Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
BioViotica
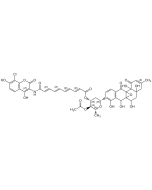
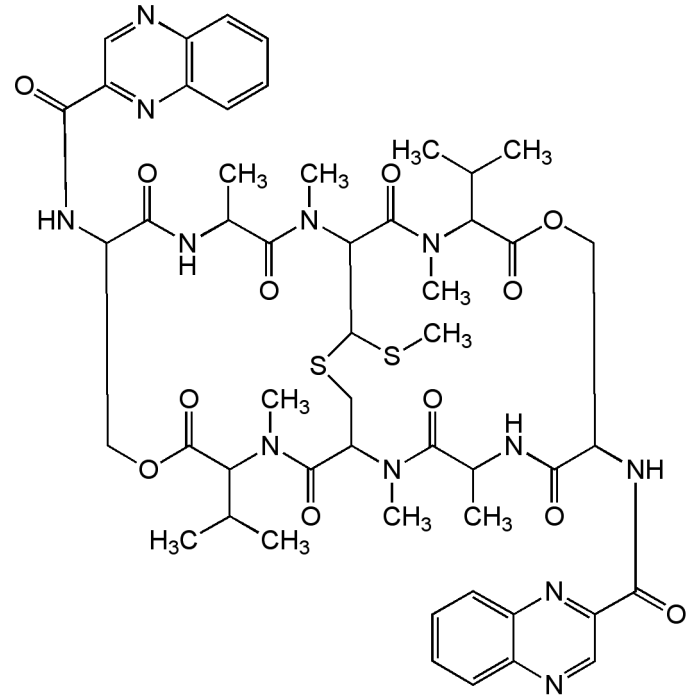
Echinomycin
As low as
110
CHF
CHF 110.00
In stock
Only %1 left
BVT-0267-M0011 mgCHF 110.00
BVT-0267-M0055 mgCHF 440.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Quinomycin A |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C51H64N12O12S2 |
| MW | 1101.3 |
| Merck Index | 14: 3497 |
| CAS | 512-64-1 |
| RTECS | JW5250000 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Isolated from Streptomyces echinatus. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid. |
| Solubility | Soluble in acetone, DMSO (5mg/ml), methanol, dichloromethane or ethyl acetate. |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by BioViotica. |
| Other Product Data |
Contains traces of water. |
| InChi Key | AUJXLBOHYWTPFV-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Smiles | CSC1SCC2N(C)C(=O)C(C)NC(=O)C(COC(=O)C(C(C)C)N(C)C(=O)C1N(C)C(=O)C(C)NC(=O)C(COC(=O)C(C(C)C)N(C)C2=O)NC(=O)C1=NC2=C(C=CC=C2)N=C1)NC(=O)C1=NC2=CC=CC=C2N=C1 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Hygroscopic. |
| Use/Stability |
Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at -20°C. After reconstitution protect from light at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Antibiotic.
- Antitumor compound.
- Powerful, selective inhibitor of nucleic acid synthesis in vitro.
- Potent hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) DNA binding activity inhibitor.
- Apoptosis inducer.
- Antibacterial, antifungal and antiviral.
- Shown to inhibit the type I IFN−MHC class I pathway in muscle precursor cells (myoblasts).
Product References
- A "quinoxaline antibiotic" similar to the triostins, q.v.: I. Kuroya, et al.; J. Antibiot. 14A, 324 (1961)
- The mode of action of quinoxaline antibiotics. Interaction of quinomycin A with deoxyribonucleic acid: K. Sato, et al.; J. Antibiot. 20, 270 (1967)
- Echinomycin binding sites on DNA: M.M. Van Dyke & P.B. Dervan; Science 225, 1122 (1984)
- Kinetic evidence that echinomycin migrates between potential DNA binding sites: K.R. Fox & M.J. Waring; Nucl. Acids Res. 13, 595 (1985)
- Effect of echinomycin on DNA methylation: R.L. Adams & A. Rinaldi; FEBS Lett. 215, 266 (1987)
- Echinomycin and a novel analogue induce apoptosis of HT-29 cells via the activation of MAP kinases pathway: J.Y. Park, et al.; Pharmacol. Res. 50, 201 (2004)
- Echinomycin, a small-molecule inhibitor of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 DNA-binding activity: D. Kong, et al.; Cancer Res. 65, 9047 (2005)
- Molecular signaling cascade in DNA bisintercalator, echinomycin-induced apoptosis of HT-29 cells: evidence of the apoptotic process via activation of the cytochrome c-ERK-caspase-3 pathway: J.Y. Park, et al.; Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 38, 244 (2006)
- Effects of the HIF1 inhibitor, echinomycin, on growth and NOTCH signalling in leukaemia cells: S. Yonekura, et al.; Anticancer Res. 33, 3099 (2013)
- Echinomycin, a potential binder of FKBP12, shows minor effect on calcineurin activity: V. Singh, et al.; J. Biomol. Screen. 19, 1275 (2014)
- Effects of the hypoxia-inducible factor-1 inhibitor echinomycin on vascular endothelial growth factor production and apoptosis in human ectopic endometriotic stromal cells: T. Tsuzuki, et al.; Gynecol. Endocrinol. 32, 323 (2016)
- miRNA profile of neuroprotection mechanism of echinomycin in parkinson's disease: D. Kwon & H. Liew; Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 13, 229 (2017)
- Molecular and cellular toxicological profiling of DNA bis-intercalator, quinoxaline compounds: echinomycin as the versatile lead: Y.-S. Park, et al.; Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 14, 9 (2018)
- Encapsulation of echinomycin in cyclodextrin inclusion complexes into liposomes: in vitro anti-proliferative and anti-invasive activity in glioblastoma: W. Alshaer, et al.; RSC Adv. 9, 30976 (2019)
- Design, synthesis, and conformation-activity study of unnatural bridged bicyclic depsipeptides as highly potent hypoxia inducible Factor-1 inhibitors and antitumor agents: K. Koike, et al.; J. Med. Chem. 63, 4022 (2020)
- Therapeutic targeting of TP53-mutated acute myeloid leukemia by inhibiting HIF-1a with echinomycin: Y. Wang, et al.; Oncogene 39, 3015 (2020)
- High-Throughput Screening to Identify Inhibitors of the Type I Interferon-Major Histocompatibility Complex Class I Pathway in Skeletal Muscle: T.B. Kinder, et al.; ACS Chem. Biol. 15, 1974 (2020)
- HIF-1a is involved in blood-brain barrier dysfunction and paracellular migration of bacteria in pneumococcal meningitis: G. Devraj, et al.; Acta Neuropathol. 140, 183 (2020)