Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
BioViotica
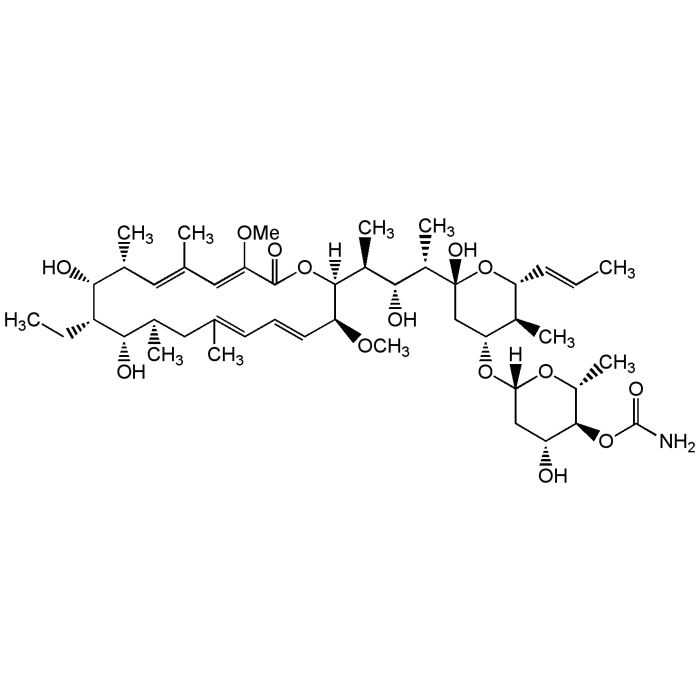
Concanamycin A (high purity)
As low as
85
CHF
CHF 85.00
In stock
Only %1 left
BVT-0237-C02525 µgCHF 85.00
BVT-0237-C100100 µgCHF 145.00
BVT-0237-M0011 mgCHF 335.00
BVT-0237-M0055 mgCHF 1’500.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Folimycin; Antibiotic TAN 1323B; Antibiotic X4357B |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
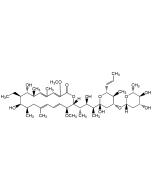
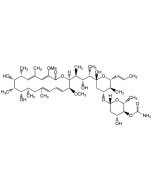
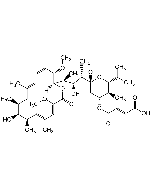
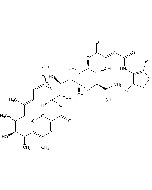
| Formula | C46H75NO14 |
| MW | 866.1 |
| CAS | 80890-47-7 |
| RTECS | CB9732000 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Isolated from Streptomyces sp. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid. |
| Solubility | Soluble in methanol, DMSO or acetonitrile; insoluble in water. |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by BioViotica. |
| InChi Key | DJZCTUVALDDONK-MSPZYORZSA-N |
| Smiles | [H][C@@]1(C[C@@H](O)[C@H](OC(N)=O)[C@@H](C)O1)O[C@@H]1C[C@@](O)(O[C@H](\C=C\C)[C@H]1C)[C@@H](C)[C@H](O)[C@H](C)[C@]1([H])OC(=O)\C(OC)=C\C(\C)=C\[C@@H](C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H](CC)[C@@H](O)[C@H](C)CC(C)=C\C=C\[C@@H]1OC |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light when in solution. |
| Use/Stability |
Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at -20°C. After reconstitution protect from light at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Antibiotic.
- More potent and specific H+-ATPase inhibitor than bafilomycin A1 (Prod. No. BVT-0252).
- Inhibits acidification of organelles such as lysosomes and the Golgi apparatus.
- Inhibitor of autophagic degradation by rising lysosomal pH and thus inactivating the lysosomal acid hydrolases.
- Blocks cell surface expression of viral glycoproteins without affecting their synthesis.
- Cytotoxic in a number of cell lines in a cell viability assay.
- Induces nitric oxide (NO) production.
- Concanamycin A enables the immune system to kill HIV-infected cells. Nef is an HIV-encoded accessory protein that enhances pathogenicity by down-regulating major histocompatibility class I (MHC-I) expression to evade killing by cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs). Concanamycin A has been identified as potent inhibitor of Nef that restores MHC-I and enhances the clearance of HIV-infected primary cells by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Concanamycin A counteracts Nef from diverse clades of HIV targeting multiple allotypes of MHC-I, indicating the potential for broad therapeutic utility.
Product References
- Isolation and characterization of concanamycins A, B and C: H. Kinashi, et al.; J. Antibiot. 37, 1333 (1984)
- Folimycin (concanamycin A), a specific inhibitor of V-ATPase, blocks intracellular translocation of the glycoprotein of vesicular stomatitis virus before arrival to the Golgi apparatus: M. Muroi, et al.; Cell Struct. Funct. 18, 139 (1993)
- Folimycin (concanamycin A), an inhibitor of V-type H(+)-ATPase, blocks cell-surface expression of virus-envelope glycoproteins: M. Muroi, et al.; BBRC 193, 999 (1993)
- Inhibitory effect of modified bafilomycins and concanamycins on P- and V-type adenosinetriphosphatases: S. Drose, et al.; Biochemistry 32, 3902 (1993)
- Involvement of the vacuolar H(+)-ATPases in the secretory pathway of HepG2 cells: M. Yilla, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 268, 19092 (1993)
- Characterization of the ATPase activity of P-glycoprotein from multidrug-resistant Chinese hamster ovary cells: F.J. Sharom, et al.; Biochem. J. 308 (Pt2), 381 (1995)
- Specific inhibitors of vacuolar type H(+)-ATPases induce apoptotic cell death: T. Nishihara, et al.; BBRC 212, 255 (1995)
- Concanamycin A, the specific inhibitor of V-ATPases, binds to the V(o) subunit c: M. Huss, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 277, 40544 (2002)
- Nitric oxide production by the vacuolar-type (H+)-ATPase inhibitors bafilomycin A1 and concanamycin A and its possible role in apoptosis in RAW 264.7 cells: J. Hong, et al.; J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 319, 672 (2006)
- Degradation of oxidized proteins by autophagy during oxidative stress in Arabidopsis: Y. Xiong, et al.; Plant Physiol. 143, 291 (2007)
- Inhibitors of the V0 subunit of the vacuolar H+-ATPase prevent segregation of lysosomal- and secretory-pathway proteins: J.A. Sobota, et al.; J. Cell Sci. 122, 3542 (2009)
- Inhibitors of V-ATPase: old and new players: M. Huss, et al.; J. Exp. Biol. 212, 341 (2009)
- Increased production of reactive oxygen species by the vacuolar-type (H+)-ATPase inhibitors bafilomycin A1 and concanamycin A in RAW 264 cells: A. Yokomakura, et al.; J. Toxicol. Sci. 37, 1045 (2012)
- Inhibition of vacuolar ATPase attenuates the TRAIL-induced activation of caspase-8 and modulates the trafficking of TRAIL receptosomes: V. Horova, et al.; FEBS J. 280, 3436 (2013)
- Estimating the rotation rate in the vacuolar proton-ATPase in native yeast vacuolar membranes: Z. Ferencz, et al.; Eur. Biophys. J. 42, 147 (2013)
- Inhibitors of vacuolar ATPase proton pumps inhibit human prostate cancer cell invasion and prostate-specific antigen expression and secretion: V. Michel, et al.; Int. J. Cancer 132, E1 (2013)
- Loss of vacuolar H+-ATPase activity in organelles signals ubiquitination and endocytosis of the yeast plasma membrane proton pump Pma1p: A. M. Smardon & P. M. Kane; J. Biol. Chem. 289, 32316 (2014)
- Combined effects of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors and vATPase inhibitors in NSCLC cells: H. Jin, et al.; Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 278, 17 (2015)
- Appropriate vacuolar acidification in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is associated with efficient high sugar fermentation: T.D. Nguyen, et al.; Food Microbiology 70, 262 (2018)
- Concanamycin A counteracts HIV-1 Nef to enhance immune clearance of infected primary cells by cytotoxic T lymphocytes: M.M. Painter, et al.; PNAS 117, 23835 (2020)
- The V-type ATPase enhances photosynthesis in marine phytoplankton and further links phagocytosis to symbiogenesis: D.P. Yee, et al.; Curr. Biol. in press (2023)