Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
CD40L (human) ELISA Kit
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | CD40 Ligand; CD154; Tumor Necrosis Factor Ligand Superfamily Member 5; TNFSF5; Gp39; TRAP |
| Product Type | Kit |
| Properties | |
| Application Set | Quantitative ELISA |
| Specificity |
Detects soluble human CD40L in serum and cell culture supernatant. |
| Crossreactivity | Human |
| Quantity |
1 x 96 wells |
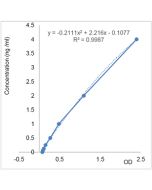
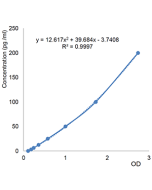
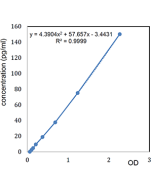
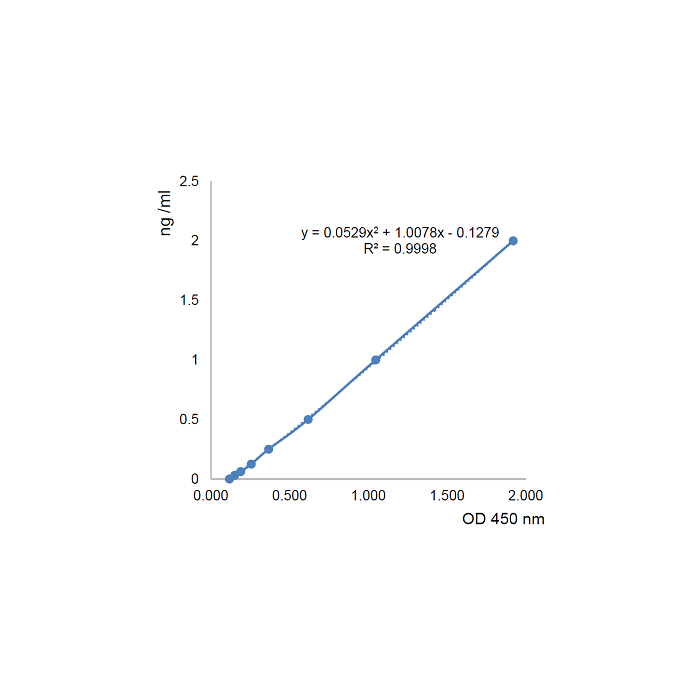
| Sensitivity | 20pg/ml |
| Range | 0.03125 to 2ng/ml |
| Sample Type |
Cell Culture Supernatant Serum |
| Assay Type | Sandwich |
| Detection Type | Colorimetric |
| Other Product Data |
UniProt link P29965: CD40L (human) |
| Declaration | In collaboration with Suzhou Bright Scistar Biotechnology |
| Accession Number | P29965 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | BLUE ICE |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | +4°C |
| Handling Advice |
After standard reconstitution, prepare aliquots and store at -20°C. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. Plate and reagents should reach room temperature before use. |
| Use/Stability | 12 months after the day of manufacturing. See expiry date on ELISA Kit box. |
| Documents | |
| Manual |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
CD40 (also called, Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 5 or TNFRSF5), a transmembrane type I glycoprotein, belongs to the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) gene superfamily and behaves as a co-stimulatory molecule found on B cells, monocytes, antigen presenting cells, endothelial, smooth muscle cells, fibroblasts and platelets. Its ligand, CD40L (also called CD154), a type II transmembrane protein, is a 261 amino acid (aa) glycoprotein that forms homotrimers. CD40L is found on activated T cells, B cells, platelets, endothelial, epithelial and smooth muscle cells. Proteolytic cleavage can produce a soluble form of CD40L (sCD40L). Platelets are the main source of sCD40L.
CD40-CD40L interaction is an essential signal for B cell proliferation, expression of activation markers, immunoglobulin production and isotype switching, formation of B memory cells and germinal centers. It also prevents apoptosis of germinal center B cells. Defective expression of CD40L in humans leads to an inability to produce isotypes other than IgM (hyper IgM syndrome) and to an absence of germinal centers. In dendritic cells, CD40 ligation induces more effective antigen, enhances T-cell stimulatory capacity and induces production of several inflammatory cytokines and chemokines. CD40-CD40L interactions are crucially involved in development of autoimmune disease and have also impact on growth regulation of certain carcinomas. Elevated levels of sCD40L have been observed in sera from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and unstable angina.