Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
JaICA
8-OHdG Check ELISA Kit (High Sensitivity)
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | 8-hydroxy-2' -deoxyguanosine |
| Product Type | Kit |
| Properties | |
| Application Set | Quantitative ELISA |
| Specificity | Specific for 8-OHdG. Has been tested to 8-OHdG analogues (guanosine(G),7-methyl-G, 6-SH-G, 8-Bromo-G, dA, dC, dT, dI, dU, dG, O6-methyl-dG,8-OHdA, guanine(Gua),O6-methyl-Gua, 8-OH-Gua, uric acid, urea, creatine, creatinine, 8-sulfhydryl-G, 8-OH-G). |
| Crossreactivity | All |
| Quantity | 96 wells |
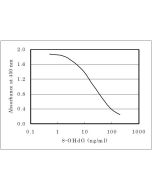
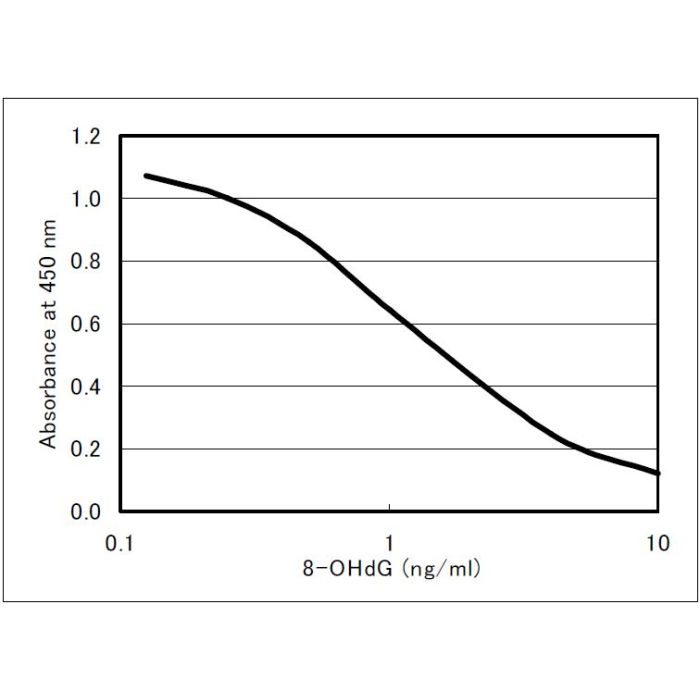
| Range | 0.125 to 10 ng/mL |
| Sample Type |
Plasma Serum Urine |
| Assay Type | Competitive |
| Detection Type | Colorimetric |
| Other Product Data |
This ELISA Kits works also for DNA extracted from cultured cells or tissues. Detection Guide for Serum/Plasma Detection Guide for tissue samples or cultured cells |
| Declaration | Manufactured by JaICA. |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | BLUE ICE |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | +4°C |
| Handling Advice | Do not freeze. |
| Use/Stability | 12 months after the day of manufacturing. See expiry date on ELISA Kit box. |
| Documents | |
| Manual |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) is a modified base that occurs in DNA due to attack by hydroxyl radicals (incl. singlet oxygen and direct photodynamic action) that are formed as byproducts and intermediates of aerobic metabolism and during oxidative stress. There is increasing evidence to support the involvement of free radical reactions in the damage of biomolecules that eventually lead to several diseases in humans, such as atherosclerosis, cerebral and heart ischemia-reperfusion injury, cancer, rheumatoid arthritis, inflammation, diabetes, aging, and neurodegenerative conditions, such as Alzheimer’s disease. 8-OHdG is popular as a sensitive, stable and integral marker of oxidative damage in cellular DNA and can be detected in tissue, serum, urine and other biomaterials.
- Quantitative determination of urinary 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine (8-OH-dg) by using ELISA: S. Saito, et al.; Res. Commun. Mol. Pathol. Pharmacol. 107, 39 (2000) [Development and assessment of 8-OHdG Check ELISA]
- Discrepancies in the measurement of UVC-induced 8-oxo-2'-deoxyguanosine: Implications for the analysis of oxidative DNA damage: M.D. Evans, et al.; BBRC 259, 374 (1999) [High correlation between HPLC-ECD when 8-OHdG in DNA samples]
- Mutagenicity of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species as detected by co-culture of activated inflammatory leukocytes and AS52 cells: H.W. Kim, et al.; Carcinogenesis 24, 235 (2003) [Detection of 8-OHdG in cultured cells]
- Significance of 8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine levels in patients with idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy: E. Watanabe, et al.; J. Card. Fail. 12, 527 (2006) [Serum 8-OHdG in IDC patients]
- Acute encephalopathy with refractory status epilepticus: Bilateral mesial temporal and claustral lesions, associated with a peripheral marker of oxidative DNA damage: T. Shiihara, et al.; J. Neurol. Sci. 250, 159 (2006) [Measurement of 8-OHdG in human urine, serum and cerebro spinal fluid(CSF)]
- Effects of caloric restriction on post-spawning death of ayu: R. Nagasaka, et al.; Exp. Gerontol. 40, 556 (2005) [Detection of 8-OHdG in fish tissues (brain and liver)]
- Salivary 8-OHdG: a useful biomarker for predicting severe ED and hypogonadism: M. Yasuda, et al.; J. Sex. Med. 5, 1482 (2008) [Detection of 8-OHdG in saliva]






![anti-8-Hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine [8-OHdG], mAb (N45.1)](https://adipogen.com/media/catalog/product/cache/60eb5af712bc93baae8d55513bd31b01/j/a/jai-mog-ihc-8ohdg_stain_3.jpg)