Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
IL-37 (human) ELISA Kit
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Interleukin-1 Family Member 7; IL-1F7; FIL1 zeta; IL-1X; Interleukin-1 Homolog 4; IL-1H4; Interleukin-1 zeta; IL-1 zeta; IL-1RP1; IL1F7; FIL1Z, IL1H4, IL1RP1 |
| Product Type | Kit |
| Properties | |
| Application Set | Quantitative ELISA |
| Specificity |
Detects human IL-37 (monomeric and dimeric forms). Does not cross-react with human IL-33, IL-38, IL-6, IL-23, IL-24 or mouse IL-33 and IL-38. |
| Crossreactivity | Human |
| Quantity |
1 x 96 wells |
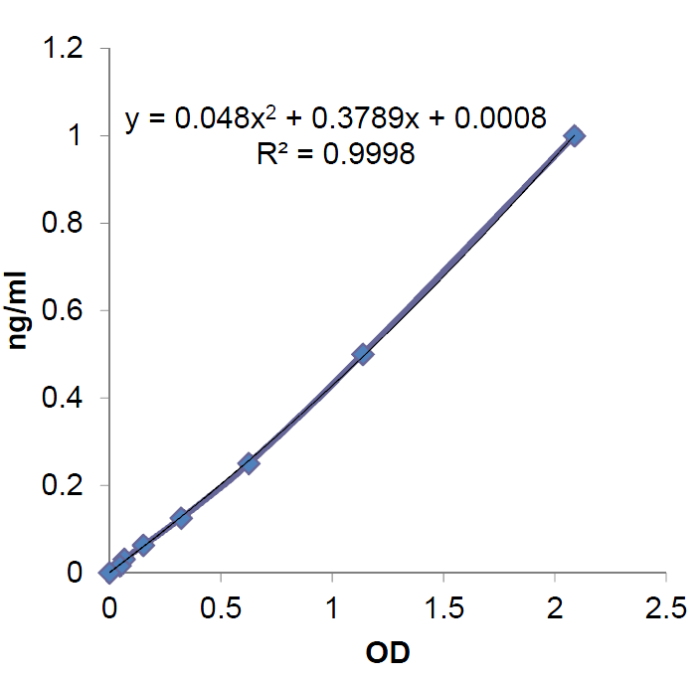
| Sensitivity | 10pg/ml |
| Range | 0.016 to 1ng/ml |
| Sample Type |
Plasma Serum |
| Assay Type | Sandwich |
| Detection Type | Colorimetric |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | BLUE ICE |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | +4°C |
| Handling Advice |
After standard reconstitution, prepare aliquots and store at -20°C. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. Plate and reagents should reach room temperature before use. |
| Use/Stability | 12 months after the day of manufacturing. See expiry date on ELISA Kit box. |
| Documents | |
| Manual |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
IL-37 (IL-1F7; IL-1H4) is an IL-1 family member that is expressed only in certain types of human organs and cells such as heart, thymus, testis, kidney, mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and dendritic cells. IL-37 is an inhibitor of innate immunity with anti-inflammatory properties. It binds to the interleukin-18 receptor (IL-18R) and its co-receptor SIGIRR. IL-37 is secreted as a full-length and as a processed form starting from amino acid Val46. It plays an important role as a link between innate and adaptive immunity and acts as an inhibitor of autoimmune diseases and tumor growth. IL-37 also inhibited Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced immunological reaction and LPS-induced osteoclast formation and bone resorption. New insights indicate that IL-37 protein forms a head-to-head homodimer and this structure limits its bioactivity. Variants with mutations converting the cytokine into a monomeric form are 13-fold more active than the dimeric IL-37. Circulating concentrations of IL-37 have been shown to be lower in older compared with younger adults, despite chronic low-grade elevations in pro-inflammatory cytokines in older adults. A recent study provides evidence that IL-37 concentrations decline in older age and are related to selective markers of healthspan in healthy humans and suggests a possible role of IL-37 in biological aging in humans.
- Serum Interleukin-37 Concentrations and HBeAg Seroconversion in Chronic HBV Patients During Telbivudine Treatment: C. Li, et al.; J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 33, 612 (2013)
- Elevated levels of cerebrospinal fluid and plasma interleukin-37 in patients with guillain-barré syndrome: C. Li, et al.; Mediators Inflamm. 2013, 639712 (2013)
- IL-37 inhibits the production of inflammatory cytokines in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: its correlation with disease activity: L. Ye, et al.; J. Transl. Med. 12, 69 (2014)
- Plasma Levels of IL-37 and Correlation with TNF-α, IL-17A, and Disease Activity during DMARD Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis: P.-W. Zhao, et al.; PLOS One 9, e95346 (2014)
- Evaluating the levels of interleukin-1 family cytokines in sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: P. Italiani, et al.; J. Neuroinflamm. 11, 94 (2014)
- Elevated plasma IL-37, IL-18, and IL-18BP concentrations in patients with acute coronary syndrome: Q. Ji, et al.; Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, ID165742 (2014)
- Interleukin-37 is increased in ankylosing spondylitis patients and associated with disease activity: B. Chen, et al.; J. Transl. Med. 13, 36 (2015)
- The Evaluation of Plasma and Leukocytic IL-37 Expression in Early Inflammation in Patients with Acute ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction after PCI: X. Wang, et al.; Med. Inflamm. 2015, 626934 (2015)
- Plasma Interleukin-37 Is Elevated in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: Its Correlation with Disease Activity and Th1/Th2/Th17-Related Cytokines: T. Xia, et al., Dis. Markers 2015, 795043 (2015)
- Interleukin-37 suppresses tumor growth through inhibition of angiogenesis in non-small cell lung cancer: G. Ge, et al.; J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 35, 13 (2016)
- Clinical associations of IL-10 and IL-37 in systemic lupus erythematosus: J. Godsell, et al.; Sci. Reports 6, 34604 (2016)
- Elevated serum interleukin-37 level is a predictive biomarker of poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer patients: J. Huo, et al.; Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 295, 459 (2017)
- Interleukin-37 elevation in patients with atrial fibrillation: W. Li, et al.; Clin. Cardiol. 40, 66 (2017)
- Homodimerization attenuates the anti-inflammatory activity of interleukin-37: A.M. Ellisdon, et al.; Sci. Immunol. 2, eaaj1548 (2017)
- Elevated IL-37 levels in the plasma of patients with severe coronary artery calcification: M. Chai, et al.; J. Geriatr. Cardiol. 14, 285 (2017)
- Interleukin-37 mediates the antitumor activity in colon cancer through β-catenin suppression: X. Yan, et al.; Oncotarget 8, 49064 (2017)
- IL-37 increased in patients with acute coronary syndrome and associated with a worse clinical outcome after ST-segment elevation acute myocardial infarction: K. Liu, et al.; Clin. Chim. Acta 468, 140 (2017)
- Plasma IL-37 Elevated in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure and Predicted Major Adverse Cardiac Events: A 1-Year Follow-Up Study: X. Shou, et al.; Dis. Markers 9134079 (2017)
- Measurement of Elevated IL-37 Levels in Acute Ischemic Brain Injury: A Cross-sectional Pilot Study. A. Zafar, et al. Cureus 9, e1767 (2017)
- Transgenic Overexpression of IL-37 Protects Against Atherosclerosis and Strengthens Plaque Stability: J. Liu, et al.; Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 45, 1034 (2018)
- Interleukin-37 is increased in adult-onset Still’s disease and associated with disease activity: H. Chi, et al.; Arthr. Res. Ther. 20, 54 (2018)
- Plasma interleukin-37 is increased and inhibits the production of inflammatory cytokines in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis patients: M. Feng, et al.; J. Transl. Med. 16, 277 (2018)
- IL-37 Attenuates Lung Fibrosis by Inducing Autophagy and Regulating TGF-b1 Production in Mice: M.S. Kim, et al.; J. Immunol. 203, 2265 (2019)
- IL-37 increases in patients after ischemic stroke and protects from inflammatory brain injury, motor impairment and lung infection in mice: S.R. Zhang, et al.; Sci. Rep. 9, 6922 (2019)
- Interleukin-37 sensitize the elderly type 2 diabetic patients to insulin therapy through suppressing the gut microbiota dysbiosis: T. Li, et al.; Mol. Immunol. 112, 322 (2019)
- Influenza A virus inhibits influenza virus replication by inducing IL‐37: F. Zhou, et al.; J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 33, e22638 (2019)
- Plasma levels and expression of interleukin‑37 in patients with immune thrombocytopenia: F. Zhang, et al.; Exp. Therap. Med. 18, 2739 (2019)
- Short‐term interleukin‐37 treatment improves vascular endothelial function, endurance exercise capacity, and whole‐body glucose metabolism in old mice: D.C. Ballak, et al.; Aging Cell 19, e13074 (2020)
- Correlation Between Level of Interleukin-37 and Rheumatoid Arthritis Progression: J. Zhu, et al.; Int. J. Gen. Med. 14, 1905 (2021)
- Circulating Interleukin-37 Levels in Healthy Adult Humans – Establishing a Reference Range: D.M. Santarelli, et al.; Front. Immunol. 12, 708425 (2021)
- Protein engineering of a stable and potent anti-inflammatory IL-37-Fc fusion with enhanced therapeutic potential: A. Bujotzek, et al.; Cell Chem. Biol. 29, 2451 (2022)
- Circulating interleukin‑37 declines with aging in healthy humans: relations to healthspan indicators and IL37 gene SNPs: V.E. Brunt, et al.; Geroscience 45, 65 (2022)
- Interleukin-37: associations of plasma levels and genetic variants in gout: LA. Cerezo, et al.; Arthritis Res. Ther. 25, 203 (2023)