Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
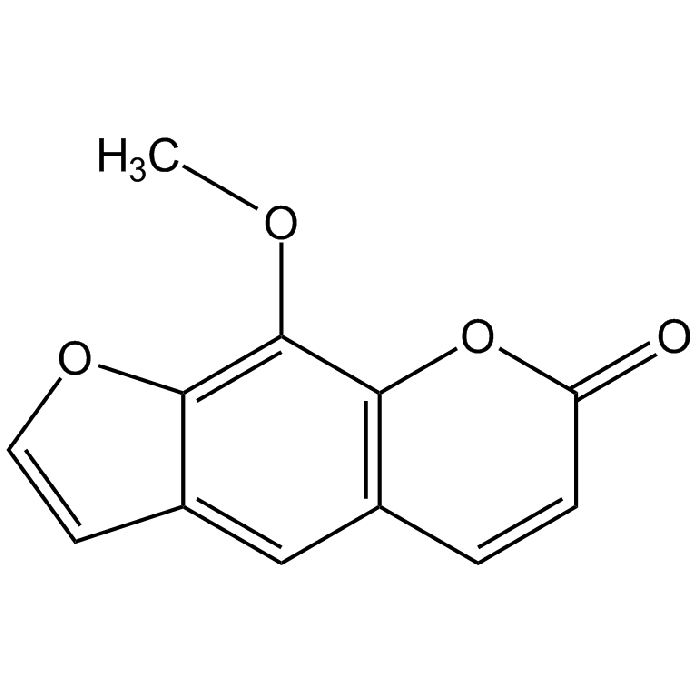
8-Methoxypsoralen
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | 8-MP; 8-MOP; 8-Methoxy-6,7-furanocoumarin; 9-Methoxyfuro[3,2-g][1]benzopyran-7-one; 5-Demethoxyisoimpinellin; Ammoidin; Methoxsalen; Xanthotoxin |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula | C12H8O4 |
| MW | 216.19 |
| CAS | 298-81-7 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Synthetic. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥95% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | White to yellow powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in acetic acid or water (slightly). |
| Identity | Determined by NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | QXKHYNVANLEOEG-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Smiles | COC1=C2OC=CC2=CC2=C1OC(=O)C=C2 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice |
Keep cool and dry. Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Methoxsalen (8-Methoxypsoralen) is a potent tricyclic furocoumarin suicide inhibitor of CYP (cytochrome P-450). Has more potency than 5-MOP, 5-OH-P, DH-8-MOP and psoralen in inhibiting CYP2B1 (cytochrome P-450 2B1). Completely inhibits the metabolism of nicotine in vitro. Inhibits the metabolism of caffeine. Methoxsalen is a drug with photoactivating properties used to treat psoriasis, eczema, vitiligo and some cutaneous lymphomas in conjunction with exposing the skin to UVA light. Upon photoactivation, ultraviolet A (UVA) irradiation induces monoadducts and interstrand cross-links in DNA and therefore can be used to study DNA repair and recombination mechanisms.
(1) A. Lassus, et al.; Photodermatol. 1, 170 (1984) | (2) F.A. de Wolff, et al.; Clin. Pharmacokinet. 11, 62 (1986) | (3) G. Labbe, et al.; Biochem. Pharmacol. 36, 907 (1987) | (4) D.C. Mays, et al.; Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 42, 621 (1987) | (5) G. Labbe, et al.; J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 250, 1034 (1989) | (6) H.G. Jeong, et al.; BBRC 208, 1124 (1995) | (7) J.H. Gwang; Cancer Lett. 109, 115 (1996) | (8) M. Farhadi, et al.; Cell J. 15, 348 (2014) | (9) D. Bagdas, et al.; Neuropharmacol. 85, 67 (2014)