Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
BAFF, Soluble (human) ELISA Kit (hypersensitive)
As low as
630
CHF
CHF 630.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-45B-0001-KI0196 wellsCHF 630.00

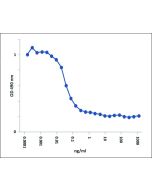
Figure 1: Specific quantitation of BAFF in human serum. Method: Serum from a healthy patient or patient with multiple sclerosis is left untreated or treated with 0.5 μg/ml of a BAFF receptor, TACI (human):Fc (human) (Prod. No. AG-40B-0079). BAFF levels are measured using the BAFF, Soluble (human) ELISA Kit (hypersensitive) (Prod. No. AG-45B-0001).
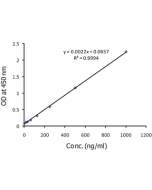
Figure 2: Standardcurve
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | BlyS; B Cell Activating Factor, |
| Product Type | Kit |
| Properties | |
| Application Set | Quantitative ELISA |
| Specificity | Detects human BAFF. Does not detect mouse BAFF. |
| Crossreactivity | Human |
| Quantity | 1 x 96 wells |
| Sensitivity | 8pg/ml |
| Range | 15.6 - 500 pg/ml |
| Sample Type |
Cell Culture Supernatant Plasma Serum |
| Assay Type | Sandwich |
| Detection Type | Colorimetric |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | BLUE ICE |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | +4°C |
| Handling Advice |
After standard reconstitution, prepare aliquots and store at -20°C. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. Plate and reagents should reach room temperature before use. |
| Use/Stability | 12 months after the day of manufacturing. See expiry date on ELISA Kit box. |
| Documents | |
| Manual |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
BAFF (B cell-activating factor; BLyS; B lymphocyte stimulator; TNFSF13B; TALL-1; CD257), belonging to the TNF family, is a master regulator of peripheral B cell survival, and together with IL-6, promotes Ig class-switching and plasma cell differentiation. BAFF co-stimulates activated T cells. Increased levels of soluble BAFF have been detected in the serum of patients with various autoimmune diseases, such as Sjögren’s syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Furthermore, BAFF is found in inflammatory sites in which there is lymphoid neogenesis. BAFF levels are elevated in patients with multiple myeloma and B cell chronic lymphoid leukemia (B-CCL).
Product References
- CVID-associated TACI mutations affect autoreactive B cell selection and activation: N. Romberg, et al.; J. Clin. Invest. 123, 4283 (2013)
- Effects of age on H1N1-specific serum IgG1 and IgG3 levels evaluated during the 2011–2012 influenza vaccine season: D. Frasca, et al.; Immun. Ageing 10, 14 (2013)
- Selective Activation of Human Dendritic Cells by OM-85 through a NF-kB and MAPK Dependent Pathway: C. Parola, et al.; PLOS One 8, e82867 (2013)
- Innate lymphoid cells integrate stromal and immune signals to enhance antibody production by splenic marginal zone B cells: G. Magri, et al.; Nat. Immunol. 15, 354 (2014)
- TACI expression and signaling in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: A. Mamara, et al.; J. Immunol. Res. 2015, 478753 (2015)
- Increased BAFF and APRIL levels in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-related hypertrophic pachymeningitis: Y. Shimojima, et al.; Cytokine 99, 305 (2017)
- Inhibition of membrane-bound BAFF by the anti-BAFF antibody belimumab: C. Kowalczyk-Quintas, et al.; Front. Immunol. 9, 2698 (2018)
- B‐cell profile, B‐cell activating factor concentration and IgG levels in human cutaneous and mucosal leishmaniasis: C. Parodi, et al.; Parasite Immunol. e12759 (2020)
- Evolutionarily Selected Overexpression of the Cytokine BAFF Enhances Mucosal Immune Response Against P. falciparum: V. Lodde, et al.; Front. Immunol. 11, 575103 (2020)
- BAFF 60-mer, and differential BAFF 60-mer dissociating activities in human serum, cord blood and cerebrospinal fluid: M. Eslamy, et al.; Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 8, 577662 (2020)
- BAFF antagonism via the BAFF receptor 3 binding site attenuates BAFF 60-mer-induced classical NF-κB signaling and metabolic reprogramming of B cells: M. Lempicki, et al.; Cell. Immunol. 22 (2022)
- Kinetics of free and ligand-bound atacicept in human serum: M. Eslami, et al.; Front. Immunol. 13, 1035556 (2022)