Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
TIGIT – CD155 – CD112 – CD226 Network
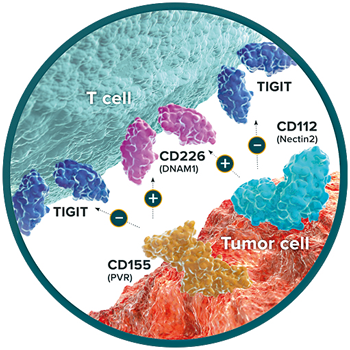 T Cell Immunoreceptor with Immunoglobulin and ITIM domains (TIGIT) is an immune checkpoint receptor expressed on the surface of cytotoxic, memory and regulatory T cells (Tregs) as well as natural killer (NK) cells. TIGIT binds strongly to CD155 (PVR) and weakly to CD112 (Nectin-2). TIGIT suppresses immune activation on cytotoxic T cells and NK cells. In the normal immune system, the suppressive effect of TIGIT is counterbalanced by the immune-activating receptor CD226 (DNAM1), which competes with TIGIT to bind CD155 and CD112. The inhibitory signal provided by TIGIT overpowers the ability of CD226 to stimulate T cell activation. Tumor cells exploit the dominance of the inhibitory TIGIT pathway to avoid immune-mediated destruction. Recently, a high affinity receptor of the ligand CD112/Nectin-2, called CD112R/PVRIG has been described and may become a new attractive cancer immunotherapy target. Overexpression of TIGIT and reduced CD226 activity are frequently observed in exhausted T cells within tumors, making the TIGIT/CD226 axis a key focus for immune checkpoint blockade strategies.
T Cell Immunoreceptor with Immunoglobulin and ITIM domains (TIGIT) is an immune checkpoint receptor expressed on the surface of cytotoxic, memory and regulatory T cells (Tregs) as well as natural killer (NK) cells. TIGIT binds strongly to CD155 (PVR) and weakly to CD112 (Nectin-2). TIGIT suppresses immune activation on cytotoxic T cells and NK cells. In the normal immune system, the suppressive effect of TIGIT is counterbalanced by the immune-activating receptor CD226 (DNAM1), which competes with TIGIT to bind CD155 and CD112. The inhibitory signal provided by TIGIT overpowers the ability of CD226 to stimulate T cell activation. Tumor cells exploit the dominance of the inhibitory TIGIT pathway to avoid immune-mediated destruction. Recently, a high affinity receptor of the ligand CD112/Nectin-2, called CD112R/PVRIG has been described and may become a new attractive cancer immunotherapy target. Overexpression of TIGIT and reduced CD226 activity are frequently observed in exhausted T cells within tumors, making the TIGIT/CD226 axis a key focus for immune checkpoint blockade strategies.
LIT: Identification of CD112R as a novel checkpoint for human T cells: Y. Zhu, et al.; J. Exp. Med. 213, 167 (2016) • Interaction of PVR/PVRL2 with TIGIT/DNAM-1 as a novel immune checkpoint axis and therapeutic target in cancer: H. Stamm, et al.; Mamm. Genome 29, 694 (2018) • Hitting the complexity of the TIGIT-CD96-CD112R-CD226 axis for next-generation cancer immunotherapy: H.-S. Jin & Y. Park; BMP Rep. 54, 2 (2021) • TIGIT-CD226-PVR axis: advancing immune checkpoint blockade for cancer immunotherapy: E.Y. Chiang & I. Mellman; J. Immunother. Cancer 10, e004711 (2022) • TIGIT: An emerging immune checkpoint target for immunotherapy in autoimmune disease and cancer: J. Zhao, et al.; Int. Immunopharmacol. 120, 110358 (2023) • Targeting TIGIT for cancer immunotherapy: recent advances and future directions: P. Zhang, et al.; Review Biomark. Res. 12, 7 (2024)
Biologically Active TIGIT, CD112R and CD155 Proteins
| Product Name | PID | Source | Endotoxin | Species |
| CD112R (mouse):Fc (human) (rec.) | AG-40B-0170 | HEK 293 cells | <0.01EU/µg | Mouse |
| CD155 [PVR] (human)-muIg Fusion Protein |
ANC-555-020 |
CHO cells | n.d. | Human |
| TIGIT (human):Fc (human) (rec.) | AG-40B-0162 | HEK 293 cells | <0.01EU/µg | Human |
| TIGIT (human)-muIg Fusion Protein |
ANC-556-020 |
CHO cells | n.d. | Human |
VALIDATED Antibodies for TIGIT, CD112R and CD155 Research
| Product Name | PID | Isotype | Applications | Species |
| CD112R (mouse), pAb (IN109) | AG-25B-0035 | Rabbit | ELISA, WB | Mouse |
| CD155 [PVR] (human), mAb (ANC2B2) |
ANC-255-020 |
Mouse IgG1κ | ELISA, FACS | Human |
| CD155 [PVR] (human), mAb (ANC6A3) |
ANC-350-020 |
Mouse IgG1κ | ELISA, FACS | Human |
| anti-CD155 [PVR] (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM514) |
REV-31-1406-00 |
Rabbit IgG | IHC, WB | Human |
| TIGIT (human), mAb (ANCTG6/10A6) |
ANC-340-020 |
Mouse IgG1κ | ELISA, FACS | Human |
NEW VSTM Family Member
The V-set and transmembrane domain-containing protein (VSTM) family is composed of 8 proteins: VSTM1v1, VSTM1v2, VSTM2a, VSTM2b, VSTM2L, VSTM3, VSTM4 and VSTM 5. Members of the VSTM family are associated with the regulation of functions of immune cells, adipose cells and neuronal cells. The VSTM family is an immunoglobulin (Ig) superfamily that shares structural similarities with the B7-like transmembrane proteins involved in immune regulation. VSTM1 and VSTM4 play positive and negative roles in macrophage activation, respectively. VSTM3 (TIGIT) acts as a co-inhibitory receptor that suppresses the cytokine production of T cells and NK cells.
V-set and transmembrane domain-containing protein 5 (Vstm5), a newly characterized small membrane glycoprotein highly expressed in the CNS, facilitates the formation of neuronal dendrites and protrusions such as dendritic filopodia. Regulatory roles of VSTM5 for in vitro and in vivo immune responses have been reported. VSTM5 functions as a novel immune checkpoint by regulating T cell proliferation and cytokine production, Treg generation by maintenance of T cell energy and possibly induction of T cell apoptosis.
LIT: VSTM5 is a novel immune checkpoint that promotes oral tolerance of cell-mediated and antibody responses: O.E. Oludada, et al.; BBRC 635, 283 (2022)
| Product Name | PID | Source | Endotoxin | Species |
| VSTM5 (mouse):Fc (mouse) (rec.) (non-lytic) | AG-40B-0239 | CHO cells | <0.01EU/µg | Mouse |
| VSTM5 (human):Fc (human) (rec.) (non-lytic) | AG-40B-0239 | HEK 293 cells | <0.01EU/µg | Human |
|
More Information |
|
Downloadable Flyer |
|
TIGIT Signaling Pathway Product Flyer Released - September 2025 |
Download |
