Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
BellBrook
SIRT2 (human) (rec.) (His) (active) (100µg)

| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Sirtuin2; NAD-dependent Deacetylase Sirtuin-2; SIR2-like protein 2; SIR2L2 |
| Product Type | Protein |
| Properties | |
| Source/Host | Insect cells |
| Sequence |
Full-length human SIRT2 (aa 1-389) with a C-terminal His-tag. |
| Crossreactivity | Human |
| Application |
Drug Discovery |
| Biological Activity |
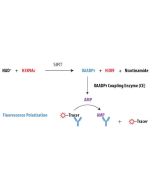
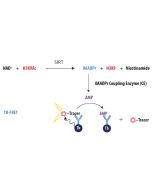
The enzyme has been thoroughly validated with the Transcreener OAADPr Assay Kit. For specific activity, please refer to the Certificate of Analysis for each individual enzyme lot. Currently used with the Transcreener assay at a concentration of 12nM in a 10 μL reaction. |
| MW | 44kDa |
| Purity | ≥90% (SDS-PAGE) |
| Accession Number | Q8IXJ6 |
| Formulation | Liquid in 50 mM Tris, 500 mM NaCl, and 5% Glycerol (pH 8.0). |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Complete Information from the Original Manufacturer Human SIRT2: Q8IXJ6 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | DRY ICE |
| Short Term Storage | -20°C |
| Long Term Storage | -80°C |
| Handling Advice | Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 6 months after receipt when stored at -80°C. |
| Documents | |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Sirtuins (Silent information regulators; SIRTs) deacetylate and/or ADP-ribosylate lysine residues of target proteins in an NAD+-dependent manner. Sirtuins are critical regulators of many cellular processes, including insulin secretion, the cell cycle and apoptosis. Sirtuins, in particular SIRT1, emerged as critical regulators of longevity and aging in several model organisms. Furthermore, a variety of age-associated diseases such as type 2 diabetes, obesity, osteoporosis, and Alzheimer’s disease are associated with sirtuins. Sirtuin-2 is a NAD-dependent protein deacetylase, which deacetylates the 'Lys-40' of a-tubulin. It is involved in the control of mitotic exit in the cell cycle. Furthermore, a variety of age-associated diseases such as type 2 diabetes, obesity, osteoporosis, and Alzheimer’s disease are associated with sirtuins. Selective inhibition of Sirtuin-2 achieves neuroprotection and identifies Sirtuin-2 to be a potential therapeutic avenue in Huntington’s and Parkinson’s disease.