Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
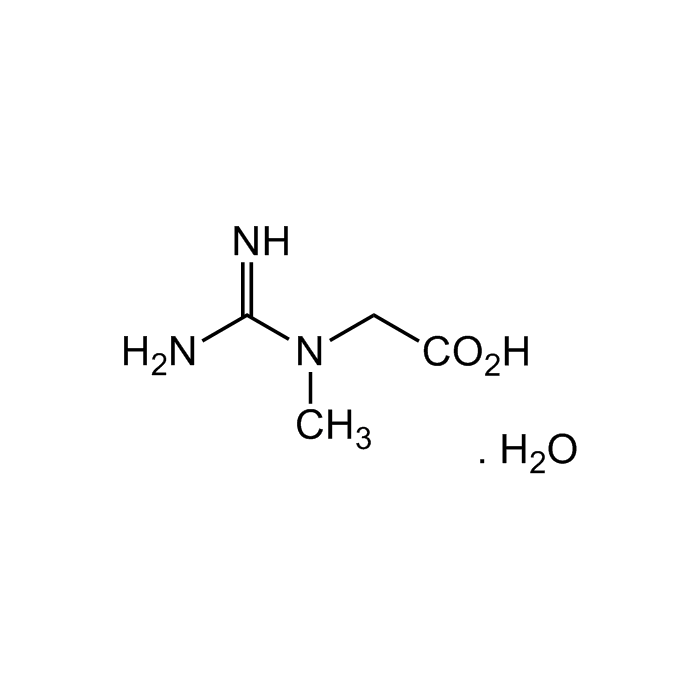
Creatine . monohydrate
As low as
40
CHF
CHF 40.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CR1-3679-G0055 gCHF 40.00
AG-CR1-3679-G02525 gCHF 65.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | N-(Aminoiminomethyl)-N-methylglycine monohydrate |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C4H9N3O2 . H2O |
| MW | 131.1 . 18.0 |
| CAS | 6020-87-7 |
| RTECS | MB7706000 |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% |
| Appearance | White solid. |
| Solubility | Soluble in water (10mg/ml). |
| InChi Key | MEJYXFHCRXAUIL-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Smiles | NC(N(C)CC(O)=O)=N.O |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Keep cool and dry. |
| Use/Stability |
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. Store solutions at -20°C in the dark. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- A nitrogenous organic acid that occurs naturally in vertebrates. Can be acquired through dietary consumption or formed from L-arginine, glycine and L-methionine in a multi-step reaction that occurs in the kidney and liver.
- High-energy reservoir for the rapid regeneration of ATP. Its main role is to facilitate recycling of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) primarily in muscle and brain tissue via the action of creatine kinase(s).
- Supplementation is investigated for the use in myopathies and enhancement of sports performance, primarily by increasing muscle mass. It is also investigated as a treatment of neuromuscular diseases, where it may aid in neuroprotection and by improving the cellular bioenergetic state.
- Antioxidant compound.
- Thermogenesis enhancer in beige adipocytes. Creatine cycling is important for thermogenesis and an altered creatine cycle could lead to obesity.
- Enhancer of energy expenditure through stimulation of mitochondrial ATP turnover.
Product References
- Creatine: endogenous metabolite, dietary, and therapeutic supplement: J.T. Brosnan & M.E. Brosnan; Annu. Rev. Nutr. 27, 241 (2007) (Review)
- Creatine as an antioxidant: P. Sestili, et al.; Amino Acids 40, 1385 (2011) (Review)
- Creatine inhibits adipogenesis by downregulating insulin-induced activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling pathway: N. Lee, et al.; Stem Cells Dev. 24, 983 (2015)
- Genetic depletion of adipocyte creatine metabolism inhibits diet-induced thermogenesis and drives obesity: L. Kazak, et al.; Cell Metab. 26, 660 (2017)
- Creatine fuels the thermic effect of feeding: A.R. Saltiel; Cell Metab. 26, 594 (2017) (Review)
- Targeting thermogenesis in brown fat and muscle to treat obesity and metabolic disease: M.J. Betz & S. Enerbaeck; Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. (Epub ahead of print) (2017) (Review)