Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
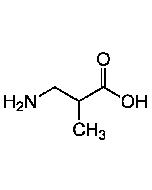
R-BAIBA

| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | D-3-Amino-isobutyric acid, D-BAIBA |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula | C4H9NO2 |
| MW | 103.12 |
| CAS | 2140-95-6 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Synthetic |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥99% (TLC) |
| Appearance | White powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in methanol or water. |
| Identity | Determined by NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | QCHPKSFMDHPSNR-GSVOUGTGSA-N |
| Smiles | C[C@H](CN)C(O)=O |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice |
Keep cool and dry. Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Beta-Aminoisobutyric acid is a non-protein amino acid originating from the catabolism of thymine and valine. beta-Aminoisobutyric acid occurs in two isomeric forms and both enantiomers of beta-Aminoisobutyric acid can be detected in human urine and plasma. In plasma, the S-enantiomer is the predominant type due to active renal reabsorption. In contrast, urine almost exclusively contains the R-enantiomer of beta-Aminoisobutyric acid, which is eliminated both by filtration and tubular secretion. The S-enantiomer of beta-Aminoisobutyric acid is predominantly derived from the catabolism of valine, the R-enantiomer is the product of the catabolism of the pyrimidine bases uracil and thymine by the enzyme dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPD), in what constitutes the first step of the pyrimidine degradation pathway. Transient high levels of beta-Aminoisobutyric acid have been observed under a variety of pathological conditions such as lead poisoning, starvation, in total body irradiation and in a number of malignancies. Recently R-/S-enantiomer mixtures have been shown to be browning inducer of white adipose tissue.
(1) S. Landaas & E. Solem; Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Invest. 43, 95 (1983) | (2) F. Podebrad, et al.; Clin. Chim. Acta 292, 93 (2000) | (3) A.B. Van Kuilenburg, et al.; Biochem. J. 379, 119 (2004) | (4) Z. Wang, et al., Commun. Biol. 3, 837 (2020) | (5) K. Awad, et al.; Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 497 (2021) | Ch. Lyssikatos, et al. Res. Square doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-2492688/v1 (2023)