of other reagents; improves signal to noise by reducing the titer of other reagents in the assay protocol and enables multi-target detection in both IHC and (F)ISH applications.
(1) B. Hunyady, et al.; J. Histochem. Cytochem. 44, 1353 (1996) | (2) G. Mayer, et al.; J. Histochem. Cytochem. 45, 1449 (1997) | (3) J.A. McKay, et al.; Mol. Path. 50, 322 (1997) | (4) M.F. Evans, et al.; Mod. Pathol. 15, 1339 (2002) | (5) Q. Chenac, et al.; Anal. Lett. 45, 219 (2012) | (6) H. Gong, et al.; Anal. Bioch. 426, 27 (2012) | (7) E. Draberova, et al.; J. Immunol. Methods 395, 63 (2013) | (8) C.Y. Yang, et al.; Int. J. Oral Sci. 10, 3 (2018) | (9) N. Zuzow, et al.; MBoC, 29, 1258 (2018) | (10) M. Pan, et al.; J. Proteom. Res. 18.319 (2019) | (11) M.G. Olson, et al.; Infect. Immun. 87, e00537 (2019) | (12): D.P. Narendra, et al.; J. Cell Biol. 219, e201901097 (2020) | (13) J. Jia, et al.; Dev. Cell 52, 69 (2020) | (14) S. Wang, et al.; Sci. Adv. 7, (2021) | (15) S. Kumar, et al.; Cell 184, 5950 (2021)