Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
anti-LYVE-1 (mouse), pAb

| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Lymphatic Vessel Endothelial Hyaluronic Acid Receptor 1; CRSBP-1 |
| Product Type | Polyclonal Antibody |
| Properties | |
| Source/Host | Rabbit |
| Immunogen/Antigen | Recombinant mouse soluble LYVE-1 (aa24-228). |
| Application |
ELISA: (1-15μg/ml) |
| Crossreactivity | Mouse |
| Specificity |
Recognizes mouse LYVE-1. |
| Purity | Protein A purified. |
| Purity Detail | Protein A purified. |
| Formulation | Lyophilized. |
| Reconstitution | Centrifuge vial prior to opening. Reconstitute with sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0mg/ml. |
| Isotype Negative Control | |
| Other Product Data |
UniProt ID Q8BHC0: Lyve-1 (mouse) |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | BLUE ICE |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice |
After opening, prepare aliquots and store at -20°C. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 6 months after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
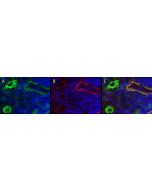
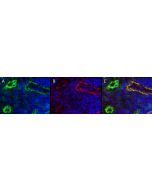
LYVE-1 has been identified as a major receptor for HA (extracellular matrix glycosaminoglycan hyaluronan) on the lymph vessel wall. Like CD44, the LYVE-1 molecule binds both soluble and immobilized HA. However, unlike CD44, the LYVE-1 molecule co-localizes with HA on the luminal face of the lymph vessel wall and is completely absent from blood vessels. Hence, LYVE-1 is the first lymph-specific HA receptor to be characterized and is a uniquely powerful marker for lymph vessels themselves.
- The Sialomucin CD34 Is a Marker of Lymphatic Endothelial Cells in Human Tumors: U. Fidler, et al.; Am. J. Pathol. 168, 1045 (2006)
- Platelets Play an Essential Role in Separating the Blood and Lymphatic Vasculatures During Embryonic Angiogenesis: L. Carramolino, et al.; Circ. Res. 106, 1197 (2010)
- Spatiotemporal histological changes observed in mouse subcutaneous tissues during the foreign body reaction to silicone: S. Oe, et al.; J. Biomed. Material Res. A 109, 1220 (2021)