Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
BioViotica
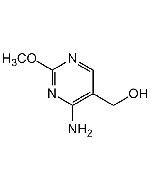
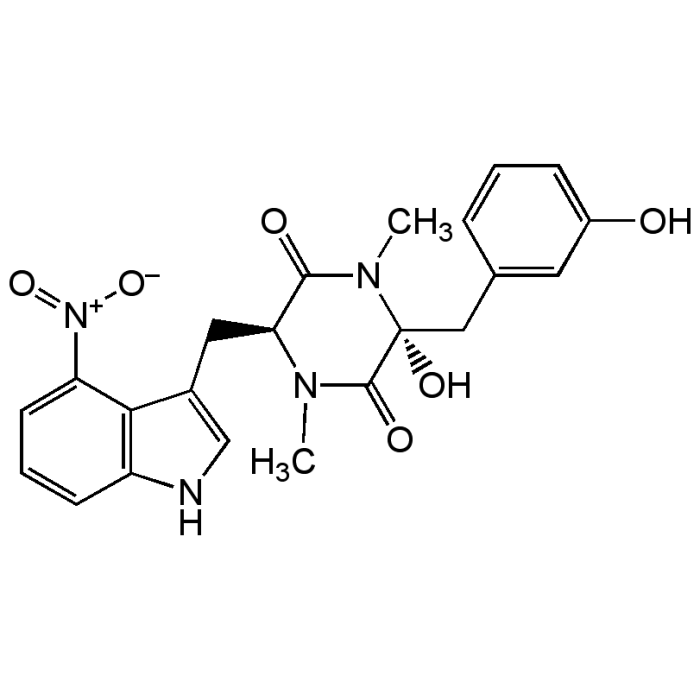
Thaxtomin A
As low as
215
CHF
CHF 215.00
In stock
Only %1 left
BVT-0206-M0011 mgCHF 215.00
BVT-0206-M0055 mgCHF 755.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Thaztomin A |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C22H22N4O6 |
| MW | 438.4 |
| CAS | 122380-18-1 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Isolated from Streptomyces bottropensis Gö-Dra 17. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | Yellow powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO or dimethyl formamide; partially soluble in methanol or 100% ethanol; poorly soluble in water. |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by BioViotica. |
| InChi Key | QRDNJYNIEGRRKV-PGRDOPGGSA-N |
| Smiles | CN1[C@@H](CC2=CNC3=C2C(=CC=C3)[N+]([O-])=O)C(=O)N(C)[C@@](O)(CC2=CC(O)=CC=C2)C1=O |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Use/Stability |
Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at -20°C. After reconstitution protect from light at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Diketopiperazine antibiotic.
- Phytotoxin.
- Herbicide.
- Natural cellulose synthesis inhibitor.
- Plant cell necrosis inducer.
- Induces common scab disease of potato.
Product References
- Isolation and characterization of phytotoxins associated with Streptomyces scabies: R. R. King, et al.; J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 13, 849 (1989)
- An Arabidopsis mutant resistant to thaxtomin A, a cellulose synthesis inhibitor from Streptomyces species: W.R. Scheible, et al.; Plant Cell 15, 1781 (2003)
- Thaxtomin A induces programmed cell death in Arabidopsis thaliana suspension-cultured cells: I. Duval, et al.; Planta 222, 820 (2005)
- The Thaxtomin phytotoxins: Sources, synthesis, biosynthesis, biotransformation and biological activity: R. R. King & L. A. Calhoun; Phytochemistry 70, 833 (2009) (Review)
- Streptomyces scabiei and its toxin thaxtomin A induce scopoletin biosynthesis in tobacco and Arabidopsis thaliana: S. Lerat, et. al.; Plant Cell Rep. 28, 1895 (2009)
- Two different signaling pathways for Thaxtomin A-induced cell death in Arabidopsis and tobacco BY2: P. Meimoun, et al.; Plant Sign. Behav. 4, 142 (2009)
- Relationship of resistance to common scab disease and tolerance to thaxtomin A toxicity within potato cultivars: R. S. Tegg, et al.; Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 128, 143 (2010)
- Total synthesis of thaxtomin A and its stereoisomers and findings of their biological activities: H. Zhang, et al.; Org. Lett. 15, 5670 (2013)
- Thaxtomin A production and virulence are controlled by several bld gene global regulators in Streptomyces scabies: D. Bignell, et al.; Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 27, 875 (2014)
- Mechanisms of thaxtomin A-induced root toxicity revealed by a thaxtomin A sensitive Arabidopsis mutant (ucu2-2/gi-2): R.S. Tegg, et al.; Plant Cell Rep. 35, 347 (2016)
- De novo biosynthesis of "non-natural" thaxtomin phytotoxins: M. Winn, et al.; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 57, 6830 (2018)
- Evaluation of Streptomyces common scab toxins diffusion in potato tubers and through the intestinal barrier: C. Leclerc, et al.; Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 6, 1662 (2017)
- The emergence of nitric oxide in the biosynthesis of bacterial natural products: J D. Caranto; Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 49, 130 (2019)
- Chemical activation of EDS1/PAD4 signaling leading to pathogen resistance in Arabidopsis: S. Joglekar, et al.; Plant Cell Physiol. 59, 1592 (2018)
- Reactive oxygen species alleviate cell death induced by thaxtomin A in Arabidopsis thaliana cell cultures: F. Awwad, et al.; Plants 8, 332 (2019)