Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
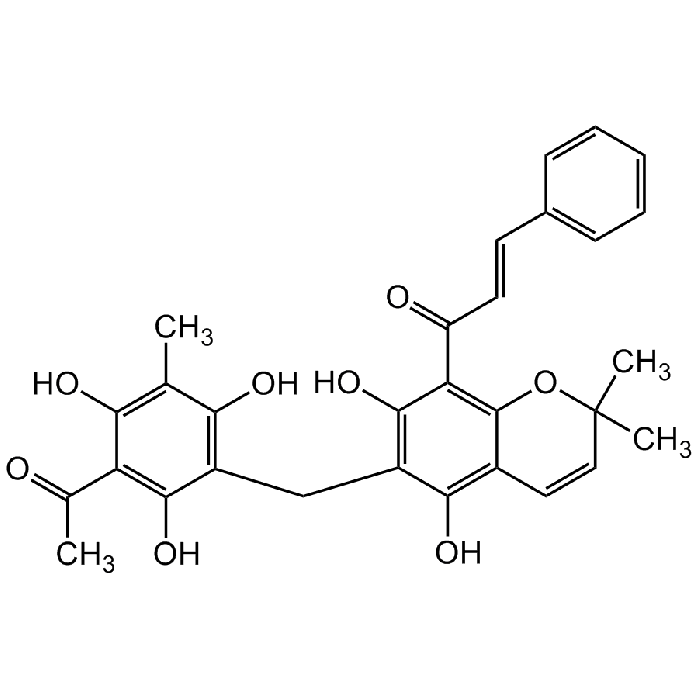
Rottlerin
As low as
50
CHF
CHF 50.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CN2-0526-M01010 mgCHF 50.00
AG-CN2-0526-M05050 mgCHF 150.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Mallotoxin; NSC94525; NSC56346; Kamalin |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C30H28O8 |
| MW | 516.5 |
| CAS | 82-08-6 |
| RTECS | AM6913800 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Isolated from Mallotus philippinensis. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | Orange to brown solid. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO (50mg/ml) or ethanol (1mg/ml). Insoluble in water. |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR and MS. |
| InChi Key | DEZFNHCVIZBHBI-ZHACJKMWSA-N |
| Smiles | CC1(C)C=CC2=C(O)C(CC3=C(O)C(C)=C(O)C(C(C)=O)=C3O)=C(O)C(C(/C=C/C4=CC=CC=C4)=O)=C2O1 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Keep cool and dry. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Anticancer agent that can inhibit cell growth, induce apoptosis, autophagy and cell cycle arrest, inhibit cell invasion and shows anti-angiogenic activity.
- OXPHOS inhibitor. Mitochondrial uncoupler that depolarizes the mitochondrial membrane potential, reduces cellular ATP levels, activates 5'-AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and affects mitochondrial production of reactive oxygen species (ROS).
- Useful for immunometabolism research.
- Potent activator of multiple Ca2+-sensitive K+ channels. Naturally occurring hERG channel activator. Antioxidant and ROS scavanger. Might have cardioprotective effects.
- Has been widely used as a selective inhibitor of protein kinase Cδ (PKCδ) (IC50=3-6µM), although there has been controversy in the literature over this claim.
- Inhibits CAM kinase III and a wide range of other kinases and non-kinase proteins in vitro. Most potently inhibits PRAK and MAPKAP-K2.
- Induces autophagy by inhibition of mTORC1 signaling.
- Displays neuroprotective effects.
Product References
- Rottlerin, a novel protein kinase inhibitor: M. Gschwendt, et al.; BBRC 199, 93 (1994)
- Effects of rottlerin, an inhibitor of calmodulin-dependent protein kinase III, on cellular proliferation, viability, and cell cycle distribution in malignant glioma cells: T.G. Parmer, et al.; Cell Growth Differ. 8, 327 (1997)
- Specificity and mechanism of action of some commonly used protein kinase inhibitors: S.P. Davies, et al.; Biochem. J. 351, 95 (2000)
- Rottlerin is a mitochondrial uncoupler that decreases cellular ATP levels and indirectly blocks protein kinase Cdelta tyrosine phosphorylation: S.P. Soltoff; J. Biol. Chem. 276, 37986 (2001)
- Rottlerin inhibits insulin-stimulated glucose transport in 3T3-L1 adipocytes by uncoupling mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation: A.G. Kayali, et al.; Endocrinol. 143, 3884 (2002)
- Kinase inhibitors: Not just for kinases anymore: S.L. McGovern & B.K. Shoichet; J. Med. Chem. 46, 1478 (2003)
- Mitochondrial Ca2+-activated K+ channels in cardiac myocytes: a mechanism of the cardioprotective effect and modulation by protein kinase A: T. Sato, et al.; Circulation 111, 198 (2005)
- Mallotoxin is a novel human ether-a-go-go-related gene (hERG) potassium channel activator: H. Zeng, et al.; JPET 319, 957 (2006)
- Rottlerin: an inappropriate and ineffective inhibitor of PKCdelta: S.P. Soltoff; TIPS 28, 453 (2007)
- Neuroprotective effect of protein kinase C delta inhibitor rottlerin in cell culture and animal models of Parkinson's disease: D. Zhang, et al.; J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 322, 913 (2007)
- Rottlerin induces autophagy and apoptotic cell death through a PKC-delta-independent pathway in HT1080 human fibrosarcoma cells: the protective role of autophagy in apoptosis: K.S. Song, et al.; Autophagy 4, 650 (2008)
- Screen for Chemical Modulators of Autophagy Reveals Novel Therapeutic Inhibitors of mTORC1 Signaling: A.D. Balgi, et al.; PLOS One 4, e7124 (2009)
- Rottlerin exhibits antiangiogenic effects in vitro: G. Valacchi, et al.; Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 77, 460 (2011)
- Rottlerin induces autophagy and apoptosis in prostate cancer stem cells via PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway: D. Kumar, et al.; Cancer Lett. 343, 179 (2014)
- Rottlerin inhibits cell growth, induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest, and inhibits cell invasion in human hepatocellular carcinoma: J. Shi, et al.; Mol. Med. Rep. 17, 459 (2018)
- Non-conventional rottlerin anticancer properties: E. Maioli, et al.; Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 645, 50 (2018)