Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
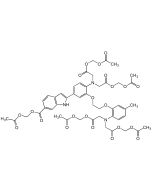
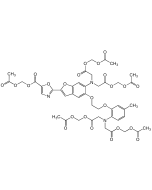
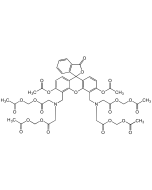
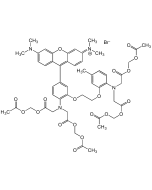
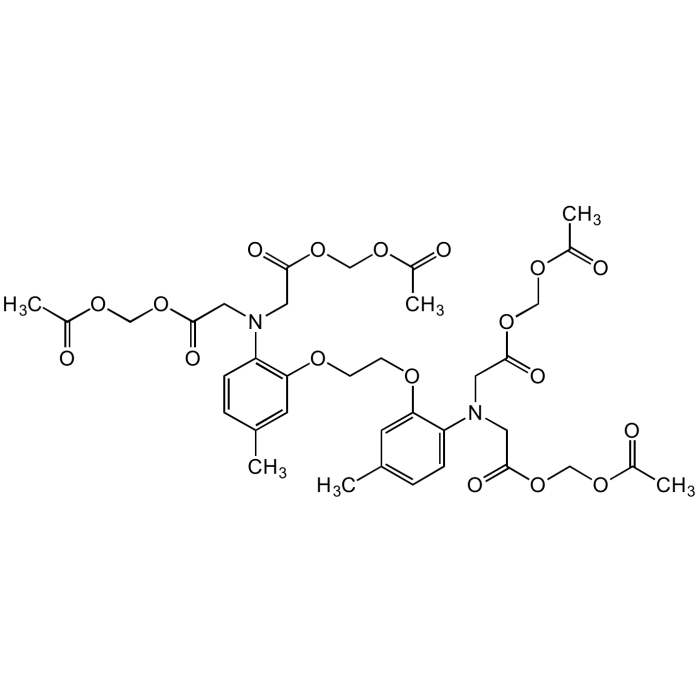
MAPTAM
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | 5,5'-Dimethyl-BAPTA-AM; 1,2-Bis(2-amino-5-methylphenoxy) ethane; 1,2-Bis(2-amino-5-methylphenoxy)ethane-N,N,N′,N′-tetraacetic acid tetrakis(acetoxymethyl) ester |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula | C36H44N2O18 |
| MW | 792.74 |
| CAS | 147504-94-7 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Synthetic. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥94% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | White to off-white powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO, DMF, acetonitrile, ethyl acetate or chloroform. |
| Identity | Determined by NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | HEOJVQZWOLQUDR-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Smiles | CC1=CC(OCCOC2=CC(C)=CC=C2N(CC(OCOC(C)=O)=O)CC(OCOC(C)=O)=O)=C(N(CC(OCOC(C)=O)=O)CC(OCOC(C)=O)=O)C=C1 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice |
Keep cool and dry. Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
MAPTAM is a cell permeable intracellular Ca2+ chelator that can be loaded non-invasive into cells by incubation. MAPTAM itself does not bind calcium, but once inside the cell is converted into it's derivative Dimethyl-BAPTA by cytoplasmic esterases. This type of calcium chelators are commonly used to form calcium buffers with well-defined calcium concentrations. By injecting the chelators into cells or by incubating cells with the AM ester form of the chelators, one can control the cytosolic calcium concentration, an important means to study the roles of calcium. Key advantages of these calcium chelators include relative insensitivity toward intracellular pH change and fast release of calcium. Recent studies have shown that BAPTA derivative might have microtubule disruptive activity (unrelated to it's calcium chelating activity) and should be used with caution in studies of cytoskeleton-related cell functions.
(1) Biochemistry 19, 2396 (1980) | (2) R.Y. Tsein; Nature 290, 527 (1981) | (3) J.B. Lefkowith, et al.; J. Immunol. 149, 1729 (1992) | (4) K.A. Birch, et al.; J. Cell Biol. 118, 1501 (1992) | (5) E. Poch, et al.; Biochem. J. 290, 617 (1993) | (6) J.M. Dubinsky; Neurosci. Lett. 150, 129 (1993) | (7) T. Tiffert & V.L. Lew; J. Physiol. 505, 403 (1997) | (8) J.R. Wu-Wong, et al.; Clin. Sci. 103 Suppl.48, 418S (2002) | (9) A. Furuta, et al.; Endocr. J. 56, 235 (2009) | (10) R. Chen, et al.; Microb. Pathog. 83-84, 29 (2015)