Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
Astaxanthin
As low as
60
CHF
CHF 60.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CN2-0055-M0055 mgCHF 60.00
AG-CN2-0055-M02525 mgCHF 150.00
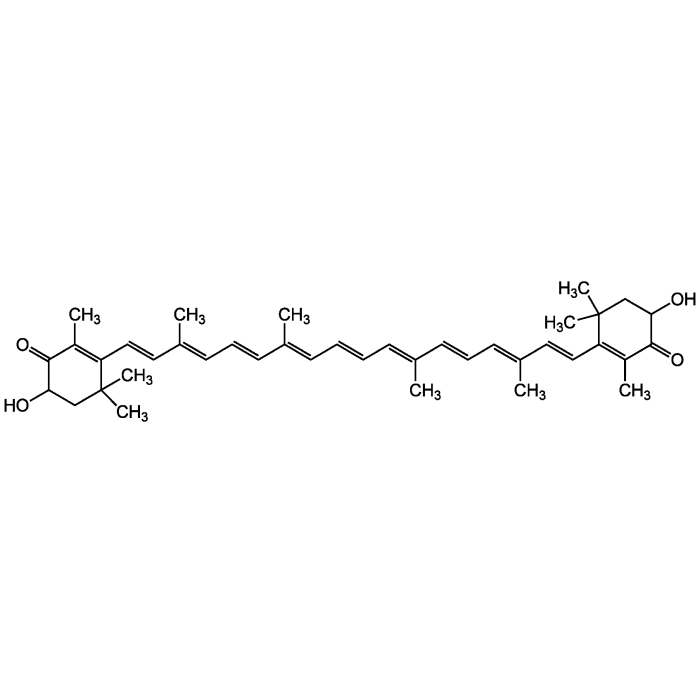
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | 3,3'-Dihydroxy-β-carotene-4,4'-dione; all-trans-Astaxanthin; Ovoester; NSC635689; CCRIS 7118; HSDB 7468 |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C40H52O4 |
| MW | 596.8 |
| CAS | 472-61-7 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Synthetic. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | Dark violet red solid. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO, chloroform or DMF. Soluble in ethanol or methanol if heated. Insoluble in water. |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| Other Product Data |
Solubility in aqueous buffers: Further dilutions of the organic solvent solution into aqueous or isotonic saline should be made prior to performing biological experiments. Store aqueous solutions on ice and use within 12 hours of preparation. It is strongly recommended using fresh perparations each day. |
| InChi Key | MQZIGYBFDRPAKN-QISQUURKSA-N |
| Smiles | C\C(\C=C\C=C(/C)\C=C\C1=C(C)C(=O)C(O)CC1(C)C)=C/C=C/C=C(\C)/C=C/C=C(\C)/C=C/C1=C(C)C(=O)C(O)CC1(C)C |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Keep cool and dry. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Potent antioxidant carotenoid [1].
- Free radical scavenger [1, 3].
- Reduces oxidative stress [1, 3].
- Anticancer compound [2].
- Anti-inflammatory. Blocks NF-κB activation [3, 18].
- Anti-hypertensive. Cardiovascular protective [4, 6].
- Improves neuronal stem cell potential [7, 9].
- Neuroprotective [10].
- Inhibits tumor invasion [11].
- Apoptosis inducer [14].
- Increases insulin sensitivity [12].
- Attenuates diabetes associated coagulatory, oxidative and inflammatory stress [17].
- PPARα agonist and PPARγ antagonist [19, 20].
- Shows positive effects on obesity and insulin resistance [17, 19, 20]
- Hepatoprotective [21].
- Reviews [5, 6, 15, 16].
Product References
- Antioxidant activities of astaxanthin and related carotenoids: Y.M. Naguib; J. Agric. Food Chem. 48, 1150 (2000)
- Antitumor activity of astaxanthin and its mode of action: H. Jyonouchi, et al.; Nutr. Cancer 36, 59 (2000)
- Astaxanthin inhibits nitric oxide production and inflammatory gene expression by suppressing I(kappa)B kinase-dependent NF-kappaB activation: S.J. Lee, et al.; Mol. Cells 16, 97 (2003)
- Antihypertensive potential and mechanism of action of astaxanthin: II. Vascular reactivity and hemorheology in spontaneously hypertensive rats: G. Hussein, et al.; Biol. Pharm. Bull. 28, 967 (2005)
- Astaxanthin: a novel potential treatment for oxidative stress and inflammation in cardiovascular disease: F.J. Pashkow, et al.; Am. J. Cardiol. 101, 58D (2008) (Review)
- Astaxanthin, oxidative stress, inflammation and cardiovascular disease: R.G. Fassett & J.S. Coombes; Future Cardiol. 5, 333 (2009) (Review)
- Astaxanthin Improves Stem Cell Potency via an Increase in the Proliferation of Neural Progenitor Cells: J.H. Kim, et al.; Int. J. Mol. Sci. 11, 5109 (2010)
- Astaxanthin decreased oxidative stress and inflammation and enhanced immune response in humans: J.S. Park, et al.; Nutr. Metab. (Lond). 7, 18 (2010)
- Astaxanthin improves the proliferative capacity as well as the osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation potential in neural stem cells: J.H. Kim, et al.; Food Chem. Toxicol. 48, 1741 (2010)
- Neuroprotective effect of astaxanthin on H(2)O(2)-induced neurotoxicity in vitro and on focal cerebral ischemia in vivo: Y.P. Lu, et al.; Brain Res. 1360, 40 (2010)
- Astaxanthin inhibits tumor invasion by decreasing extracellular matrix production and induces apoptosis in experimental rat colon carcinogenesis by modulating the expressions of ERK-2, NFkB and COX-2: P. Nagendraprabhu & G. Sudhandiran; Invest. New Drugs. 29, 207 (2011)
- High dose astaxanthin lowers blood pressure and increases insulin sensitivity in rats: are these effects interdependent?: H.G. Preuss, et al.; Int. J. Med. Sci. 8, 126 (2011)
- Ameliorative effect of astaxanthin on endothelial dysfunction in streptozotocin-induced diabetes in male rats: Z.W. Zhao, et al.; Arzneimittelforschung 61, 239 (2011)
- Astaxanthin induces mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in rat hepatocellular carcinoma CBRH-7919 cells: X.D. Song, et al.; Biol. Pharm. Bull. 34, 839 (2011)
- Astaxanthin, cell membrane nutrient with diverse clinical benefits and anti-aging potential: P. Kidd; Altern. Med. Rev. 16, 355 (2011) (Review)
- Astaxanthin: a potential therapeutic agent in cardiovascular disease: R.G. Fassett & J.S. Coombes; Mar. Drugs 9, 447 (2011) (Review)
- Anticoagulatory and antiinflammatory effects of astaxanthin in diabetic rats: K.C. Chan, et al.; J. Food Sci. 77, H76 (2012)
- Astaxanthin Treatment Reduced Oxidative Induced Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines Secretion in U937: SHP-1 as a Novel Biological Target: L. Speranza, et al.; Mar. Drugs 10, 890 (2012)
- The natural carotenoid astaxanthin, a PPAR-a agonist and PPAR-g antagonist, reduces hepatic lipid accumulation by rewiring the transcriptome in lipid-loaded hepatocytes: Y. Jai, et al.; Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 56, 878 (2012)
- Astaxanthin functions differently as a selective peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor g modulator in adipocytes and macrophages: M. Inoue, et al.; Biochem. Pharmacol. 84, 692 (2012)
- Hepatoprotective potential of astaxanthin against 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in cultured rat hepatocytes: H. Turkez, et al.; Toxicol. Ind. Health. 30, 101 (2012)