Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
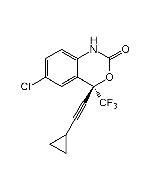
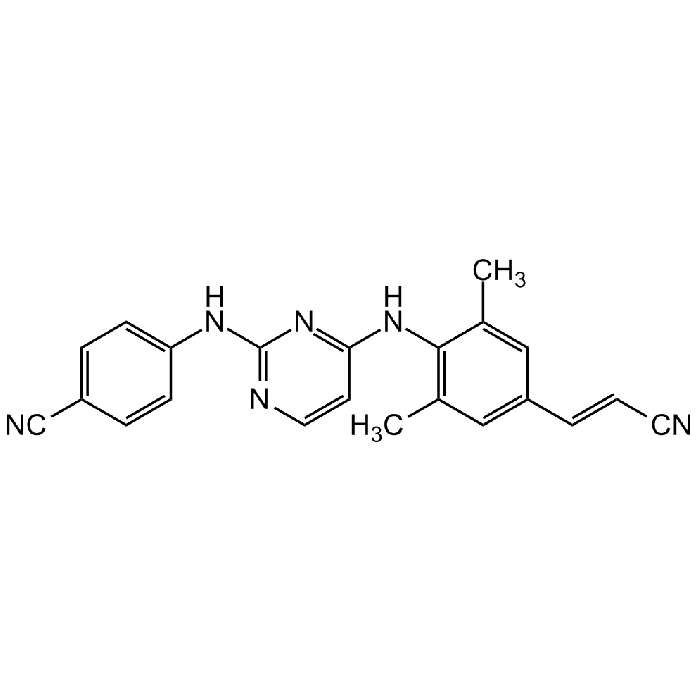
Rilpivirine
As low as
60
CHF
CHF 60.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CR1-3750-M0055 mgCHF 60.00
AG-CR1-3750-M02525 mgCHF 240.00
AG-CR1-3750-M100100 mgCHF 490.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | R278474; TMC278; DB08864 |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C22H18N6 |
| MW | 366.4 |
| CAS | 500287-72-9 |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO (25mg/ml). Warming and sonication may be needed. |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| InChi Key | YIBOMRUWOWDFLG-ONEGZZNKSA-N |
| Smiles | CC1=CC(/C=C/C#N)=CC(C)=C1NC2=NC(NC3=CC=C(C=C3)C#N)=NC=C2 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Keep cool and dry. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Rilpivirine is a non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI) that inhibits growth of wild-type HIV with an EC50 value of 0.51nM. It is active against NNRTI-resistant HIV strains with EC50 values less than 1nM for L100I, K103N, V106A, G190A and G190S mutants in vitro. Rilpivirine also reduces growth of greater than 80% of 1,500 NNRTI-resistant clinical isolates (EC50s = <10nM), including strains containing up to eight resistance mutations.
- NNRTIs work by binding to and blocking HIV reverse transcriptase, which prevents HIV from replicating and lowers the amount of HIV in the blood.
- Rilpivirine is an antiviral anti-HIV drug, active against wild-type and NNRTI-resistant HIV-1 with higher potency, longer half-life and reduced side-effect profile compared with Efavirenz (Prod. No. AG-CR1-3751).
- CARD8 inflammasome senses HIV-1 protease activity. In HIV1-infected cells, CARD8 cannot detect the virus because the viral protease remains inactive as a subunit of unprocessed Gag-Pol polyprotein. HIV-1-specific non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs), such us Rilpivirine, can trigger CARD8 sensing because they bind to HIV-1 Pol and enhance intracellular Gag-Pol polyprotein dimerization, which causes premature viral protease activation. Treating HIV-1-infected macrophages and CD4+ T cells with NNRTIs leads to CARD8-mediated caspase-1 activation and pyroptotic cell death. Induction of the CARD8 inflammasome activation has led to rapid clearance of latent HIV-1 in patient CD4+ T cells after virus reactivation.
Product References
- Synthesis of novel diarylpyrimidine analogues and their antiviral activity against human immunodeficiency virus type 1: J. Guillemont, et al.; J. Med. Chem. 48, 2072 (2005)
- In search of a novel anti-HIV drug: multidisciplinary coordination in the discovery of 4-[[4-[[4-[(1E)-2-cyanoethenyl]-2,6-dimethylphenyl]amino]-2- pyrimidinyl]amino]benzonitrile (R278474, rilpivirine): P.A. Janssen, et al.; J. Med. Chem. 48, 1901 (2005) (Review)
- Short-term antiviral activity of TMC278 -a novel NNRTI- in treatment-naive HIV-1-infected subjects: F. Goebel, et al.; AIDS 20, 1721 (2006)
- Rilpivirine: A novel non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor: L. Garvey & A. Winston; Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 18, 1035 (2009)
- TMC278, a next-generation nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI), active against wild-type and NNRTI-resistant HIV-1: H. Azijn, et al.; Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 54, 718 (2010)
- Rilpivirine, a novel non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor for the management of HIV-1 infection: a systematic review: J.J. Schafer & W.R. Short; Antivir. Ther. 17, 1495 (2012) (Review)
- Biochemical Mechanism of HIV-1 Resistance to Rilpivirine: K. Singh, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 287, 38110 (2012)
- Preexisting mutations in the rilpivirine Phase III trials ECHO and THRIVE: prevalence and impact on virologic response: J. Vingerhoets, et al.; Antivir. Ther. 18, 253 (2013)
- A mature macrophage is a principal HIV-1 cellular reservoir in humanized mice after treatment with long acting antiretroviral therapy: M. Arainga, et al.; Retrovirology 14, 17 (2017)
- CARD8 is an inflammasome sensor for HIV-1 protease activity: Q. Wang, et al.; Science 371, 6535 (2021)