Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
anti-APRIL (mouse), mAb (rec.) (blocking) (Apry-1-1) (Fc LAEA-PG)

| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | A Proliferation Inducing Ligand; TNFSF13; CD256; TALL-2 |
| Product Type | Recombinant Antibody |
| Properties | |
| Clone | Apry-1-1 |
| Isotype | Mouse IgG2bλ |
| Source/Host | Produced without the use of animals. Purified from HEK 293 cell culture supernatant. |
| Immunogen/Antigen | Mouse APRIL (aa 98-232). |
| Application |
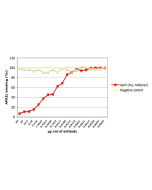
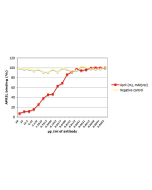
ELISA |
| Crossreactivity | Mouse |
| Specificity |
Recognizes mouse APRIL. Does not recognize human APRIL and mouse/human BAFF. |
| Purity | ≥95% (SDS-PAGE) |
| Purity Detail | Protein A-affinity purified. |
| Endotoxin Content | <0.001EU/μg purified protein (LAL-test; Lonza) |
| Concentration | 1mg/ml |
| Formulation | Liquid. In PBS and 0.02% Proclin-300. |
| Isotype Negative Control |
Fc (LAEA-PG)-KIH (mouse) IgG2b Control (rec.) (Prod. No. AG-35B-0019) |
| Other Product Data |
APRIL (mouse), mAb (rec.) (Blocking) (Apry-1-1) (Fc LAEA-PG) is composed of human variable regions (VH and VL) (λ-chain) of immunoglobulin fused to the mouse lgG2b Fc domain containing mutations LAEA-PG that inhibit binding to FcγRs and C1q while FcRn binding and Fc stability remain unaffected. |
| Accession Number | Q9D777 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | BLUE ICE |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice |
After opening, prepare aliquots and store at -20°C. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Use/Stability |
Stable for at least 1 month after receipt when stored at +4°C. Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
APRIL is a secreted cytokine, belonging to the TNF superfamily that binds to transmembrane activator and CAML interactor (TACI), B cell maturation antigen (BCMA) and can interact with carbohydrate side chains of heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPG) that may trigger cross-linking. APRIL maintains B cell homeostasis by acting at a later stage, modulating the function and survival of antigen-experienced B cells. APRIL (as well as BAFF) stimulates class-switch recombination (CSR), hence contributes to shaping humoral effector mechanisms. With regards to humoral memory, APRIL is involved in the establishment and survival of the long-lived plasma cell (LLPC) pool in the bone marrow (BM). Recently, APRIL has been shown to confer atheroprotection via binding to heparan sulfate (HS) chains of heparan-sulfate proteoglycan 2 (HSPG2), which limits LDL retention, macrophage accumulation and necrotic core formation. BAFF and APRIL are implicated in several human autoimmune diseases with autoreactive B cell involvement, including systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), Sjögren’s syndrome (SS), IgA nephropathy (IgAN), and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). APRIL might also function in enhancing the proliferation of some tumor cells, especially B cell malignancies. BAFF and APRIL contribute to maintaining IgG, IgA, and IgM plasma cells in the bone marrow (BM), spleen and intestine and rely mainly on three ligand/receptor pairs: APRIL-BCMA, BAFF-TACI, and APRIL-TACI. APRIL plays an important role in B cell survival and proliferation, so blocking it can modulate immune responses. APRIL blocking antibodies can be useful for vaccine research, particularly to assess how APRIL inhibition affects normal immune responses to vaccination.
anti-APRIL (mouse), mAb (rec.) (Blocking) (Apry-1-1) (Fc LAEA-PG) is an antibody developed by antibody phage display technology using a human naive antibody gene library. These libraries consist of scFv (single chain fragment variable) composed of VH (variable domain of the human immunoglobulin heavy chain) and VL (variable domain of the human immunoglobulin light chain) connected by a polypeptide linker. The antibody fragments are displayed on the surface of filamentous bacteriophage (M13). This scFv was selected by affinity selection on antigen in a process termed panning. Multiple rounds of panning are performed to enrich for antigen-specific scFv-phage. Monoclonal antibodies are subsequently identified by screening after each round of selection. The selected monoclonal scFv is cloned into an appropriate vector containing a Fc mouse portion with mutations LAEA-PG and then produced in mammalian cells to generate an IgG like scFv-Fc (LAEA-PG) fusion protein. Mutations LAEA-PG inhibit binding to FcγRs and C1q while FcRn binding and Fc stability remain unaffected.