Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
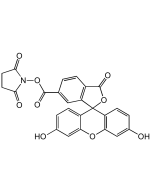
5-FAM N-succinimidyl ester
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | 5-Carboxyfluorescein NHS ester; 5-CFSE; 5-FAM, SE |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula | C25H15NO9 |
| MW | 473.39 |
| CAS | 92557-80-7 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Synthetic |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | Light yellow to orange powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO, methanol or dimethylformamide. |
| Identity | Determined by NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | TWOKNYRPKCLMAR-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Smiles | OC(=O)C1=C(C=CC(=C1)C(=O)ON1C(=O)CCC1=O)C1=C2C=CC(=O)C=C2OC2=CC(O)=CC=C12 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice |
Keep cool and dry. Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Popular green fluorescent cell-permeable dye. Covalently couples via its succinimidyl group to intracellular molecules. The amine-reactive succinimidyl ester of 5-FAM acid is a common fluorescent derivatization reagent for covalently labeling peptides, proteins and nucleotides. Due to this covalent coupling reaction it can be retained within cells for extremely long periods and due to this stable linkage, once incorporated within cells the dye is not transferred to adjacent cells. Yields carboxyamides which are more resistant to hydrolysis than fluorescein conjugates prepared with FITC. Better retained in cells than fluorescein. Used in fluorescent small molecule preparations. Spectral data: λex 494 nm| λem 520 nm (Buffer pH 9.0).
(1) P. Breeuwer, et al.; Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 62, 178 (1996) | (2) M. Adamczyk, et al.; Bioconjugate Chem. 8, 253 (1997) | (3) S. K. Lau, et al.; J. Chromatogr. A. 809, 203 (1998) | (4) D.A. Fulcher & S.W. J. Wong; Immunol. Cell Biol. 77, 559 (1999) | (5) S. Nampalli, et al.; Bioconjugate Chem. 13, 468 (2002) | (6) L. Milroy, et al.; JACS 134, 8480 (2012)