Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
FasL, Soluble (human) (rec.)
As low as
190
CHF
CHF 190.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-40B-0001-C01010 µgCHF 190.00
AG-40B-0001-30103 x 10 µgCHF 385.00

| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | APO-1L; CD95L; CD178; TNFSF6; Fas Ligand |
| Product Type | Protein |
| Properties | |
| Source/Host | HEK 293 cells |
| Sequence | The extracellular domain of human FasL (aa 103-281) is fused at the N-terminus to a FLAG®-tag. |
| Crossreactivity |
Human Mouse |
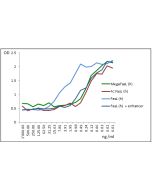
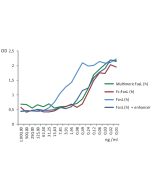
| Biological Activity | Induces apoptosis of human Jurkat T cells at a concentration of <1ng/ml in the presence of 0.1 to 1μg/ml TNF Ligands Enhancer (Prod. No. AG-35B-0001). In the absence of TNF Ligands Enhancer, FasL is working at 50-100 fold higher concentrations. |
| MW | ~33kDa (SDS-PAGE) |
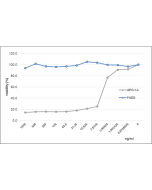
| Purity | ≥95% (SDS-PAGE) |
| Endotoxin Content | <0.05EU/μg purified protein (LAL test; Lonza). |
| Concentration | 0.1mg/ml after reconstitution. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute with 100μl sterile water. |
| Formulation | Lyophilized. Contains PBS. |
| Other Product Data |
UniProt link P48023: FasL (human) FLAG is a registered trademark of Sigma-Aldrich Co. |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | BLUE ICE |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice |
After reconstitution, prepare aliquots and store at -20°C. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. Centrifuge lyophilized vial before opening and reconstitution. PBS containing at least 0.1% BSA should be used for further dilutions. |
| Use/Stability |
Stable for at least 6 months after receipt when stored at -20°C. Working aliquots are stable for up to 3 months when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
FasL is a cytokine that binds to TNFRSF6/Fas, a receptor that transduces the apoptotic signal into cells. Is involved in cytotoxic T cell mediated apoptosis and in T cell development.
Product References
- Tumor necrosis factor receptor family costimulation increases regulatory T-cell activation and function via NF-κB: M. Lubrano di Ricco, et al.; Eur. J. Immunol. 50, 972 (2020)
- Targeting adrenergic receptors to mitigate invariant natural killer T cells-induced acute liver injury: MB. Gonzatti, et al.; iScience 26, 107947 (2023)






![CD95 [Fas] (human)-huIg Fusion Protein (preservative free)](https://adipogen.com/media/catalog/product/placeholder/default/adipogen_logo_bw_3.png)