Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
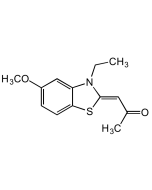
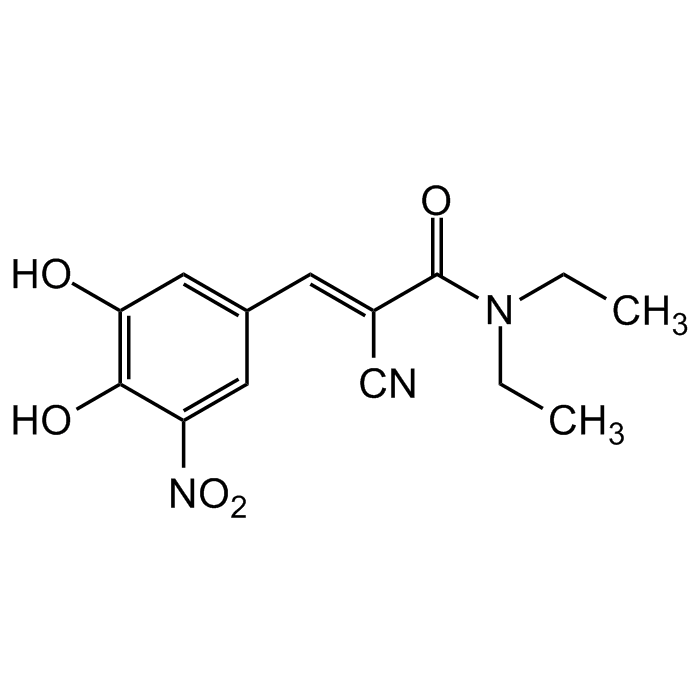
Entacapone
As low as
30
CHF
CHF 30.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CR1-3708-M0055 mgCHF 30.00
AG-CR1-3708-M02525 mgCHF 85.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | OR-611; (E)-2-Cyano-3-(3,4-dihydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)-N,N-diethylacrylamide |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C14H15N3O5 |
| MW | 305.3 |
| CAS | 130929-57-6 |
| RTECS | UC6316195 |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | Yellow powder |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO (30mg/ml), dimethylformamide (30mg/ml) or ethanol (5mg/ml). Insoluble in water. |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| InChi Key | JRURYQJSLYLRLN-BJMVGYQFSA-N |
| Smiles | OC1=C(O)C([N+]([O-])=O)=CC(/C=C(C#N)/C(N(CC)CC)=O)=C1 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Keep cool and dry. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Potent FTO (fat mass and obesity-associated gene) inhibitor for in vivo studies. FTO belongs to the Fe2+ and α-ketoglutarate (α-KG)-dependent oxygenase family. It demethylates N6-adenosine-modified (m6A) sites and N6,2'-O-dimethyladenosine-modified (m6Am) sites of mRNA. With its demethylase activity, FTO regulates the expression of some uncharacterized genes. The transcription factor FOXO1 has been shown to be a substrate of FTO. FTO demethylated m6A sites on forkhead box protein O1 (FOXO1) mRNA to up-regulate FOXO1 expression, thereby modulating gluconeogenesis and thermogenesis explaining in part the function of FTO on metabolic disorders such as obesity and diabetes.
- Potent selective and reversible catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) inhibitor, an enzyme involved in the metabolism of catecholamine neurotransmitters and related drugs. Entacapone is selective for COMT over monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) and MAO-B and phenolsulphotransferase M (PST-M) and PST-P (IC50s = >50 µM). It is used for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease, administered concomittantly with levodopa and a decarboxylase inhibitor (e.g. carbidopa).
- Inhibits α-synuclein aggregation in an in vitro assay and blocks α-synuclein-induced cell death in PC-12 cells.
- Shown to uncouple oxidative phosphorylation and inhibit mitochondrial enzyme complexes I and IV.
- Antioxidant that can scavenge toxic HOCl and ONOO--species and inhibit oxidative stress-induced cell death.
Product References
- Biochemical and pharmacological properties of a peripherally acting catechol-O-methyltransferase inhibitor entacapone: E. Nissinen, et al.; Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 346, 262 (1992)
- Different in vivo properties of three new inhibitors of catechol O-methyltransferase in the rat: P.T. Mannisto, et al.; Br. J. Pharmacol. 105, 569 (1992)
- The effect of entacapone (OR-611) on brain [18F]-6-L-fluorodopa metabolism: implications for levodopa therapy of Parkinson's disease: G.V. Sawle, et al.; Neurology 44, 1292 (1994)
- Entacapone, a novel catechol-O-methyltransferase inhibitor for Parkinson's disease, does not impair mitochondrial energy production: E. Nissinen, et al.; Eur. J. Pharmacol. 340, 287 (1997)
- Entacapone. A review of its use in Parkinson's disease: K.J. Holm & C.M. Spencer; Drugs 58, 159 (1999)
- Entacapone and tolcapone, two catechol O-methyltransferase inhibitors, block fibril formation of alpha-synuclein and beta-amyloid and protect against amyloid-induced toxicity: S. Di Giovanni, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 285, 14941 (2010)
- Entacapone is an Antioxidant More Potent than Vitamin C and Vitamin E for Scavenging of Hypochlorous Acid and Peroxynitrite, and the Inhibition of Oxidative Stress-Induced Cell Death: A.Y. Chen, et al.; Med. Sci. Monit. 22, 687 (2016)
- The catechol-O-methyltransferase inhibitors tolcapone and entacapone uncouple and inhibit the mitochondrial respiratory chain in HepaRG cells: D. Grunig, et al.; Toxicol. In Vitro 42, 337 (2017)
- Identification of entacapone as a chemical inhibitor of FTO mediating metabolic regulation through FOXO1: S. Peng, et al.; Sci. Transl. Med. 11, eaau7116 (2019)