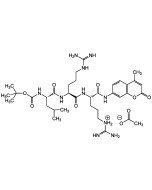Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
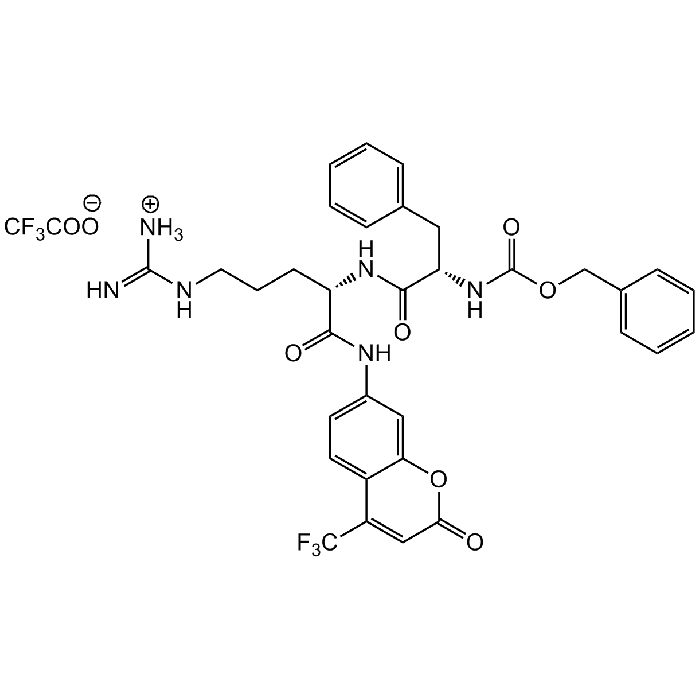
Z-Phe-Arg-AFC
As low as
90
CHF
CHF 90.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CP3-0028-M0055 mgCHF 90.00
AG-CP3-0028-M02525 mgCHF 360.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Z-FR-AFC . TFA |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C33H33F3N6O6 . C2HF3O2 |
| MW | 666.7 . 114.0 |
| Sequence |
Z-Phe-Arg-7-amino-4-trifluoromethylcoumarin |
| CAS | 93753-73-2 (free base) |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥95% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO. Moderately soluble and highly stable in water-based solvents. |
| InChi Key | FLPBOIDNDJASFK-CCQIZPNASA-N |
| Smiles | [NH3+]C(NCCC[C@@H](C(NC1=CC=C(C(C(F)(F)F)=CC(O2)=O)C2=C1)=O)NC([C@H](CC3=CC=CC=C3)NC(OCC4=CC=CC=C4)=O)=O)=N.FC(F)(C([O-])=O)F |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Keep cool and dry. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Fluorogenic substrate, specifically used to determine the enzyme activity of Cathepsin L.
- Useful for the study of cathepsin activity and for screening small molecule inhibitors for drug discovery and HTS applications. Likely to be cleaved by cathepsins B, F, K, S and L, cathepsins L-like proteases and proteases such as papain, cruzipain, plasma kallikrein, soybean trypsin-like enzyme and the falcipains-1 and -2 (malaria hemoglobinases).
- Hydrolysis of this substrate is monitored by observing fluorescence at an Excitation of 400nm and Emission at 505nm.
Product References
- New fluorogenic substrates for alpha-thrombin, factor Xa, kallikreins, and urokinase: T. Morita, et al.; J. Biochem. 82, 1495 (1977)
- Separation and identification of cathepsins in newborn rat epidermis: R.J. Harvima, et al.; J. Invest. Dermatol. 88, 393 (1987)
- Preliminary studies on cysteine and serine proteinase activities in inflamed human gingiva using different 7-amino-4-trifluoromethyl coumarin substrates and protease inhibitors: S.W. Cox & B.M. Eley; Arch. Oral Biol. 32, 599 (1987)
- Photometric or fluorometric assay of cathepsin B, L and H and papain using substrates with an aminotrifluoromethylcoumarin leaving group: J.R. Tchoupe, et al.; Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1076, 149 (1991)
- Developmentally regulated secretion of cathepsin L-like cysteine proteases by Haemonchus contortus : M.L. Rhoads & R.H. Fetterer; J. Parasitol. 81, 505 (1995)
- Taenia saginata Oncosphere Excretory/Secretory Peptidases: A. Clinton White, Jr. ; J. Parasitol. 82, 7 (1996)
- Human cathepsin F: expression in baculovirus system, characterization and inhibition by protein inhibitors: M. Fonovic, et al.; Biol. Chem. 385, 505 (2004)
- Identification and biochemical characterization of vivapains, cysteine proteases of the malaria parasite Plasmodium vivax : B.-K. NA, et al.; Biochem. J. 378, 529 (2004)
- Crosstalk between the ubiquitin-proteasome system and autophagy in a human cellular model of Alzheimer's disease: V. Cecarini, et al.; Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1822, 1741 (2012)
- Cysteine Protease Inhibitor (AcStefin) Is Required for Complete Cyst Formation of Acanthamoeba: J-Y. Lee, et al.; Eukaryot. Cell 12, 567 (2013)
- Phospholamban overexpression in mice causes a centronuclear myopathy-like phenotype: V.A. Fajardo, et al.; Dis. Model Mech. 8, 999 (2015)
- Data on skeletal muscle apoptosis, autophagy, and morphology in mice treated with doxorubicin: T.L. Campbell, et al.; Data Brief 7, 786 (2016)
- Sarcolipin deletion exacerbates soleus muscle atrophy and weakness in phospholamban overexpressing mice: V.A. Fajardo, et al.; PLoS One 12, e0173708 (2017)










![Z-Leu-Leu-Nva-CHO [MG-115]](https://adipogen.com/media/catalog/product/cache/60eb5af712bc93baae8d55513bd31b01/a/g/ag-cp3-0015_mg-115.png)