Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
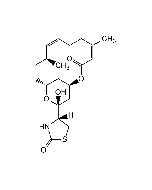
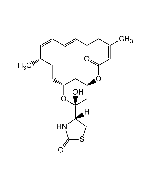
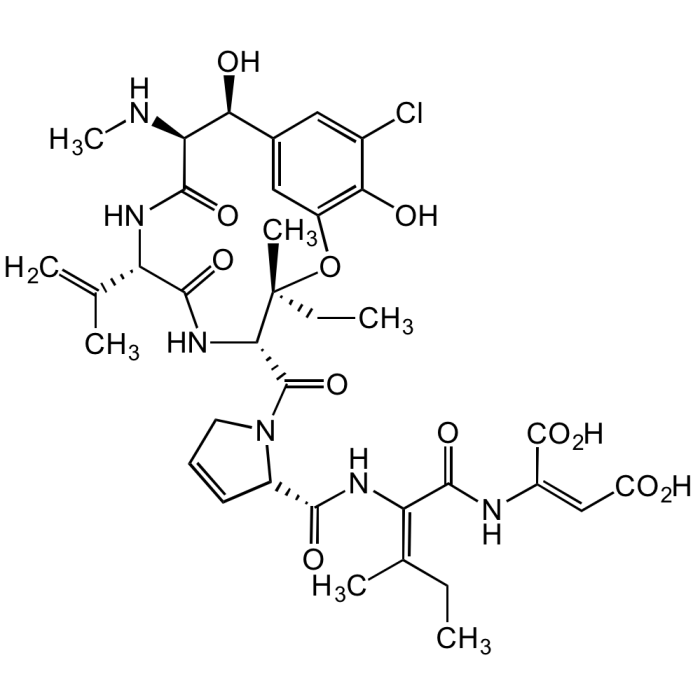
Phomopsin A
As low as
480
CHF
CHF 480.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CN2-0515-M0011 mgCHF 480.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | PHO-A; NSC 381839 |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C36H45ClN6O12 |
| MW | 789.2 |
| CAS | 64925-80-0 |
| RTECS | SY2593000 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Isolated from Phomopsis leptostromiformis. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC, TLC) |
| Appearance | White solid. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO (10mg/ml), ethanol, methanol (5mg/ml) or DMF. |
| InChi Key | FAFRRYBYQKPKSY-KBIMZEDXSA-N |
| Smiles | ClC1=CC([C@H](O)[C@@H]2NC)=CC(O[C@@](C)(CC)[C@H](C(N3CC=C[C@H]3C(N/C(C(N/C(C(O)=O)=C/C(O)=O)=O)=C(C)/CC)=O)=O)NC([C@H](C(C)=C)NC2=O)=O)=C1O |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Keep cool and dry. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Macrocyclic heptapeptide mycotoxin.
- Potent anti-mitotic compound that can cause cell death.
- Microtubule assembly inhibitor. Binds selectively to dimeric tubulin, inhibiting the formation of the microtubule spindle to block cell division. Binds at a site different from the colchicine binding site and overlapping the vinblastine binding site. Inhibits tubulin-dependent GTP hydrolysis. Binds β-tubulin from higher organisms but not α-tubulin or fungal mycelial tubulin.
- Causes lupinosis (a degenerative disorder) in livestock fed infected lupins.
Product References
- Interaction of phomopsin A and related compounds with purified sheep brain tubulin: E. Lacey, et al.; Biochem. Pharmacol. 36, 2133 (1987)
- Effect of phomopsin A on the alkylation of tubulin: R.F. Luduena, et al.; Biochem. Pharmacol. 39, 1603 (1990)
- Dolastatin 10, a powerful cytostatic peptide derived from a marine animal. Inhibition of tubulin polymerization mediated through the vinca alkaloid binding domain: R. Bai, et al.; Biochem. Pharmacol. 39, 1941 (1990)
- Binding selectivity of rhizoxin, phomopsin A, vinblastine, and ansamitocin P-3 to fungal tubulins: differential interactions of these antimitotic agents with brain and fungal tubulins: Y. Li, et al.; BBRC 187, 722 (1992)
- Interaction of phomopsin A with porcine brain tubulin. Inhibition of tubulin polymerization and binding at a rhizoxin binding site: Y. Li, et al.; Biochem. Pharmacol. 43, 219 (1992)
- Natural products which interact with tubulin in the vinca domain: maytansine, rhizoxin, phomopsin A, dolastatins 10 and 15 and halichondrin B: E. Hamel; Pharmacol. Ther. 55, 31 (1992)
- Interaction of phomopsin A with normal and subtilisin-treated bovine brain tubulin: A.R. Chaudhuri & R.F. Luduena; J. Protein Chem. 16, 99 (1997)
- Localization of the antimitotic peptide and depsipeptide binding site on beta-tubulin: A. Mitra & D. Sept; Biochemistry 43, 13955 (2004)
- Structural insight into the inhibition of tubulin by vinca domain peptide ligands: A. Cormier, et al.; EMBO Rep. 9, 1101 (2008)