Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
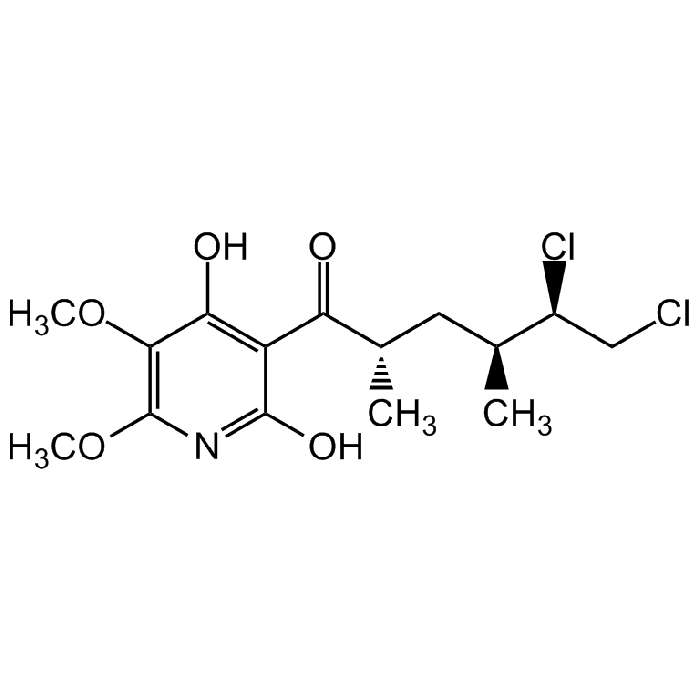
Atpenin A5
As low as
160
CHF
CHF 160.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CN2-0100-C250250 µgCHF 160.00
AG-CN2-0100-M0011 mgCHF 450.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | 3-[(2S,4S,5R)-5,6-Dichloro-2,4-dimethyl-1-oxohexyl]-4-hydroxy-5,6-dimethoxy-2(1H)-pyridinone |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C15H21Cl2NO5 |
| MW | 366.2 |
| CAS | 119509-24-9 |
| RTECS | CJ8800000 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Synthetic. Originally isolated from Penicillium sp. strain FO-125. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥95% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid. |
| Solubility | Soluble in acetone, acetonitrile, chloroform, ethyl acetate, DMSO, methanol or ethanol. Insoluble in water or hexane. |
| InChi Key | OVULNOOPECCZRG-CIUDSAMLSA-N |
| Smiles | COC1=C(OC)C(O)=C(C(=O)[C@@H](C)C[C@H](C)[C@@H](Cl)CCl)C(O)=N1 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | After reconstitution, prepare aliquots and store at -20°C. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 3 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Antibiotic [1-3].
- Antifungal [1-3].
- Potent and specific mitochondrial complex II (succinate-ubiquinone oxidoreductase) inhibitor [4, 5, 7].
- Mitochondrial ATP-sensitive potassium (mK(ATP)) channel activator [6, 8].
- Cardioprotective [6, 8].
- Modulates mitochondrial ROS generation during cardioprotection [9].
Product References
- Atpenins, new antifungal antibiotics produced by Penicillium sp. Production, isolation, physico-chemical and biological properties: S. Omura, et al.; J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 41, 1769 (1988)
- Mechanism of action of atpenin B on Raji cells: K. Oshino, et al.; J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 43, 1064 (1990)
- The structures of atpenins A4, A5 and B, new antifungal antibiotics produced by Penicillium sp: H. Kumagai, et al.; J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 43, 1553 (1990)
- Atpenins, potent and specific inhibitors of mitochondrial complex II (succinate-ubiquinone oxidoreductase): H. Miyadera, et al.; PNAS 100, 473 (2003)
- Structural and computational analysis of the quinone-binding site of complex II (succinate-ubiquinone oxidoreductase): a mechanism of electron transfer and proton conduction during ubiquinone reduction: R. Horsefield, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 281, 7309 (2006)
- The complex II inhibitor atpenin A5 protects against cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury via activation of mitochondrial KATP channels.: A. P. Wojtovich & P. S. Brooks; Basic Res. Cardiol. 104, 121 (2009)
- Synthetic atpenin analogs: Potent mitochondrial inhibitors of mammalian and fungal succinate-ubiquinone oxidoreductase: T.P. Selby, et al.; Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 20, 1665 (2010)
- The mitochondrial complex II and ATP-sensitive potassium channel interaction: quantitation of the channel in heart mitochondria: A.P. Wojtovich, et al.; Acta Biochim. Pol. 57, 431 (2010)
- A common mechanism links differently acting complex II inhibitors to cardioprotection: modulation of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species production: S. Drose, et al.; Mol. Pharmacol. 79, 814 (2011)